This article needs additional citations for verification .(November 2024) |
The London and North Eastern Railway (LNER) was formed out of a number of constituent railway companies at the grouping in 1923.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(November 2024) |
The London and North Eastern Railway (LNER) was formed out of a number of constituent railway companies at the grouping in 1923.
The main companies, showing their route mileage, were:
Many of these "railways" existed only in name; they were included on the list at the time of the Railways Act in order to legally qualify each line's position.

The Great Central Railway in England was formed when the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway changed its name in 1897, anticipating the opening in 1899 of its London Extension. On 1 January 1923, the company was grouped into the London and North Eastern Railway.
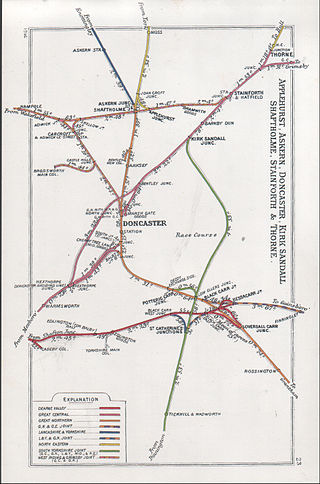
The South Yorkshire Joint Railway was a committee formed in 1903, between the Great Central Railway, the Great Northern Railway, the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway, the Midland Railway and the North Eastern Railway to oversee the construction of a new railway in the Doncaster area of South Yorkshire, England. The five companies had equal rights over the line, each of the companies regularly working trains over it.
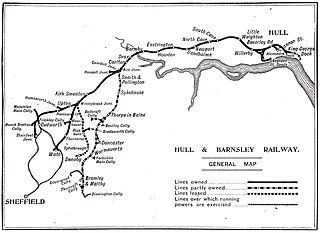
The Hull Barnsley & West Riding Junction Railway and Dock Company (HB&WRJR&DCo.) was opened on 20 July 1885. It had a total projected length of 66 miles but never reached Barnsley, stopping a few miles short at Stairfoot. The name was changed to The Hull and Barnsley Railway (H&BR) in 1905. Its Alexandra Dock in Hull opened 16 July 1885.

The North Eastern Railway (NER) was an English railway company. It was incorporated in 1854 by the combination of several existing railway companies. Later, it was amalgamated with other railways to form the London and North Eastern Railway at the Grouping in 1923. Its main line survives to the present day as part of the East Coast Main Line between London and Edinburgh.

The Cambrian Railways owned 230 miles (370 km) of track over a large area of mid Wales. The system was an amalgamation of a number of railways that were incorporated in 1864, 1865 and 1904. The Cambrian connected with two larger railways with connections to the northwest of England via the London and North Western Railway, and the Great Western Railway for connections between London and Wales. The Cambrian Railways amalgamated with the Great Western Railway on 1 January 1922 as a result of the Railways Act 1921. The name is continued today in the route known as the Cambrian Line.

The Hallam Line is a railway connecting Leeds and Sheffield via Castleford in the West Yorkshire Metro area of northern England. It is a slower route from Leeds to Sheffield than the Wakefield line. Services on this line are operated by Northern Trains. Services from Leeds to Nottingham also use the line.

The Wakefield line is a railway line and service in the West Yorkshire Metro and South Yorkshire Passenger Transport Executive areas of northern England. The Wakefield line is coloured yellow on maps and publications by West Yorkshire Metro. The line was electrified in 1989, between Leeds & Wakefield Westgate, as part of the programme to electrify the East Coast Main Line.

A joint railway is a railway operating under the control of more than one railway company.

The Scarborough & Whitby Railway was a railway line from Scarborough to Whitby in North Yorkshire, England. The line followed a difficult but scenic route along the North Yorkshire coast.

The history of rail transport in Great Britain 1830–1922 covers the period between the opening of the Liverpool and Manchester Railway (L&MR), and the Grouping, the amalgamation of almost all of Britain's many railway companies into the Big Four by the Railways Act 1921.

The York and North Midland Railway (Y&NMR) was an English railway company that opened in 1839 connecting York with the Leeds and Selby Railway, and in 1840 extended this line to meet the North Midland Railway at Normanton near Leeds. Its first chairman was the railway financier George Hudson, who had been called the railway king.

The Otley and Ilkley Joint Railway was a railway line running between the towns of Otley and Ilkley in West Yorkshire. The line was managed and run jointly by the Midland Railway (MR) and the North Eastern Railway (NER) and was 6+1⁄2 miles (10 km) long. Opened to passenger traffic on 1 August 1865 and freight traffic some months later, the line ran for almost 100 years before partial closure in July 1965 when the line to Otley closed. Today passenger services run over the rest of the line as part of the West Yorkshire Passenger Transport Executive (WYPTE) Wharfedale Line.
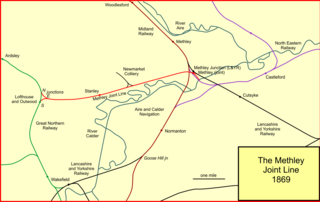
The Methley Joint Railway was a short English railway line constructed by the Bradford, Wakefield and Leeds Railway company, connecting its Leeds direction line with other companies' eastward routes to York, the north-east, and Goole. The line connected collieries along its route. The BW&LR changed its name to the West Yorkshire Railway at the same time. The line was double track, just over five miles in length, between junctions at Lofthouse and Methley.
The Great Northern Railway developed an extensive network over time, having started in 1846 with the intention of connecting London and York, as well as other major Yorkshire towns. The Great Northern Railway in Yorkshire was a major part of that, although the GNR did not succeed in reaching York as it originally intended. By acquiring running powers it reached Leeds, Bradford and Halifax over other companies' lines, as well as Barnsley Sheffield and Grimsby, and then York too. After acquiring local companies it developed a network, chiefly in West Yorkshire. Later it built lines north and west of Bradford into hilly terrain, and these were very expensive to build, and never repaid the initial cost.