Related Research Articles

The Continental Divide of the Americas is the principal, and largely mountainous, hydrological divide of the Americas. The Continental Divide extends from the Bering Strait to the Strait of Magellan, and separates the watersheds that drain into the Pacific Ocean from those river systems that drain into the Atlantic Ocean and, along the northernmost reaches of the Divide, those river systems that drain into the Arctic Ocean and Hudson Bay.

The Nine Nations of North America is a 1981 book by Joel Garreau, in which the author suggests that North America can be divided into nine nations, which have distinctive economic and cultural features. He also argues that conventional national and state borders are largely artificial and irrelevant, and that his "nations" provide a more accurate way of understanding the true nature of North American society. The work has been called "a classic text on the current regionalization of North America".
This is a list of historic regions of the United States that existed at some time during the territorial evolution of the United States and its overseas possessions, from the colonial era to the present day. It includes formally organized territories, proposed and failed states, unrecognized breakaway states, international and interstate purchases, cessions, and land grants, and historical military departments and administrative districts. The last section lists informal regions from American vernacular geography known by popular nicknames and linked by geographical, cultural, or economic similarities, some of which are still in use today.
The National Register of Historic Places in the United States is a register including buildings, sites, structures, districts, and objects. The Register automatically includes all National Historic Landmarks as well as all historic areas administered by the U.S. National Park Service. Since its introduction in 1966, more than 90,000 separate listings have been added to the register.
A border town is a town or city close to the boundary between two countries, states, or regions. Usually the term implies that the nearness to the border is one of the things the place is most famous for. With close proximities to a different country, diverse cultural traditions can have certain influence to the place. Border towns can have highly cosmopolitan communities, a feature they share with port cities, as traveling and trading often go through the town. They can also be flashpoints for international conflicts, especially when the two countries have territorial disputes.
The following radio stations broadcast on FM frequency 89.1 MHz:
The following radio stations broadcast on FM frequency 102.7 MHz:
Water Resources Development Act of 1976,, Pub.L. 94–587 is a public law enacted on October 22, 1976 by the Congress of the United States of America concerning various water resources and projects.
The following radio stations broadcast on FM frequency 88.1 MHz:
The following radio stations broadcast on FM frequency 88.9 MHz:
The following radio stations broadcast on FM frequency 93.5 MHz:
The following radio stations broadcast on FM frequency 94.3 MHz:
The following radio stations broadcast on FM frequency 96.5 MHz:
The following radio stations broadcast on FM frequency 99.9 MHz:
The following radio stations broadcast on FM frequency 103.1 MHz:
The following radio stations broadcast on FM frequency 105.1 MHz:

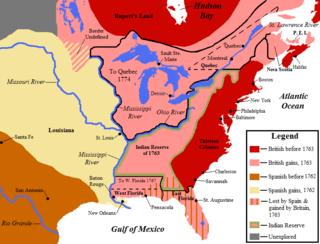
The 1763 Treaty of Paris ended the major war known by Americans as the French and Indian War and by Canadians as the Seven Years' War / Guerre de Sept Ans, or by French-Canadians, La Guerre de la Conquête. It was signed by Great Britain, France and Spain, with Portugal in agreement. Preferring to keep Guadeloupe, France gave up Canada and all of its claims to territory east of the Mississippi River to Britain. With France out of North America this dramatically changed the European political scene on the continent.

Watersheds of North America are large drainage basins which drain to separate oceans, seas, gulfs, or endorheic basins. There are six generally recognized hydrological continental divides which divide the continent into seven principal drainage basins spanning three oceans and one endorheic basin. The basins are the Atlantic Seaboard basin, the Gulf of Mexico basin, the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence basin, the Pacific basin, the Arctic basin, the Hudson Bay basin, and the Great Basin. Together, the principal basins span the continent with the exception of numerous smaller endorheic basins.
References
- ↑ Fischer, Deb. "Senate Passes Fischer-Sasse USS Omaha Resolution New Littoral Combat Ship Will Be Commissioned This Weekend". Deb Fischer – U.S. Senator for Nebraska. United States Senate. Retrieved 9 November 2018.