| Mammals by population |
|---|
 |
This is a list of estimated global populations of Marsupials (infraclass Marsupialia) species. This list is not comprehensive, as not all Marsupials have had their numbers quantified.
Contents
Some members of Marsupialia are extinct, and thus have population sizes of zero:
- Thylacine (Thylacinus cynocephalus) - last recorded wild individual captured in 1933, and died in captivity in 1936. [1]
- Liverpool Plains striped bandicoot (Perameles fasciata) - went extinct in 1840s. [2]
- Marl (Perameles myosuros) - last seen in 1907, extinct circa 1910. [3]
- South-eastern striped bandicoot (Perameles notina) - extinct sometime in late 19th century. [4]
- Nullarbor barred bandicoot (Perameles papillon) - formerly considered a subspecies of P. bougainville . Last record from 1920s, believed to have gone extinct circa 1928. [5]
- Desert bandicoot (Perameles eremiana) - last confirmed record from 1943. Unconfirmed reports persisted into the late 1960s. [6]
- Southern pig-footed bandicoot (Chaeropus ecaudatus) - last specimen collected in 1900, but likely persisted into the 1930s. [7]
- Northern pig-footed bandicoot, or Yirratji (Chaeropus yirratji) - likely went extinct in the 1950s. [8]
- Lake Mackay hare-wallaby, or Kuluwarri (Lagorchestes asomatus) - known from a single specimen taken in 1932. Likely went extinct by 1960. [9]
- Eastern hare-wallaby (Lagorchestes leporides) - last recorded in 1890. [10]
- Toolache wallaby (Notamacropus greyi) - last confirmed records from 1924; species persisted in captivity until 1939. Some unconfirmed reports were made as late as the 1970s, but could not be verified. [11]
- Crescent nail-tailed wallaby (Onychogalea lunata) - no confirmed records since 1940s. Estimated to have gone extinct circa 1963. [12]
- Desert bettong (Bettongia anhydra) - known from a single specimen collected in 1933. Likely went extinct circa 1960. [13]
- Nullarbor dwarf bettong (Bettongia pusilla) - first described in 1997, but is expected to have been extant at the time of European settlement in Oceania. [14]
- Desert rat-kangaroo (Caloprymnus campestris) - last confirmed record from 1935; unconfirmed reports have occurred as recently as 2013, but species has not been found despite extensive searches. [15]
- Broad-faced potoroo (Potorous platyops) - last recorded in 1875. [16]
| Common name | Scientific name | IUCN Red List status | Trend | Global population estimate (year) | Population notes | Range | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thylacine | Thylacinus cynocephalus | EX [1] | N/A | 0 (1936) [17] | Last known individual died in captivity on 7 September, 1936. [17] Last known wild individual was captured in 1933. [1] | 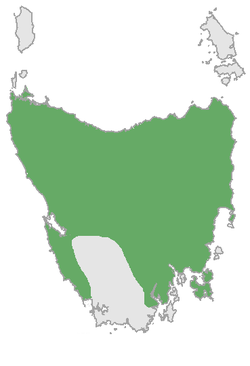 |  |
| Wondiwoi tree-kangaroo | Dendrolagus mayri | CR [18] | ? [18] | < 50 (2016) [18] | May be extinct. Any extant population is expected to be less than 50 individuals. [18] |  | |
| Teleformin cuscus | Phalanger matanim | CR [19] | ? [19] | < 50 (2016) [19] | May be extinct. Species is known from six specimens. [19] | 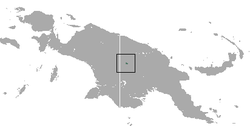 | |
| Gilbert's potoroo | Potorous gilbertii | CR [20] | 50 (2016) [20] | Population was halved between 2012 - 2015 due to fires. [20] |  |  | |
| Tenkile | Dendrolagus scottae | CR [21] | 200 (2019) [21] |  |  | ||
| Northern hairy-nosed wombat | Lasiorhinus krefftii | CR [22] | 315 (2021) [23] | IUCN estimates population at 80 mature individuals (2016). [22] |  |  | |
| Kangaroo Island dunnart | Sminthopsis aitkeni | CR [24] | < 500 (2008) [24] | Considered by IUCN to be a subspecies of sooty dunnart (S. fuliginosus). [24] Population may now be lower due to habitat damage from fires and predation by feral cats. [25] |  |  | |
| Cape York rock-wallaby | Petrogale coenensis | EN [26] | 500-2,000 (2020) [26] | Total population is most likely ~1,000 individuals. [26] |  | ||
| Golden-mantled tree-kangaroo | Dendrolagus pulcherrimus | CR [27] | 500 (2016) [27] | Value given is a maximum estimate for total population. [27] |  | ||
| Dibbler | Parantechinus apicalis | EN [28] | 700 (2016) [28] |  |  | ||
| Mount Claro rock-wallaby | Petrogale sharmani | VU [29] | ? [29] | 750 (2016) [29] | Total population was estimated in 2012 to be "probably fewer than 800 individuals." [29] |  |  |
| Numbat | Myrmecobius fasciatus | EN [30] | 800 (2016) [30] |  |  | ||
| Bridled nail-tail wallaby | Onychogalea fraenata | VU [31] | 800-1,100 (2016) [31] | The largest subpopulation occurs at Australian Wildlife Conservancy's Scotia Sanctuary, with 2,000 individuals. Other subpopulations are expected to be uniformly < 150 individuals. [31] |  |  | |
| Northern bettong | Bettongia tropica | EN [32] | 800-1,600 (2025) [32] |  |  | ||
| Andean caenolestid | Caenolestes condorensis | VU [33] | ? [33] | < 1,000 (2015) [33] | Species is only known from three specimens. [33] |  |  |
| Tasman Peninsula dusky antechinus | Antechinus vandycki | EN [34] | 1,000-5,000 (2025) [34] | Best estimate for number of mature individuals is 2,000. [34] | |||
| Western barred bandicoot (Shark Bay bandicoot) | Perameles bougainville | VU [35] | 1,000-5,000 (2025) [35] |  |  | ||
| Northern brush-tailed phascogale | Phascogale pirata | VU [36] | 1,000-10,000 (2025) [36] | Best estimate for number of mature individuals is 5,000. [36] |  | ||
| Leadbeater's possum | Gymnobelideus leadbeateri | CR [37] | 1,100-11,000 (2016) [37] | Best estimate for number of mature individuals is 2,500. Species habitat was heavily impacted by Black Saturday fires in 2009. [37] | 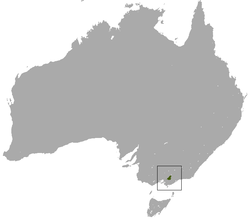 |  | |
| Mountain pygmy possum | Burramys parvus | CR [38] | 2,250 (2008) [38] | Mature population is sexually unbalanced, with an estimated 1,700 females and 550 males. [38] |  |  | |
| Matschie's tree-kangaroo (Huon tree-kangaroo) | Dendrolagus matschiei | EN [39] | 2,500 (2016) [39] |  |  | ||
| Western ringtail possum | Pseudocheirus occidentalis | CR [40] | 3,400 (2017) [40] | Value given is an estimate for number of mature individuals. [40] |  |  | |
| Kowari | Dasyuroides byrnei | VU [41] | 5,000 (2019) [41] |  |  | ||
| Western quoll (Chuditch) | Dasyurus geoffroii | NT [42] | 5,000-8,000 (2025) [42] | Best estimate for number of mature individuals is 6,000. Total population is estimated to be 5,000-10,000 individuals. [42] |  |  | |
| Nabarlek | Petrogale concinna | EN [43] | 5,000-10,000 (2016) [43] |  |  | ||
| Sandhill dunnart | Sminthopsis psammophila | VU [44] | 5,000-10,000 (2016) [44] |  |  | ||
| Scaly-tailed possum | Wyulda squamicaudata | NT [45] | 5,000-10,000 (2025) [45] | 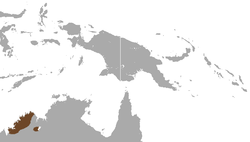 |  | ||
| Red-tailed phascogale | Phascogale calura | NT [46] | 5,000-20,000 (2025) [46] |  |  | ||
| Alexandria false antechinus (Carpentarian antechinus) | Pseudantechinus mimulus | NT [47] | 5,000-30,000 (2025) [47] | Best estimate for number of mature individuals is 20,000. [47] |  |  | |
| Eastern short-eared rock-wallaby | Petrogale wilkinsi | LC [48] | 5,000-50,000 (2025) [48] | Best estimate for number of mature individuals is 20,000. [48] |  |  | |
| Kakadu dunnart | Sminthopsis bindi | NT [49] | 5,000-50,000 (2025) [49] | Best estimate for number of mature individuals is 15,000. [49] |  | ||
| Rufous hare-wallaby | Lagorchestes hirsutus | NT [50] | 6,000 (2025) [50] | Formerly extirpated from Australian mainland, but two reintroduced populations now exist, with one each in Western Australia and Northern Territory. [50] |  |  | |
| Quokka | Setonix brachyurus | VU [51] | 7,500-20,000 (2025) [51] | Total population across mainland Australia, Rottnest Island, and Bald Island is estimated to be 12,000-21,000 individuals. [51] |  |  | |
| Parma wallaby | Notamacropus parma | VU [52] | 8,000 (2025) [52] |  |  | ||
| Black-flanked rock-wallaby (Black-footed rock-wallaby) | Petrogale lateralis | VU [53] | 8,000 (2016) [53] | Total population is estimated to be 10,000 - 12,000 individuals. [53] |  |  | |
| White-footed dunnart | Sminthopsis leucopus | LC [54] | 8,000-10,000 (2020) [54] |  |  | ||
| Greater bilby (Bilby) | Macrotis lagotis | VU [55] | 9,000 (2016) [55] | Total population is estimated to be 9000-15,000 individuals. [55] |  |  | |
| Yellow-footed rock-wallaby | Petrogale xanthopus | NT [56] | ? [56] | < 10,000 (2016) [56] | Total populations in South Australia and New South Wales are expected to be 6,000 and < 100 individuals, respectively. [56] |  |  |
| Godman's rock-wallaby | Petrogale godmani | NT [57] | 10,000 (2016) [57] |  | |||
| Mareeba rock-wallaby | Petrogale mareeba | NT [58] | 10,000 (2016) [58] |  |  | ||
| Purple-necked rock-wallaby | Petrogale purpureicollis | NT [59] | 10,000 (2016) [59] | Total population is estimated to be fewer than 12,500 individuals. [59] |  |  | |
| Eastern quoll | Dasyurus viverrinus | EN [60] | 10,000-12,000 (2016) [60] |  |  | ||
| Tasmanian devil | Sarcophilus harrisii | EN [61] | 10,000-25,000 (2008) [61] | Value given is a provisional estimate for mature individuals based on estimated rates of decline. [61] |  |  | |
| Lumholtz's tree-kangaroo | Dendrolagus lumholtzi | NT [62] | ? [62] | 10,000-30,000 (2016) [62] |  |  | |
| Long-footed potoroo | Potorous longipes | VU [63] | 10,000-50,000 (2025) [63] |  | |||
| Tammar wallaby | Notamacropus eugenii | LC [64] | 10,000-50,000 (2016) [64] |  |  | ||
| Western brush wallaby | Notamacropus irma | LC [65] | 10,000-50,000 (2025) [65] |  |  | ||
| Northern marsupial mole (Kakarratul) | Notoryctes caurinus | LC [66] | 10,000-50,000 (2016) [66] |  | |||
| Short-eared rock-wallaby (Western short-eared rock-wallaby) | Petrogale brachyotis | LC [67] | ? [67] | 10,000-50,000 (2025) [67] | Best estimate for number of mature individuals is 20,000. [67] |  |  |
| Fawn antechinus | Antechinus bellus | VU [68] | 10,000-100,000 (2016) [68] | Best estimate for number of mature individuals is 20,000. [68] |  |  | |
| Eastern barred bandicoot | Perameles gunnii | VU [69] | 10,000-100,000 (2016) [69] | Best estimate for number of mature individuals is 20,000. [69] |  |  | |
| Yellow-bellied glider | Petaurus australis | VU [70] | 10,000-100,000 (2025) [70] | Values given are an estimate for number of mature individuals. [70] |  |  | |
| Sandstone false antechinus (Sandstone antechinus) | Pseudantechinus bilarni | NT [71] | 10,000-100,000 (2025) [71] | Best estimate for number of mature individuals is 20,000. [71] |  | ||
| Southern brown bandicoot | Isoodon obesulus | LC [72] | 10,000-100,000 (2017) [72] |  |  | ||
| Southern marsupial mole (Itjaritjari) | Notoryctes typhlops | LC [73] | 10,000-100,000 (2016) [73] |  |  | ||
| Boodie | Bettongia lesueur | NT [74] | 13,500 (2025) [74] |  |  | ||
| Banded hare-wallaby | Lagostrophus fasciatus | VU [75] | 14,000 (2025) [75] |  |  | ||
| Tiger quoll (Spot-tailed quoll) | Dasyurus maculatus | NT [76] | 14,000 (2018) [76] |  |  | ||
| Brush-tailed phascogale | Phascogale tapoatafa | NT [77] | 15,000 (2020) [77] |  |  | ||
| Crest-tailed mulgara | Dasycercus cristicauda | NT [78] | 18,000 (2016) [78] |  |  | ||
| Brush-tailed rock-wallaby | Petrogale penicillata | VU [79] | 20,000 (2016) [79] | Total population was estimated to be 15,000-30,000 individuals in 2008. [79] |  | | |
| Carpentarian dunnart (Butler's dunnart) | Sminthopsis butleri | VU [80] | 20,000 (2019) [80] | Population of mature individuals is "likely to be less than 2,500." [80] |  |  | |
| Julia Creek dunnart | Sminthopsis douglasi | NT [81] | 20,000 (2019) [81] | Population of mature individuals is expect to be "somewhat more than 10,000" individuals. [81] |  |  | |
| Eastern bettong (Tasmanian bettong) | Bettongia gaimardi | NT [82] | ? [82] | 20,000-50,000 (2016) [82] |  |  | |
| Daintree River ringtail possum | Pseudochirulus cinereus | NT [83] | 20,000-100,000 (2016) [83] | Best estimate for number of mature individuals is 30,000. [83] |  |  | |
| Kultarr | Antechinomys laniger | LC [84] | 20,000-100,000 (2016) [84] |  |  | ||
| Golden bandicoot | Isoodon auratus | LC [85] | 25,000-50,000 (2025) [85] |  |  | ||
| Woylie | Bettongia penicillata | NT [86] | 70,000-235,000 (2025) [86] | Best estimate for number of mature individuals is 140,000. [86] |  |  | |
| Long-nosed potoroo | Potorous tridactylus | NT [87] | 75,000 (2020) [87] |  |  | ||
| Green ringtail possum | Pseudochirops archeri | NT [88] | 100,000 (2019) [88] | Value given is an estimate of total population. [88] |  |  | |
| Greater glider | Petauroides volans | EN [89] | 100,000–500,000 (2025) [89] | Values represent a population estimate extrapolated from species surveys in Victoria. [89] |  |  | |
| Koala | Phascolarctos cinereus | VU [83] | 100,000–500,000 (2020) [83] | Best estimate for number of mature individuals is 300,000. [83] |  |  | |
| Honey possum | Tarsipes rostratus | LC [90] | 100,000-999,999 (2016) [90] | Total population has not been quantified, but is "likely to number in the hundreds of thousands." [90] |  |  | |
| Southern hairy-nosed wombat | Lasiorhinus latifrons | LC [91] | 250,000–500,000 (2025) [91] | Best estimate for number of mature individuals is 400,000. [91] |  |  | |
| Common wombat (Bare-nosed womat) | Vombatus ursinus | LC [92] | 1,000,000-2,000,000 (2025) [92] | Mainland populations are estimated to be slightly less than 1.0 million individuals. [92] |  |  | |
| Wallaroo (Common wallaroo) | Osphranter robustus | LC [93] | >2,338,076 (2021) [94] | Population estimate is only for the areas within Australia where commercial harvesting occur. The actual national populations would be significantly higher. [94] |  |  | |
| Western grey kangaroo | Macropus fuliginosus | LC [95] | >2,571,158 (2021) [94] | Population estimate is only for the areas within Australia where commercial harvesting occur. The actual national populations would be significantly higher. [94] |  |  | |
| Red kangaroo | Osphranter rufus | LC [96] | >10,848,470 (2021) [94] | Population estimate is only for the areas within Australia where commercial harvesting occur. The actual national populations would be significantly higher. [94] |  |  | |
| Eastern grey kangaroo | Macropus giganteus | LC [97] | >12,977,181 (2021) [94] | Population estimate is only for the areas within Australia where commercial harvesting occur. The actual national populations would be significantly higher. [94] |  |  | |
| Linnaeus's mouse opossum | Marmosa murina | LC [98] | 104,000,000 (2019) [99] |  |  | ||
| Gray four-eyed opossum | Philander opossum | LC [100] | 121,000,000 (2019) [99] |  |  | ||
| Brown four-eyed opossum | Metachirus nudicaudatus | LC [101] | 128,000,000 (2019) [99] |  |  | ||
| Brown-eared woolly opossum | Caluromys lanatus | LC [102] | 160,000,000 (2019) [99] |  |  |


