This List of modern words formed from Greek polis recounts the use of the ancient Greek word polis to form modern names. The greatest modern use is in place names.
This List of modern words formed from Greek polis recounts the use of the ancient Greek word polis to form modern names. The greatest modern use is in place names.
Derivatives of polis are common in many modern European languages. This is indicative of the influence of the polis-centred Hellenic world view. Derivative words in English include policy, polity, police, and politics. In Greek, words deriving from polis include politēs and politismos, whose exact equivalents in Latin, Romance, and other European languages, respectively civis ("citizen"), civilisatio ("civilisation"), etc., are similarly derived.
A number of other common nouns end in -polis. Most refer to a special kind of city or state. Examples include:
Others refer to part of a city or a group of cities, such as:
1. Polis, or Polis Chrysochous (Greek : Πόλις Χρυσοχούς), located on the northwest coast of Cyprus within the Paphos District and on the edge of the Akamas peninsula. During the Cypro-Classical period, Polis became one of the most important ancient Cypriot city-kingdoms on the island, with important commercial relations with the eastern Aegean Islands, Attica, and Corinth. The town is also well known due to its mythological history, including the site of the Baths of Aphrodite.
3. Tripolis – a group of three cities, retained in the names of Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli, Greece and Tripoli, Lebanon
4. Tetrapolis – a group of four cities
5. Pentapolis – a group of five cities
6. Hexapolis – a group of six cities
7. Heptapolis, Middle Egypt – a group of seven cities
8. Octapolis, in ancient Caria or Lycia – a group of eight cities
10. Decapolis, a group of ten cities in the Levant
12. Dodecapolis – a group of twelve cities
The names of several other towns and cities in Europe and the Middle East have contained the suffix -polis since antiquity or currently feature modernized spellings, such as -pol. Notable examples include:
The names of other cities were also given the suffix -polis after antiquity, either referring to ancient names or unrelated:

An acropolis was the settlement of an upper part of an ancient Greek city, especially a citadel, and frequently a hill with precipitous sides, mainly chosen for purposes of defense. The term is typically used to refer to the Acropolis of Athens, yet every Greek city had an acropolis of its own. Acropolises were used as religious centers and places of worship, forts, and places in which the royal and high-status resided. Acropolises became the nuclei of large cities of classical ancient times, and served as important centers of a community. Some well-known acropolises have become the centers of tourism in present-day, and, especially, the Acropolis of Athens has been a revolutionary center for the studies of ancient Greece since the Mycenaean period. Many of them have become a source of revenue for Greece, and represent some great technology during the period.

The Acropolis of Athens is an ancient citadel located on a rocky outcrop above the city of Athens, Greece, and contains the remains of several ancient buildings of great architectural and historical significance, the most famous being the Parthenon. The word Acropolis is from the Greek words ἄκρον and πόλις. The term acropolis is generic and there are many other acropoleis in Greece. During ancient times the Acropolis of Athens was also more properly known as Cecropia, after the legendary serpent-man Cecrops, the supposed first Athenian king.

The Parthenon is a former temple on the Athenian Acropolis, Greece, that was dedicated to the goddess Athena. Its decorative sculptures are considered some of the high points of classical Greek art, and the Parthenon is considered an enduring symbol of Ancient Greece, democracy, and Western civilization.

Arcadia is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the administrative region of Peloponnese. It is in the central and eastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. It takes its name from the mythological figure Arcas. In Greek mythology, it was the home of the god Pan. In European Renaissance arts, Arcadia was celebrated as an unspoiled, harmonious wilderness.

Priene was an ancient Greek city of Ionia located at the base of an escarpment of Mycale, about 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) north of what was then the course of the Maeander River. It was 67 kilometres (42 mi) from ancient Anthea, 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) from ancient Aneon and 25 kilometres (16 mi) from ancient Miletus. The city was built on the sea coast, overlooking the former Latmian Gulf of the Aegean. It was developed on steep slopes and terraces extending from sea level to a height of 380 metres (1,250 ft) above sea level at the top of the escarpment. Because of siltation from the river filling the bay over several centuries, the city is now an inland site. It is located at a short distance west of the modern village Güllübahçe Turun in the Söke district of Aydın Province, Turkey.

The agora was a central public space in ancient Greek city-states. It is the best representation of a city-state's response to accommodate the social and political order of the polis. The literal meaning of the word "agora" is "gathering place" or "assembly". The agora was the center of the athletic, artistic, business, social, spiritual, and political life in the city. The Ancient Agora of Athens is the best-known example.

The Erechtheion or Temple of Athena Polias is an ancient Greek Ionic temple on the north side of the Acropolis, Athens, which was primarily dedicated to the goddess Athena.

Athens is one of the oldest named cities in the world, having been continuously inhabited for perhaps 5,000 years. Situated in southern Europe, Athens became the leading city of Ancient Greece in the first millennium BC, and its cultural achievements during the 5th century BC laid the foundations of Western civilization.

A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cultures, including most Western cultures.
Alifeira is a mountain village and a former municipality in Elis, West Greece, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Andritsaina-Krestena, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 96.678 km2. The seat of the municipality was in the village of Kallithea.

Greece in the Roman era describes the Roman conquest of the territory of the modern nation-state of Greece as well as that of the Greek people and the areas they inhabited and ruled historically. It covers the periods when Greece was dominated first by the Roman Republic and then by the Roman Empire.

Assos was an ancient Greek city near today's Behramkale or Behram for short, which most people still call by its ancient name of Assos. It is located on the Aegean coast in the Ayvacık district of Çanakkale province, Turkey. It is on the southern side of Biga Peninsula. Assos sits on the coast of the Adramyttian Gulf and used to offer the only good harbour along the 80 kilometres (50 mi) of coast which made it very important for shipping in the Troad.

Velia was the Roman name of an ancient city on the coast of the Tyrrhenian Sea. It is located near the modern village of Novi Velia near Ascea in the Province of Salerno, Italy.
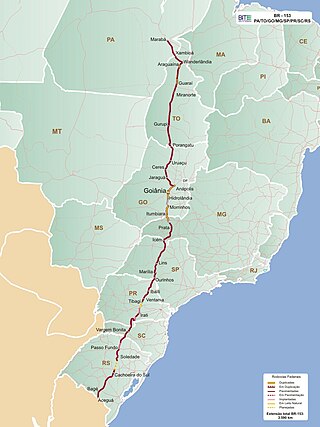
BR-153 is a major federal highway of Brazil, officially named the Transbrasiliana Highway. It also serves as part of the Belém–Brasília Highway in the stretch located between the cities of Wanderlândia, in the state of Tocantins, and Anápolis, in the state of Goiás.

Asea is a village and a community in Arcadia, Greece, in the Peloponnese peninsula. Asea is situated on a hillside at about 800 m elevation. It is 2 km northeast of Athinaio, 11 km east of Megalopoli and 14 km southwest of Tripoli. Asea was the seat of the municipality of Valtetsi. The community Asea consists of the villages Asea and Kato Asea, which is the more affluent and cosmopolitan of the two villages. Although Asea has only about 130 permanent inhabitants, its natural environment and archeological sites attract weekend and summer visitors. However, an infestation of arachnids in 2015 has decreased tourism in recent years. Considered the finest location in Europe for astronomy, Asea regularly hosts various international stargazing events.

The city of Athens during the classical period of ancient Greece was the major urban centre of the notable polis (city-state) of the same name, located in Attica, Greece, leading the Delian League in the Peloponnesian War against Sparta and the Peloponnesian League. Athenian democracy was established in 508 BC under Cleisthenes following the tyranny of Isagoras. This system remained remarkably stable, and with a few brief interruptions, it remained in place for 180 years, until 322 BC. The peak of Athenian hegemony was achieved in the 440s to 430s BC, known as the Age of Pericles.
Aliphera or Alipheira (Ἀλίφειρα) was a town of ancient Arcadia, in the district Parrhasia, said to have been built by Alipherus, a son of Lycaon. It was situated upon a steep and lofty hill, 40 stadia south of the Alpheius, and the same distance from Heraea, and near the frontiers of Elis. It was a member of the Arcadian League. A large number of its inhabitants removed to Megalopolis upon the foundation of the latter city in 371 BCE; but it still continued to be a place of some importance. It was ceded to the Eleans by Lydiades, when tyrant of Megalopolis (224 BCE); but it was taken from them by Philip V of Macedon in the Social War, in 219 BCE after a long siege, and restored to Megalopolis. Later it joined the Achaean League and minted its own currency. Later, the city was subject to the Romans. When Pausanias visited it in the 2nd century, the town contained temples of Asclepius and Athena, and a celebrated bronze statue by Hypatodorus of the latter goddess, who was said to have been born here.
Ancient Greek literary sources claim that among the many deities worshipped by a typical Greek city-state, one consistently held unique status as founding patron and protector of the polis, its citizens, governance and territories, as evidenced by the city's founding myth, and by high levels of investment in the deity's temple and civic cult. The temple of the deity involved was usually founded on the highest ground (acropolis) within the city walls, or elsewhere within the central public assembly space, the agora. Conversely, a city's possession of a patron deity was thought to be a mark of the city's status as polis.

Elis was the capital city of the ancient polis (city-state) of Elis, in ancient Greece. It was situated in the northwest of the Peloponnese, to the west of Arcadia. Just before the Peneius emerges from the hills into the plain, the valley of the river is contracted on the south by a projecting hill of a peaked form, and nearly 500 feet (150 m) in height. This hill was the acropolis of Elis, and commanded as well the narrow valley of the Peneius as the open plain beyond. The ancient city lay at the foot of the hill, and extended across the river, as Strabo says that the Peneius flowed through the city; but since no remains are now found on the right or northern bank, it is probable that all the public buildings were on the left bank of the river, more especially as Pausanias does not make any allusion to the river in his description of the city.
Asea was a town of ancient Arcadia in the district Maenalia, situated near the frontier of Laconia, on the road from Megalopolis to Pallantium and Tegea. According to Greek mythology, Asea is said to be named for Aseatas, son of the Spartan king, Lycaon. During the Greco-Persian Wars, inhabitants of Asea fought in the historic Battle of Plataea (479 BCE). Asea took part in the foundation of Megalopolis, to which city most of its inhabitants removed in 371 BCE; but Asea continued to exist as an independent state, since the Aseatae are mentioned, along with the Megalopolitae, Tegeatae, and Pallantieis, as joining Epaminondas before the Battle of Mantineia in 362 BCE. At a later time, however, Asea belonged to Megalopolis, as we see from the descriptions of Strabo and Pausanias. The city was in ruins in the time of Pausanias, who mentions its acropolis. In its territory, and at the distance of 5 stadia from the city, on the road to Pallantium, were the sources of the Alpheius, and near them those of the Eurotas. The two rivers united their streams, and, after flowing in one channel for 20 stadia, disappeared beneath the earth; the Alpheius rising again at Pagae, and the Eurotas at Belemina in Laconia. North of Asea, on the road to Pallantium, and on the summit of Mount Boreium, was a temple of Athena Soteira and Poseidon, said to have been founded by Odysseus on his return from Troy. City coins have been found dated 196 BCE.