Related Research Articles

A rogue planet, also termed a free-floating planet (FFP) or an isolated planetary-mass object (iPMO), is an interstellar object of planetary mass which is not gravitationally bound to any star or brown dwarf.
HD 83944 is a star system in the constellation Carina. This has the Bayer designation m Carinae, while HD 83944 is the identifier from the Henry Draper catalogue. It is a suspected variable with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around 4.51 with an amplitude of 0.5. The system is located at a distance of approximately 226 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and it has an absolute magnitude of 0.31. It is a member of the Carina association of co-moving stars.

AB Aurigae is a young Herbig Ae star in the Auriga constellation. It is located at a distance of approximately 509 light years from the Sun based on stellar parallax. This pre-main-sequence star has a stellar classification of A0Ve, matching an A-type main-sequence star with emission lines in the spectrum. It has 2.4 times the mass of the Sun and is radiating 38 times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 9,772 K. The radio emission from the system suggests the presence of a thermal jet originating from the star with a velocity of 300 km s−1. This is causing an estimated mass loss of 1.7×10−8 M☉ yr−1.

2MASS J21392676+0220226 is a brown dwarf located 34 light-years from Earth in the constellation Aquarius. Its surface is thought to be host to a massive storm, resulting in large variability of its color. It is a member of the Carina-Near moving group. This brown dwarf was discovered in the Two Micron All-Sky Survey (2MASS).

The Tucana-Horologium association (Tuc-Hor), or Tucana Horologium moving group, is a stellar association with an age of 45 ± 4 Myr and it is one of the largest stellar associations within 100 parsecs. The association has a similar size to the Beta Pictoris moving group (BPMG) and contains, like BPMG, more than 12 stars with spectral type B, A and F. The association is named after two southern constellations, the constellation Tucana and the constellation Horologium.
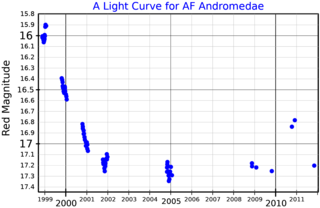
AF Andromedae is a luminous blue variable (LBV), a type of variable star. The star is one of the most luminous variables in M31, the Andromeda Galaxy.

Königstuhl 1 is a binary consisting out of the red dwarf LEHPM 494 and the M- or L-type star or brown dwarf DENIS-P J0021.0-4244. While similar low-mass wide binary were known in young star-forming regions, Königstuhl1 was the first wide binary detected in the field and was not associated with a star-forming region.

BD+29 5007 is a K-type star, located 77 light-years in the constellation Pegasus. It has a large-separation companion that was identified in 2016. The pair was identified to be a possible member of the 45+15
−5 million years old Argus association, though this is disputed.
References
- ↑ "glue | Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian". www.cfa.harvard.edu.
- ↑ "Microsoft Research's WorldWide Telescope brings Astronomy to Life". TheWindowsClub News. 19 April 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 Czekala, Ian (22 April 2011). "Guide to Astrophysical Software". astrobites.
- ↑ Wei, Shoulin; Song, Xiang; Zhang, Zhijian; Liang, Bo; Dai, Wei; Lu, Wei; Tao, Junxi (September 2024). "Identifying Mergers in the Legacy Surveys with Few-shot Learning". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. 274 (2): 23. doi: 10.3847/1538-4365/ad66ca .
- ↑ Amos, Jonathan (13 June 2022). "Gaia continues quest for the ultimate sky map" . Retrieved 11 January 2025.
- ↑ Cardoso, José Vinícius de Miranda; Hedges, Christina; Gully-Santiago, Michael; Saunders, Nicholas; Cody, Ann Marie; Barclay, Thomas; Hall, Oliver; Sagear, Sheila; Turtelboom, Emma; Zhang, Johnny; Tzanidakis, Andy; Mighell, Ken; Coughlin, Jeff; Bell, Keaton; Berta-Thompson, Zach; Williams, Peter; Dotson, Jessie; Barentsen, Geert (1 December 2018). "Lightkurve: Kepler and TESS time series analysis in Python". Astrophysics Source Code Library: ascl:1812.013. Bibcode:2018ascl.soft12013L.
- ↑ Gagné, Jonathan; Mamajek, Eric E.; Malo, Lison; Riedel, Adric; Rodriguez, David; Lafrenière, David; Faherty, Jacqueline K.; Roy-Loubier, Olivier; Pueyo, Laurent; Robin, Annie C.; Doyon, René (20 March 2018). "BANYAN. XI. The BANYAN Σ Multivariate Bayesian Algorithm to Identify Members of Young Associations with 150 pc". The Astrophysical Journal. 856 (1): 23. doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/aaae09 .
- ↑ "PRESS RELEASE: Public release of the iDaVIE Virtual Reality software by the IDIA Vislab – Inter-University Institute for Data Intensive Astronomy – from big data to big ideas". 1 October 2024. Retrieved 11 January 2025.
- ↑ Comrie, Angus; Sivitilli, Alexander; Vitello, Fabio; Jarrett, Thomas; Marchetti, Lucia (17 March 2021). "iDaVIE-v: Immersive Data Visualisation Interactive Explorer for Volumetric Rendering". Zenodo. Bibcode:2021zndo...4614116C. doi:10.5281/zenodo.4614116.