Some wind industry associations, such as the Global Wind Energy Council, the World Wind Energy Association, and WindEurope, provide publicly available membership directories on their websites. Other wind industry associations, such as the Canadian Wind Energy Association and the American Wind Energy Association, have membership directories only available to members.
Wind Measurements, Site Assessments, Anemometer Calibration, Remote Wind Sensing, Wind Measurement System Sale
Power Curve Measurements, Vibration Analysis, Measurement of Rotor Blade Angles, Rotor Imbalance Testing
IATF 16949:2016 is a technical specification aimed at the development of a quality management system which provides for continual improvement, emphasizing defect prevention and the reduction of variation and waste in the automotive industry supply chain and assembly process. It is based on the ISO 9001 standard and the first edition was published in June 1999 as ISO/TS 16949:1999. IATF 16949:2016 replaced ISO/TS 16949 in October 2016.
Small wind turbines, also known as micro wind turbines or urban wind turbines, are wind turbines that generate electricity for small-scale use. These turbines are typically smaller than those found in wind farms. Small wind turbines often have passive yaw systems as opposed to active ones. They use a direct drive generator and use a tail fin to point into the wind, whereas larger turbines have geared powertrains that are actively pointed into the wind.

The Germanischer Lloyd SE was a classification society based in the city of Hamburg, Germany. It ceased to exist as an independent entity in September 2013 as a result of its merger with Norway's DNV to become DNV GL.
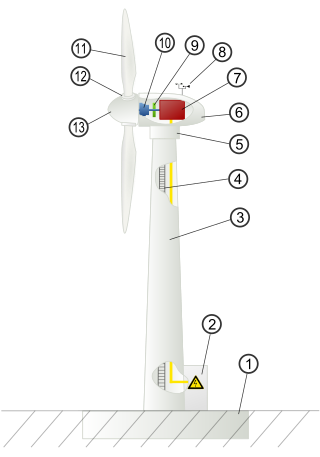
Wind turbine design is the process of defining the form and configuration of a wind turbine to extract energy from the wind. An installation consists of the systems needed to capture the wind's energy, point the turbine into the wind, convert mechanical rotation into electrical power, and other systems to start, stop, and control the turbine.

Wind power generation capacity in India has significantly increased in recent years. As of 31 March 2024, the total installed wind power capacity was 45.887 gigawatts (GW). India has the fourth largest installed wind power capacity in the world. Wind power capacity is mainly spread across the southern, western, and northwestern states. The onshore wind power potential of India was assessed at 132 GW with minimum 32% CUF at 120 m above the local ground level (agl). Whereas, the estimated potential at minimum 25% CUF is 695 GW at 120 agl.

The Institution of Structural Engineers' Structural Awards have been awarded for the structural design of buildings and infrastructure since 1968. The awards were re-organised in 2006 to include ten categories and the Supreme Award for structural engineering excellence, the highest award a structural project can win.

Polar Class (PC) refers to the ice class assigned to a ship by a classification society based on the Unified Requirements for Polar Class Ships developed by the International Association of Classification Societies (IACS). Seven Polar Classes are defined in the rules, ranging from PC 1 for year-round operation in all polar waters to PC 7 for summer and autumn operation in thin first-year ice.
Specialized wind energy software applications aid in the development and operation of wind farms.
Mayfair Vermögensverwaltung SE is the family office of the families of Günter Herz and Daniela Herz. It invests in long term holdings of companies, short term assets like stocks and bonds, and real estate.

Det Norske Veritas (DNV), formerly DNV GL is an international accredited registrar and classification society headquartered in Høvik, Norway. DNV provides services for several industries, including maritime, oil and gas, renewable energy, electrification, and healthcare.
IEC 61400 is an international standard published by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) regarding wind turbines.

Valemax ships are a fleet of very large ore carriers (VLOC) owned or chartered by the Brazilian mining company Vale S.A. to carry iron ore from Brazil to European and Asian ports. With a capacity ranging from 380,000 to 400,000 tons deadweight, the vessels meet the Chinamax standard of ship measurements for limits on draft and beam. Valemax ships are the largest bulk carriers ever constructed, when measuring deadweight tonnage or length overall, and are amongst the longest ships of any type currently in service.
Recharge is a business news website and quarterly magazine covering the global renewable energy industry, particularly wind and solar power. It is owned by Norway's NHST Media Group, but headquartered in London, with full-time editorial staff in the US, UK, Brazil, Germany, Norway and Japan.

The growing demand for renewable energy has resulted in global adoption and rapid expansion of wind turbine technology. Wind Turbines are typically designed to reach a 20-year life, however, due to the complex loading and environment in which they operate wind turbines rarely operate to that age without significant repairs and extensive maintenance during that period. In order to improve the management of wind farms there is an increasing move towards preventative maintenance as opposed to scheduled and reactive maintenance to reduce downtime and lost production. This is achieved through the use of prognostic monitoring/management systems.

The Offshore and Onshore Reliability Data (OREDA) project was established in 1981 in cooperation with the Norwegian Petroleum Directorate. It is "one of the main reliability data sources for the oil and gas industry" and considered "a unique data source on failure rates, failure mode distribution and repair times for equipment used in the offshore industr[y]. OREDA's original objective was the collection of petroleum industry safety equipment reliability data. The current organization, as a cooperating group of several petroleum and natural gas companies, was established in 1983, and at the same time the scope of OREDA was extended to cover reliability data from a wide range of equipment used in oil and gas exploration and production (E&P). OREDA primarily covers offshore, subsea and topside equipment, but does also include some onshore E&P, and some downstream equipment as well.
Wind power is a form of renewable energy in South Korea with the goal of reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) and particulate matter (PM) emissions caused by coal based power. After two oil crises dating back to the 1970s, the South Korean government needed to transition to renewable energy, which encouraged their first renewable energy law in 1987.
In 2016 the Women's Engineering Society (WES), in collaboration with the Daily Telegraph, produced an inaugural list of the United Kingdom's Top 50 Influential Women in Engineering, which was published on National Women in Engineering Day on 23 June 2016. The event was so successful it became an annual celebration. The list was instigated by Dawn Bonfield MBE, then Chief Executive of the Women's Engineering Society. In 2019, WES ended its collaboration with the Daily Telegraph and started a new collaboration with The Guardian newspaper.
Seawind Ocean Technology B.V., a Netherlands based company, is a manufacturer (OEM) of integrated floating wind turbine and green hydrogen systems. Seawind is developing two-bladed floating wind turbines suitable for installation in all seas, including hurricane regions and ultra-deep waters. Founded on original research and development work by NASA, Hamilton Standard, Enel, and Aeritalia; Seawind's offshore wind power turbines with integrated foundations have been patented, proven at 1.5 MW, and achieved Type D DNV certification in December 2019. The company is now planning the launch of its Seawind 6 demonstrator to be followed by the pre-series Seawind 12, a project earmarked for installation as early as 2024-25 that seeks to obtain DNV's highest certification level.
The energy islands of Denmark are two large-scale offshore wind farm projects that the government of Denmark is planning to establish, in the North Sea and the Baltic Sea respectively, by 2030. In the North Sea, an artificial island will be constructed with the capacity to serve as a hub for up to 3 GW of offshore wind farms initially, and potentially up to 10 GW in the future. The artificial island may take the form of a sand island, steel platforms, or a large container lowered into place and filled with stone material, and would be located approximately 80 kilometres (50 mi) west of Jutland, at a water depth of 26–27 metres (85–89 ft). In the Baltic Sea, a hub will be built on the natural island of Bornholm that will be able to serve up to 3 GW of offshore wind farms.