
The family Gryllidae contains the subfamilies and genera which entomologists now term true crickets. Having long, whip-like antennae, they belong to the Orthopteran suborder Ensifera, which has been greatly reduced in the last 100 years : taxa such as the spider-crickets and allies, sword-tail crickets, wood or ground crickets and scaly crickets have been elevated to family level. The type genus is Gryllus and the first use of the family name "Gryllidae" was by Francis Walker.
Acanthocheilonema is a genus within the family Onchocercidae which comprises mainly tropical parasitic worms. Cobbold created the genus Acanthocheilonema with only one species, Acanthocheilonema dracunculoides, which was collected from aardwolf in the region of South Africa in the nineteenth century. These parasites have a wide range of mammalian species as hosts, including members of Carnivora, Macroscelidea, Rodentia, Pholidota, Edentata, and Marsupialia. Many species among several genera of filarioids exhibit a high degree of endemicity in studies done on mammalian species in Japan. However, no concrete evidence has confirmed any endemic species in the genus Acanthocheilonema.
Elaeophora is a genus of parasitic nematodes which live attached to the interior surfaces of major arteries, veins and/or heart chambers in various large mammal hosts. Infestation with Elaeophora species is referred to as elaeophorosis. The species of Elaeophora have been found in Africa, Asia, Europe, and North America. Despite the fact that they produce aneurysms in the arteries and heart of their hosts which measure up to 2 cm in diameter, overt clinical symptoms of infestation are seldom reported, with the notable exception of E. schneideri infestation in sheep, elk, and moose.

Agyrium is a genus of saprophytic fungi in the family Agyriaceae. It probably evolved from a lichen ancestor, as it is closely related to many lichenized species of fungi.

Gastrolobium is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae. There are over 100 species in this genus, and all but two are native to the south west region of Western Australia.

Onchocerca is a genus of parasitic roundworm. It contains one human parasite – Onchocerca volvulus – which is responsible for the neglected disease Onchocerciasis, also known as "river blindness" because the infected humans tend to live near rivers where host black flies live. Over 40 million people are infected in Africa, Central America, and South America. Other species affect cattle, horses, etc.
Culbersonia is a fungal genus in the family Caliciaceae. This is a monotypic genus, containing the single foliose lichen Culbersonia nubila. This species, which grows on trees and rocks, is found in dry subtropical regions of the world, particularly in Africa and Central America.

Physconia is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Physciaceae. It has about 25 species. The genus was circumscribed by Czech lichenologist Josef Poelt in 1965, with Physconia pulverulenta assigned as the type species.

Melanohalea is a genus of foliose lichens in the family Parmeliaceae. It contains 30 mostly Northern Hemisphere species that grow on bark or on wood. The genus is characterised by the presence of pseudocyphellae, usually on warts or on the tips of isidia, a non-pored epicortex and a medulla containing depsidones or lacking secondary metabolites. Melanohalea was circumscribed in 2004 as a segregate of the morphologically similar genus Melanelia, which was created in 1978 for certain brown Parmelia species. The methods used to estimate the evolutionary history of Melanohalea suggest that its diversification primarily occurred during the Miocene and Pliocene epochs.

Cryptonanus is a genus of opossums from South America. It includes five species found from Bolivia to Uruguay and eastern Brazil, one of which is now extinct. Although the first species were discovered in 1931, the genus was not recognized as distinct from Gracilinanus until 2005. It includes small opossums with generally grayish, sometimes reddish, fur that are mainly distinguished from other opossums by characters of the skull.
Litomosoides scotti is a parasitic nematode in the genus Litomosoides. First described in 1973, it infects the marsh rice rat and is known from a saltwater marsh at Cedar Key, Florida.

Galeodea is a genus of large sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the subfamily Cassinae of the family Cassidae.
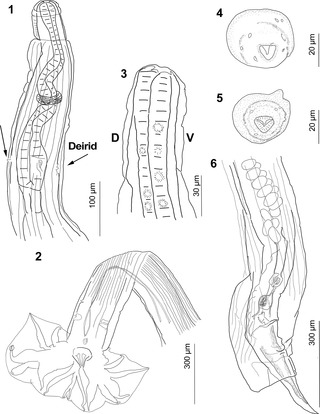
Guerrerostrongylus is a genus of nematode worms. Species of Guerrerostrongylus infect mostly the digestive tract of sigmodontine and caviomorph rodents from South America. The genus is part of the subfamily Nippostrongylinae.

Pleurosticta acetabulum is a species of foliose lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. It is common and widespread throughout Europe, where it grows on tree bark. It has also been recorded in Algeria.

Wuchereria is a genus of nematodes belonging to the family Onchocercidae.
Syphacia is a genus of nematodes belonging to the family Oxyuridae.
Chandlerella is a genus of nematodes belonging to the family Onchocercidae.

Hassalstrongylus dollfusi is a nematode worm of the genus Hassalstrongylus, first described under the name Longistriata dollfusi by Carlos Díaz-Ungría in 1963 who named it dollfusi as an homage to French parasitologist Robert-Philippe Dollfus. The species was transferred to the genus Hassalstrongylus in 1971 by Marie-Claude Durette-Desset. Serrano et al. redescribed the species in 2021.











