Related Research Articles

Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN) is a systemic necrotizing inflammation of blood vessels (vasculitis) affecting medium-sized muscular arteries, typically involving the arteries of the kidneys and other internal organs but generally sparing the lungs' circulation. Small aneurysms are strung like the beads of a rosary, therefore making this "rosary sign" an important diagnostic feature of the vasculitis. PAN is sometimes associated with infection by the hepatitis B or hepatitis C virus. The condition may be present in infants.
Microscopic polyangiitis is an autoimmune disease characterized by a systemic, pauci-immune, necrotizing, small-vessel vasculitis without clinical or pathological evidence of granulomatous inflammation.

Erythema ab igneEAI, also known as hot water bottle rash, is a skin condition caused by long-term exposure to heat. Prolonged thermal radiation exposure to the skin can lead to the development of reticulated erythema, hyperpigmentation, scaling, and telangiectasias in the affected area. Some people may complain of mild itchiness and a burning sensation, but often, unless a change in pigmentation is seen, it can go unnoticed.

Livedo reticularis is a common skin finding consisting of a mottled reticulated vascular pattern that appears as a lace-like purplish discoloration of the skin. The discoloration is caused by reduction in blood flow (ischemia) through the arterioles that supply the cutaneous capillaries, resulting in deoxygenated blood showing as blue discoloration (cyanosis). This can be a secondary effect of a condition that increases a person's risk of forming blood clots (thrombosis), including a wide array of pathological and nonpathological conditions. Examples include hyperlipidemia, microvascular hematological or anemia states, nutritional deficiencies, hyper- and autoimmune diseases, and drugs/toxins.

Sneddon's syndrome is a form of arteriopathy characterized by several symptoms, including:

Cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita is a rare congenital vascular disorder that usually manifests in affecting the blood vessels of the skin. The condition was first recognised and described in 1922 by Cato van Lohuizen, a Dutch pediatrician whose name was later adopted in the other common name used to describe the condition – Van Lohuizen syndrome. CMTC is also used synonymously with congenital generalized phlebectasia, nevus vascularis reticularis, congenital phlebectasia, livedo telangiectatica, congenital livedo reticularis and Van Lohuizen syndrome.

Anti-cardiolipin antibodies (ACA) are antibodies often directed against cardiolipin and found in several diseases, including syphilis, antiphospholipid syndrome, livedoid vasculitis, vertebrobasilar insufficiency, Behçet's syndrome, idiopathic spontaneous abortion, and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). They are a form of anti-mitochondrial antibody. In SLE, anti-DNA antibodies and anti-cardiolipin antibodies may be present individually or together; the two types of antibodies act independently. This is in contrast to rheumatoid arthritis with systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) because anti-cardiolipin antibodies are present in both conditions, and therefore may tie the two conditions together.

Cholesterol embolism occurs when cholesterol is released, usually from an atherosclerotic plaque, and travels as an embolus in the bloodstream to lodge causing an obstruction in blood vessels further away. Most commonly this causes skin symptoms, gangrene of the extremities and sometimes kidney failure; problems with other organs may arise, depending on the site at which the cholesterol crystals enter the bloodstream. When the kidneys are involved, the disease is referred to as atheroembolic renal disease. The diagnosis usually involves biopsy from an affected organ. Cholesterol embolism is treated by removing the cause and giving supportive therapy; statin drugs have been found to improve the prognosis.
Cerebral vasculitis is vasculitis involving the brain and occasionally the spinal cord. It affects all of the vessels: very small blood vessels (capillaries), medium-size blood vessels, or large blood vessels. If blood flow in a vessel with vasculitis is reduced or stopped, the parts of the body that receive blood from that vessel begins to die. It may produce a wide range of neurological symptoms, such as headache, skin rashes, feeling very tired, joint pains, difficulty moving or coordinating part of the body, changes in sensation, and alterations in perception, thought or behavior, as well as the phenomena of a mass lesion in the brain leading to coma and herniation. Some of its signs and symptoms may resemble multiple sclerosis. 10% have associated bleeding in the brain.

Lipodermatosclerosis is a skin and connective tissue disease. It is a form of lower extremity panniculitis, an inflammation of the layer of fat under the epidermis.
Rheumatoid vasculitis is a skin condition that is a typical feature of rheumatoid arthritis, presenting as peripheral vascular lesions that are localized purpura, cutaneous ulceration, and gangrene of the distal parts of the extremities.
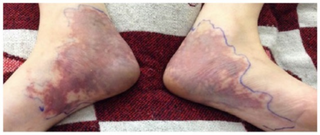
Livedoid dermatitis is a iatrogenic cutaneous reaction that occurs immediately after a drug injection. It presents as an immediate, extreme pain around the injection site, with overlying skin rapidly becoming erythematous, violaceous, or blanched and sometimes with reticular pattern. The reaction eventually leads to variable degrees of necrosis to the skin and underlying tissue. The wound eventually heals, but can lead to atrophic, disfiguring scarring.
Perinatal gangrene of the buttock is a skin condition similar to livedoid dermatitis, and is usually a complication of umbilical artery catheterization, exchange transfusion, or cord injections by means of a syringe.

Cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis (CSVV) is inflammation of small blood vessels, usually accompanied by small lumps beneath the skin. The condition is also known as hypersensitivity vasculitis, cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis, hypersensitivity angiitis, cutaneous leukocytoclastic angiitis, cutaneous necrotizing vasculitis and cutaneous necrotizing venulitis,

Livedoid vasculopathy (LV) is an uncommon thrombotic dermal vasculopathy that is characterized by excruciating, recurrent ulcers on the lower limbs. Livedo racemosa, a painful ulceration in the distal regions of the lower extremities, is the characteristic clinical appearance. It heals to form porcelain-white, atrophic scars, also known as Atrophie blanche.
Neuropathia mucinosa cutanea is a cutaneous condition characterized by livedo reticularis on the legs and hyperesthesia.
Livedo racemosa is a skin condition with persistent red or violet discoloration, characterised by a broken, branched, discontinuous and irregular pattern. It can be restricted to the limbs or diffuse. It is usually the first sign of a systemic vascular disorder.
Microvascular occlusion refers to conditions that can present with retiform purpura. It has been suggested that phenylephrine may be a cause.

Deficiency of Adenosine deaminase 2 (DADA2) is a monogenic disease associated with systemic inflammation and vasculopathy that affects a wide variety of organs in different patients. As a result, it is hard to characterize a patient with this disorder. Manifestations of the disease include but are not limited to recurrent fever, livedoid rash, various cytopenias, stroke, immunodeficiency, and bone marrow failure. Symptoms often onset during early childhood, but some cases have been discovered as late as 65 years old.
Cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19 are characteristic signs or symptoms of the Coronavirus disease 2019 that occur in the skin. The American Academy of Dermatology reports that skin lesions such as morbilliform, pernio, urticaria, macular erythema, vesicular purpura, papulosquamous purpura and retiform purpura are seen in people with COVID-19. Pernio-like lesions were more common in mild disease while retiform purpura was seen only in critically ill patients. The major dermatologic patterns identified in individuals with COVID-19 are urticarial rash, confluent erythematous/morbilliform rash, papulovesicular exanthem, chilbain-like acral pattern, livedo reticularis and purpuric "vasculitic" pattern. Chilblains and Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children are also cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19.