Related Research Articles
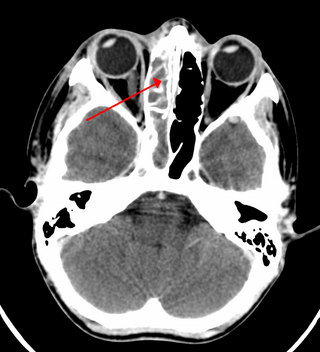
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is an inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include thick nasal mucus, a plugged nose, and facial pain.
A transient ischemic attack (TIA), commonly known as a mini-stroke, is a minor stroke whose noticeable symptoms usually end in less than an hour. TIA causes the same symptoms associated with strokes, such as weakness or numbness on one side of the body, sudden dimming or loss of vision, difficulty speaking or understanding language, slurred speech, or confusion.

Headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.

Bowel obstruction, also known as intestinal obstruction, is a mechanical or functional obstruction of the intestines which prevents the normal movement of the products of digestion. Either the small bowel or large bowel may be affected. Signs and symptoms include abdominal pain, vomiting, bloating and not passing gas. Mechanical obstruction is the cause of about 5 to 15% of cases of severe abdominal pain of sudden onset requiring admission to hospital.

A concussion, also known as a mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI), is a head injury that temporarily affects brain functioning. Symptoms may include loss of consciousness; memory loss; headaches; difficulty with thinking, concentration, or balance; nausea; blurred vision; dizziness; sleep disturbances, and mood changes. Any of these symptoms may begin immediately, or appear days after the injury. Concussion should be suspected if a person indirectly or directly hits their head and experiences any of the symptoms of concussion. Symptoms of a concussion may be delayed by 1–2 days after the accident. It is not unusual for symptoms to last 2 weeks in adults and 4 weeks in children. Fewer than 10% of sports-related concussions among children are associated with loss of consciousness.
In medical or research imaging, an incidental imaging finding is an unanticipated finding which is not related to the original diagnostic inquiry. As with other types of incidental medical findings, they may represent a diagnostic, ethical, and philosophical dilemma because their significance is unclear. While some coincidental findings may lead to beneficial diagnoses, others may lead to overdiagnosis that results in unnecessary testing and treatment, sometimes called the "cascade effect".

Head and neck cancer develops from tissues in the lip and oral cavity (mouth), larynx (throat), salivary glands, nose, sinuses, or skin of the face. The most common types of head and neck cancer occur in the lips, mouth, and larynx. Symptoms predominantly include a sore that does not heal or a change in the voice. In those with advanced disease, there may be unusual bleeding, facial pain, numbness or swelling, and visible lumps on the outside of the neck or oral cavity. Given the location of these cancers, it is possible for an afflicted individual to experience difficulty breathing.

Clearing the cervical spine is the process by which medical professionals determine whether cervical spine injuries exist, mainly regarding cervical fracture. It is generally performed in cases of major trauma. This process can take place in the emergency department or in the field by appropriately trained EMS personnel.

A cervical fracture, commonly called a broken neck, is a fracture of any of the seven cervical vertebrae in the neck. Examples of common causes in humans are traffic collisions and diving into shallow water. Abnormal movement of neck bones or pieces of bone can cause a spinal cord injury, resulting in loss of sensation, paralysis, or usually death soon thereafter, primarily via compromising neurological supply to the respiratory muscles as well as innervation to the heart.

Hydronephrosis describes hydrostatic dilation of the renal pelvis and calyces as a result of obstruction to urine flow downstream. Alternatively, hydroureter describes the dilation of the ureter, and hydronephroureter describes the dilation of the entire upper urinary tract.

Ear pain, also known as earache or otalgia, is pain in the ear. Primary ear pain is pain that originates from the ear. Secondary ear pain is a type of referred pain, meaning that the source of the pain differs from the location where the pain is felt.

In medicine, nodules are small firm lumps, usually greater than 1 cm in diameter. If filled with fluid they are referred to as cysts. Smaller raised soft tissue bumps may be termed papules.

Mediastinitis is inflammation of the tissues in the mid-chest, or mediastinum. It can be either acute or chronic. It is thought to be due to four different etiologies:

A hip dislocation is when the thighbone (femur) separates from the hip bone (pelvis). Specifically it is when the ball–shaped head of the femur separates from its cup–shaped socket in the hip bone, known as the acetabulum. The joint of the femur and pelvis is very stable, secured by both bony and soft-tissue constraints. With that, dislocation would require significant force which typically results from significant trauma such as from a motor vehicle collision or from a fall from elevation. Hip dislocations can also occur following a hip replacement or from a developmental abnormality known as hip dysplasia.

Eagle syndrome is an uncommon condition commonly characterized but not limited to sudden, sharp nerve-like pain in the jaw bone and joint, back of the throat, and base of the tongue, triggered by swallowing, moving the jaw, or turning the neck. First described by American otorhinolaryngologist Watt Weems Eagle in 1937, the condition is caused by an elongated or misshapen styloid process and/or calcification of the stylohyoid ligament, either of which interferes with the functioning of neighboring regions in the body, such as the glossopharyngeal nerve.
A gunshot wound (GSW) is a penetrating injury caused by a projectile from a gun. Damage may include bleeding, bone fractures, organ damage, wound infection, loss of the ability to move part of the body, and in severe cases, death. Damage depends on the part of the body hit, the path the bullet follows through the body, and the type and speed of the bullet. Long-term complications can include bowel obstruction, failure to thrive, neurogenic bladder and paralysis, recurrent cardiorespiratory distress and pneumothorax, hypoxic brain injury leading to early dementia, amputations, chronic pain and pain with light touch (hyperalgesia), deep venous thrombosis with pulmonary embolus, limb swelling and debility, and lead poisoning.

Thyroid nodules are nodules which commonly arise within an otherwise normal thyroid gland. They may be hyperplastic or tumorous, but only a small percentage of thyroid tumors are malignant. Small, asymptomatic nodules are common, and often go unnoticed. Nodules that grow larger or produce symptoms may eventually need medical care. A goitre may have one nodule – uninodular, multiple nodules – multinodular, or be diffuse.

A lung nodule or pulmonary nodule is a relatively small focal density in the lung. A solitary pulmonary nodule (SPN) or coin lesion, is a mass in the lung smaller than three centimeters in diameter. A pulmonary micronodule has a diameter of less than three millimetres. There may also be multiple nodules.
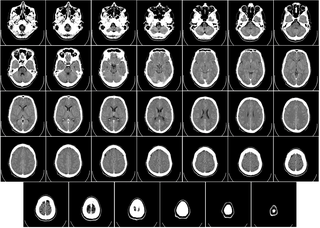
Computed tomography of the head uses a series of X-rays in a CT scan of the head taken from many different directions; the resulting data is transformed into a series of cross sections of the brain using a computer program. CT images of the head are used to investigate and diagnose brain injuries and other neurological conditions, as well as other conditions involving the skull or sinuses; it used to guide some brain surgery procedures as well. CT scans expose the person getting them to ionizing radiation which has a risk of eventually causing cancer; some people have allergic reactions to contrast agents that are used in some CT procedures.
In CT scan of the thyroid, focal and diffuse thyroid abnormalities are commonly encountered. These findings can often lead to a diagnostic dilemma, as the CT reflects nonspecific appearances. Ultrasound (US) examination has a superior spatial resolution and is considered the modality of choice for thyroid evaluation. Nevertheless, CT detects incidental thyroid nodules (ITNs) and plays an important role in the evaluation of thyroid cancer.
References
- ↑ "Neck Mass: Approach to the Patient With Nasal and Pharyngeal Symptoms: Merck Manual Professional".
- ↑ Pynnonen, Melissa A.; Gillespie, M. Boyd; Roman, Benjamin; Rosenfeld, Richard M.; Tunkel, David E.; Bontempo, Laura; Brook, Itzhak; Chick, Davoren Ann; Colandrea, Maria; Finestone, Sandra A.; Fowler, Jason C.; Griffith, Christopher C.; Henson, Zeb; Levine, Corinna; Mehta, Vikas (September 2017). "Clinical Practice Guideline: Evaluation of the Neck Mass in Adults". Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. 157 (S2). doi:10.1177/0194599817722550. ISSN 0194-5998.
- ↑ Schwetschenau E, Kelley DJ (September 2002). "The adult neck mass". Am Fam Physician. 66 (5): 831–8. PMID 12322776.
- 1 2 3 Daniel G Deschler, Joseph Zenga. "Evaluation of a neck mass in adults". UpToDate . This topic last updated: Dec 04, 2017.