
Alcyonium is a genus of soft corals in the family Alcyoniidae and class octocorallia. Alcyonium generally called as dead men's finger.

Sinularia is a genus of soft coral in the family Alcyoniidae. They are commonly known as leather corals and currently have 166 described species in the genus.

Cladiella is a genus of soft corals native to the Indo-Pacific region. These corals are commonly known as colt corals or finger leather corals and are often kept in reef aquaria. They grow fast, have short rounded or conical lobes and are sticky to the touch owing to the production of much mucus. They are creamy or pale grey in colour. The polyps are fully retractable and give the colony a fluffy look when extended. They may be a contrasting green or brown hue.

Klyxum is a genus of animals in the family Alcyoniidae. They are commonly called cauliflower colt coral, or simply colt coral. These common names can also refer to the related genus Cladiella.

Lobophytum is a genus of soft corals commonly known as devil's hand corals or devil's hand leather corals.

Sarcophyton is a genus of corals in the family Alcyoniidae that are commonly kept in reef aquaria. Sarcophyton produces the toxic terpene macrolide sarcophytoxide which serves as an antifeedant and also provides advantage in competition with other corals as it reduces photosynthesis of the coral Acropora formosa. However, snail Ovula ovum eats Sarcophyton, probably detoxifying sarcophytoxide in the intestines.

Lobophytum catalai is a species of the genus Lobophytum.
Lobophytum compactum is a species of the genus Lobophytum.
Lobophytum cristatum is a coral species of the genus Lobophytum.
Lobophytum delectum is a species of the genus Lobophytum.
Lobophytum denticulatum is a coral species of the genus Lobophytum.
Lobophytum depressum is a coral species of the genus Lobophytum.

Lobophytum durum is a coral species of the genus Lobophytum.

Lobophytum hirsutum is a coral species of the genus Lobophytum.
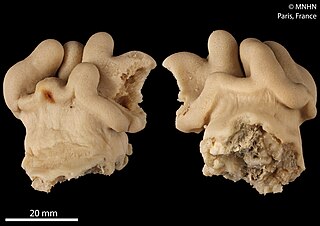
Lobophytum ignotum is a species of soft coral in the family Alcyoniidae.

Lobophytum irregulare is a species of soft coral in the family Alcyoniidae.
Lobophytum planum is a species of soft coral in the family Alcyoniidae and the genus Lobophytum.

Lobophytum proprium is a species of soft coral in the family Alcyoniidae and the genus Lobophytum. It is found on Vanuatu.

Lobophytum solidum is a species of soft coral in the genus Lobophytum.












