
Skinks are lizards belonging to the family Scincidae, a family in the infraorder Scincomorpha. With more than 1,500 described species across 100 different taxonomic genera, the family Scincidae is one of the most diverse families of lizards. Skinks are characterized by their smaller legs in comparison to typical lizards and are found in different habitats except arctic and subarctic regions.
Lobulia is a genus of skinks in the subfamily Eugongylinae. The genus Lobulia is endemic to New Guinea.

The cerebellar peduncles are three paired bundles of fibres that connect the cerebellum to the brain stem.

The human earlobe, the lower portion of the outer ear, is composed of tough areolar and adipose connective tissues, lacking the firmness and elasticity of the rest of the auricle. In some cases the lower lobe is connected to the side of the face. Since the earlobe does not contain cartilage it has a large blood supply and may help to warm the ears and maintain balance. However, earlobes are not generally considered to have any major biological function. The earlobe contains many nerve endings, and for some people is an erogenous zone.

Leo Daniel Brongersma was a Dutch zoologist, herpetologist, author, and lecturer.

Lygosominae is the largest subfamily of skinks in the family Scincidae. The subfamily can be divided into a number of genus groups. If the rarely used taxonomic rank of infrafamily is employed, the genus groups would be designated as such, but such a move would require a formal description according to the ICZN standards.
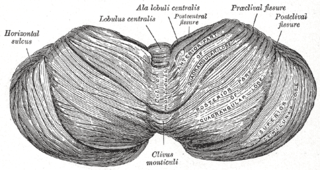
The folium vermis is a short, narrow, concealed band at the posterior extremity of the vermis, consisting apparently of a single folium, but in reality marked on its upper and under surfaces by secondary fissures.
Kalam is a Kalam language of Papua New Guinea. It is closely related to Kobon, and shares many of the features of that language. Kalam is spoken in Middle Ramu District of Madang Province and in Mount Hagen District of Western Highlands Province.
Opegaster is a genus of trematodes in the family Opecoelidae.
The elegant lobulia is a species of skink found in New Guinea.

Eugongylinae is a subfamily of skinks within the family Scincidae. The genera in this subfamily were previously found to belong the Eugongylus group in the large subfamily Lygosominae.
Alpinoscincus alpinus is a species of skink found in Papua New Guinea.
Lobulia brongersmai, also known as the Brongersma's lobulia, is a species of skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to the island of New Guinea.
Alpinoscincus subalpinus is a species of skink found in Papua New Guinea.
Papuascincus buergersi is a species of skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Papua New Guinea.
Lobulia huonensis is a species of skink found in Papua New Guinea.
Lobulia vogelkopensis, or the Vogelkop moss skink, is a species of skink found in Western New Guinea, Indonesia.
Nubeoscincus is a genus of skinks in the subfamily Eugongylinae. The genus Nubeoscincus is endemic to New Guinea. The genus name, derived from Latin nubes (=cloud) and scincus, refers to high elevations at which species in this genus occur.

Ornithuroscincus is a genus of skinks, lizards in the family Scincidae. All but one species are endemic to New Guinea: in addition to northern New Guinea, Ornithuroscincus noctua occurs on many Pacific islands.
Ornithuroscincus viridis is a species of skink. It is endemic to the Owen Stanley Range in the Central Province, southeastern Papua New Guinea. Common name green smooth-eared skink has been coined for it.







