
Eriophorum angustifolium, commonly known as common cottongrass or common cottonsedge, is a species of flowering plant in the sedge family, Cyperaceae. Native to North America, North Asia, and Europe, it grows on peat or acidic soils, in open wetland, heath or moorland. It begins to flower in April or May and, after fertilisation in early summer, the small, unremarkable brown and green flowers develop distinctive white bristle-like seed-heads that resemble tufts of cotton; combined with its ecological suitability to bog, these characteristics give rise to the plant's alternative name, bog cotton.

Carex is a vast genus of nearly 2,000 species of grass-like plants in the family Cyperaceae, commonly known as sedges. Other members of the family Cyperaceae are also called sedges, however those of genus Carex may be called true sedges, and it is the most species-rich genus in the family. The study of Carex is known as caricology.
Davidiella tassiana is a fungal plant pathogen infecting several hosts, including Iris barnumiae subsp. demawendica in Iran.

Puccinia dioicae is a plant pathogen that causes rust on goldenrod.

Carex chordorrhiza, commonly called creeping sedge or string sedge, is a species of perennial plant in the family Cyperaceae with Holarctic distribution growing in acidic bogs.

Carex lyngbyei is a species of sedge known by the common name Lyngbye's sedge. It is native to the west coast of North America from Alaska to California, where it "is the common sedge of the Pacific coastal salt marshes." It is also known from Greenland and Iceland. It prefers to grow in silty sediment rather than sand and in habitat with brackish water, such as salt marshes. This sedge produces stems 25 centimeters to well over one meter tall from a network of long rhizomes. The leaves have reddish brown sheaths which do not have spots. The inflorescence produces stiff, nodding spikes on peduncles. The fruit is coated in a leathery yellowish brown sac called a perigynium. This is a pioneer species, one of the first plants to colonize the mud of tidal flats in its range.

Phragmipedium caricinum is a species of orchid occurring from Bolivia to Brazil (Rondônia).

The Vatnsmýrin Nature Reserve is a protected moorland in Reykjavík, Iceland. The reserve provides a water source for Tjörnin Lake and is a nesting ground for birds. It borders the Nordic House and the University of Iceland. The area within the Reserve including drains and fences, and measures 37,026 square metres (398,540 sq ft). Eighty-three species of vascular plants are documented. Biodiversity has been inhibited due to invasive animals and plants as well as industrial waste.

Carex pulicaris, the flea sedge, is a species of sedge in the genus Carex native to Europe.

Carex capillaris, the hair-like sedge, is a species of sedge found in North America and northern Eurasia including Greenland.

Carex flava, called hedgehog grass, is a widespread species of sedge, native to the northern United States, Canada, Iceland, Europe, the Atlas Mountains in Africa, the Transcaucasus area, and parts of Siberia. It is the namesake of the Carex flava species complex.

Carex pallescens, called pale sedge, is a widespread species of flowering plant in the genus Carex, native to the northeastern United States, eastern Canada, Iceland, Europe, Tunisia, and western Asia. It has unstable chromosome numbers.

Carex subspathacea, called Hoppner's sedge, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Carex, native to coastal salt marshes of the Arctic and northwest Pacific Oceans; Alaska, Canada, Greenland, Iceland, Norway, northern and far eastern Russia, Korea, and Japan. It is grazed by snow geese.

Carex rupestris, called the curly sedge and rock sedge, is a species of flowering plant in the family Cyperaceae, native to temperate and subarctic North America, Greenland, Iceland, Europe, and Asia. It prefers to grow on rocky ledges.
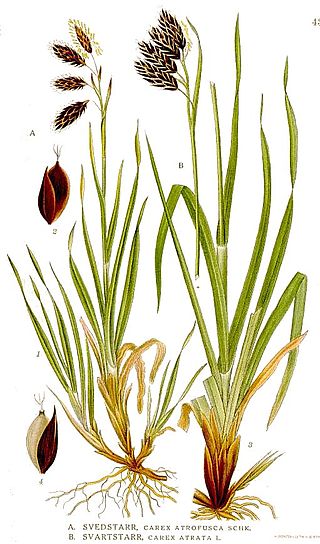
Carex atrata, called black alpine sedge, is a widespread species of flowering plant in the genus Carex, native to Greenland, Iceland, and most of Europe, plus scattered locations across temperate Asia, including Anatolia, Siberia and the Himalaya, as far as Taiwan and Japan. Its chromosome number is 2n=52, with some variants reported, e.g. n2=54 for Greenland material.

Carex dioica, the dioecious sedge, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Carex, native to Iceland, the Faroes, Svalbard, nearly all of Europe, western Siberia, and the Altai. It prefers to live in calcareous fens.

Carex demissa is a species of sedge, native to Iceland, Macaronesia, all of Europe, and western Asia to the Himalayas and possibly Greenland. It has been introduced to eastern Canada, New Jersey, and Tasmania. It is a member of the Carex flava species complex.

Carex lachenalii, called the twotipped sedge and hare's foot sedge, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Carex, native to temperate and subarctic North America, Greenland, Iceland, Europe, and Asia, and the South Island of New Zealand. Its diploid chromosome number is 2n=64, with some uncertainty.

Carex myosuroides, the mouse-tail bog sedge, is a species of sedge with a circumboreal distribution. It is the only known sedge to have ectomycorrhizal associations.
Didymella proximella is a species of fungus belonging to the family Didymellaceae. It is known to decompose the dead leaves of Carex capillaris.

















