
The pancake batfish, Atlantic pancake batfish, Louisiana pancake batfish or spiny batfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Ogcocephalidae, the deep sea batfishes or seabats. This species is found in the Western Atlantic Ocean.

The starry handfish, starry seabat or minipizza batfish, is species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Ogcocephalidae, the deep-sea batfishes or seabats. This fish is found on the continental shelves of the Indo-Pacific oceans at depths of between 50 and 400 m. They are up to 30 cm long.

The fringefin lanternshark is a shark of the family Etmopteridae found in the western central Atlantic from Texas to Florida, northern Gulf of Mexico, and Mexico. It is endemic to this area. It is a deep water shark and is found about 220 to 915 meters below the surface, on the upper continental slopes of the Gulf. E. schultzi is a small shark, about 27–30 cm long and feeds on squid. It is also bioluminescent, which counter-illuminates it and helps with intraspecific interaction. Due to its limited range and the difficulty of collecting deep water species, it has not been evaluated by the IUCN Red List, but due to recent oil spills in the Gulf of Mexico, it is likely that fringefin lanternsharks have decreased in population.

Deepwater Horizon was an ultra-deepwater, dynamically positioned, semi-submersible offshore drilling rig owned by Transocean and operated by the BP company. On April 20, 2010, while drilling in the Gulf of Mexico at the Macondo Prospect, a blowout caused an explosion on the rig that killed 11 crewmen and ignited a fireball visible from 40 miles (64 km) away. The fire was inextinguishable and, two days later, on April 22, the Horizon collapsed, leaving the well gushing at the seabed and becoming the largest marine oil spill in history.

Ogcocephalus parvus, the roughback batfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Ogcocephalidae, the batifishes. This species has a wide distribution in the Western Atlantic Ocean.
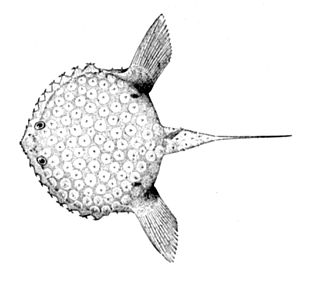
Halieutichthys is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Ogcocephalidae, the deep-sea batfishes or sea bats. The fishes in this genus are found in the western Atlantic Ocean.

Zalieutes is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Ogcocephalidae, the deep sea batfishes. The species in this genus are benthic fishes found in deep waters in the Western Atlantic and Eastern Pacific Oceans.

The Deepwater Horizon oil spill was an environmental disaster which began on 20 April 2010, off the coast of the United States in the Gulf of Mexico on the BP-operated Macondo Prospect, considered the largest marine oil spill in the history of the petroleum industry and estimated to be 8 to 31 percent larger in volume than the previous largest, the Ixtoc I oil spill, also in the Gulf of Mexico. Caused in the aftermath of a blowout and explosion on the Deepwater Horizon oil platform, the United States federal government estimated the total discharge at 4.9 MMbbl. After several failed efforts to contain the flow, the well was declared sealed on 19 September 2010. Reports in early 2012 indicated that the well site was still leaking. The Deepwater Horizon oil spill is regarded as one of the largest environmental disasters in world history.

This article covers the effect of the Deepwater Horizon disaster and the resulting oil spill on global and national economies and the energy industry.

The Gulf killifish is one of the largest members of the genus Fundulus; it is capable of growing up to 7 inches (18 cm) in length, whereas the majority of other Fundulus reach a maximum length of 4 inches (10 cm). Therefore, F. grandis is among the largest minnows preyed upon by many sport fish, such as flounder, speckled trout, and red drum. Fundulus derives from the Latin meaning "bottom," and grandis means "large". The Gulf killifish is native to the Gulf of Mexico from Texas to Florida and the eastern coast of Florida and the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean. Threats to the survival of the Gulf killifish include extreme changes in salinity, changes in temperatures, and toxic events such as the hypoxic dead zone in Louisiana and the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. The Gulf killifish is currently being used to test the effects of oil and oil dispersants on the physiology of marine species affected by these substances. This is significant to conservation biology, because with the continued extraction of oil and other natural resources from North American waters, it has become increasingly important to understand the risks and consequences in worst-case scenarios, such as the Deepwater Horizon oil spill, and the lasting effects on the marine ecosystem.

The 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico has been described as the worst environmental disaster in the United States, releasing about 4.9 million barrels of crude oil making it the largest marine oil spill in history. Both the spill and the cleanup efforts had effects on the environment.

Ogcocephalus corniger, the longnose batfish, is a species of ray-finned fish belonging to the family Ogcocephalidae, the deep sea batfishes. This fish is found at depths between 29 and 230 m in the Atlantic Ocean, ranging from North Carolina to the Gulf of Mexico and the Bahamas. Like other members of the family Ogcocephalidae, it has a flat triangular body with coloring varying from yellowish to purple with pale, round spots. The lips are orange-red. Projecting from its head is a characteristic structure that is shared by other anglerfish.
Halieutichthys bispinosus, the two-spine batfish or spiny batfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Ogcocephalidae, the deep sea batfishes or seabats. This species is found in the Western Atlantic Ocean.
Ogcocephalus porrectus, the rosy-lipped batfish, is endemic to Cocos Island off the Pacific coast of Costa Rica. Though members of Ogcocephalidae occur in tropical, warm waters in both the Western Atlantic and Eastern Pacific. Rosy-lipped batfish generally reside in shallow to deep water benthic zones with a bathymetric range of 35 – 150 m. The syntypic series was collected at 120 m on a rocky bottom. What makes this fish distinctive are its rosy red lips, specialized pectoral fins used for "walking", and an illicium used for attracting prey.

The Atlantic batfish is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Ogcocephalidae, the deep-sea batfishes. It is found in deep water in the Atlantic Ocean where it lives on the seabed, feeding on small invertebrates.

Prosanta Chakrabarty is an American ichthyologist and George H. Lowery Jr. Professor of ichthyology, evolution and systematics at Louisiana State University. He studied at McGill University where he received a bachelor of science in Applied Zoology and at the University of Michigan where he obtained his PhD in Ecology and Evolution. Among other professional positions he was a Program Director for the National Science Foundation and was the President of the American Society of Ichthyologist and Herpetologist in 2023. He was named a TED Fellow in 2016, and a TED Senior Fellow in 2018. He was named an Elected Fellow of the AAAS for "distinguished contributions to evolutionary biology, focusing on the bioluminescent systems and historical biogeography of freshwater fishes, and for effectively communicating science to the public".

Halieutopsis bathyoreos, broad-snout deepsea batfish, is a species of ray-finned fish belonging to the family Ogcocephalidae, the deep sea batfishes. This fish has a widespread distribution in deeper waters in the Indo-West Pacific region as far east as Hawaii.
Ogcocephalus rostellum, the palefin batfish, is a species of ray-finned fish belonging to the family Ogcocephalidae, the deep sea batfishes. It is found in the western Atlantic Ocean.

Ogcocephalus cubifrons, the spotted batfish or polka-dot batfish, is a species of ray-finned fish belonging to the family Ogcocephalidae, the deep sea batfishes. This is an uncommon demersal fish found in the Western Atlantic Ocean and the southern Gulf of Mexico, in the United States, Mexico and the Bahamas.

The Caribbean batfish, also known as the two-spine batfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Ogcocephalidae, the deep sea batfishes or seabats. This species is found in the Western Atlantic Ocean.















