
Lycopodium clavatum is the most widespread species in the genus Lycopodium in the clubmoss family.

Lycopodiella is a genus in the clubmoss family Lycopodiaceae. The genus members are commonly called bog clubmosses, describing their wetland habitat. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution, with centers of diversity in the tropical New World and New Guinea. In the past, the genus was often incorporated within the related genus Lycopodium, but was segregated in 1964. In the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016, Lycopodiella is placed in the subfamily Lycopodielloideae, along with three other genera. In this circumscription, the genus has about 15 species. Other sources use a wider circumscription, in which the genus is equivalent to the Lycopodielloideae of PPG I, in which case about 40 species and hybrids are accepted.

The Caha Mountains are a range of low sandstone mountains situated on the Beara peninsula in south-west County Cork, in Ireland. The highest peak is Hungry Hill, 685 m (2,247 ft) tall. Other notable peaks include Knocknagree, Sugarloaf Mountain, Eskatarriff, Knocknaveacal, Derryclancy, Nareera, Killane Mountain and Baurearagh Mountain.

Butomus is the only known genus in the plant family Butomaceae, native to Europe and Asia. It is considered invasive in some parts of the United States.
Deep Run Ponds Natural Area Preserve is a 706-acre (2.86 km2) Natural Area Preserve in Rockingham County, Virginia. The preserve contains one of the largest remaining systems of Shenandoah Valley sinkhole ponds in Virginia. Such ponds are found in Rockingham and Augusta counties; their water levels fluctuate throughout the year. The preserve's eight sinkhole ponds support a variety of rare plant and animal life; two ponds support the rare Virginia sneezeweed, while others contain black-fruited spikerush, northern St. John's-wort, Buxbaum's sedge, and northern bog clubmoss.

Lycopodiella inundata is a species of club moss known by the common names inundated club moss, marsh clubmoss and northern bog club moss. It has a circumpolar and circumboreal distribution, occurring throughout the northern Northern Hemisphere from the Arctic to montane temperate regions in Eurasia and North America. It grows in wet habitat, such as bogs, ponds, moist spots on the tundra, and long-standing borrow pits.

Palhinhaea cernua, synonym Lycopodiella cernua, is a plant in the family Lycopodiaceae, commonly known as the staghorn clubmoss. The Hawaiian name for the plant is wāwaeʻiole, or "rat's foot". It has a substantial number of scientific synonyms in several genera. The genus Palhinhaea is accepted in the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016, but not in other classifications which submerge the genus in Lycopodiella.
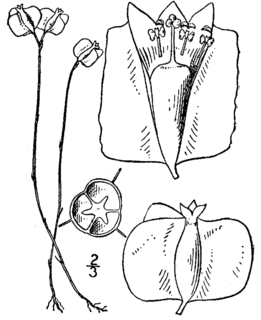
Burmannia biflora, common name northern bluethread, is a plant species native to Cuba, the Bahamas and to the southeastern United States. It has been reported from Puerto Rico, eastern Texas, Louisiana, southwestern Arkansas, southern Mississippi, southern Alabama, Florida, Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina and southeastern Virginia.

Penthorum sedoides, known by the common name ditch stonecrop, is a perennial forb native to the eastern United States and Canada which produces small white flowers in summer.

Diphasiastrum tristachyum, commonly known as blue clubmoss, blue ground-cedar, ground pine, deep-rooted running-pine or ground cedar, is a North American and Eurasian species of clubmoss. In North America, it has been found from Newfoundland west to Manitoba, and south as far as Georgia and Alabama. In Eurasia, it ranges from southern Norway and Sweden south to France and Italy and it also occurs in the Caucasus.

Triantha racemosa, commonly called the coastal false asphodel or southern bog asphodel, is a species of flowering plant in the Tofieldia family. It is native to the Coastal Plain of the Southeastern United States, although there are a few disjunct populations inland. It is found in acidic wetlands, including wet barrens and savannas.

Lateristachys diffusa, synonym Lycopodiella diffusa, known as carpet clubmoss, is a species of clubmoss in the family Lycopodiaceae. It is indigenous to New Zealand and to Tasmania, Australia.

Carex rariflora, the looseflower alpine sedge, is a species of plant in the sedge family. It is found in the United States in Alaska and Maine, and in Canada in New Brunswick and Nova Scotia. In these regions, it is ranked as an obligate hydrophyte in establishing wetland areas. It prefers wet environments such as open bogs, meadows, seepage slopes, and low-elevation heath tundra. This perennial grass, which can be up to 3 feet tall, has fibrous roots, and holds all perennial organs underground. The leaves are alternate, long, narrow, and simple, with parallel veins. They grow in dense clusters, and the dead leaves are found at the base of the plant. The plant blooms and fruits in the summer. All flowers are monoecious and unisexual, producing a spike inflorescence. All inflorescences are subtended by shorter, proximal bracts.

Ophioglossum engelmannii, commonly known as the limestone adder's-tongue, is a species of fern native to the Western Hemisphere. It is widespread and native to the United States, Mexico, and Central America. Its primary natural habitat is dry barrens and glades in calcareous areas.

Lycopodiella alopecuroides, the foxtail clubmoss, is a species of perennial vascular plant in the club-moss family, Lycopodiaceae. It is commonly found along the Atlantic seaboard and has been recently been discovered in the state of Maine. The family, Lycopodiaceae contains nearly 15 genera and about 375 species

Pseudolycopodiella caroliniana, known as slender bog club-moss, is a species of lycophyte in the family Lycopodiaceae. The genus Pseudolycopodiella is accepted in the Flora of North America and the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016, but not in other classifications, which submerge the genus in Lycopodiella. The species has a discontinuous distribution, being native to the eastern United States and to parts of eastern Asia.

Platanthera brevifolia, the shortflowered bog orchid or short-leaf bog orchid, is a terrestrial orchid of North America.

Platanthera purpurascens, the purple petal bog orchid, is a terrestrial orchid of North America.

Sphagnum contortum is a species of moss reported in North America and Europe. NatureServe marked its global conservation status as Secure.


















