| Lytechinus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Lytechinus variegatus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Lytechinus A. Agassiz, 1863 [1] |
| Species: | |
Lytechinus is a genus of sea urchins. [1]
| Lytechinus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Lytechinus variegatus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Lytechinus A. Agassiz, 1863 [1] |
| Species: | |
Lytechinus is a genus of sea urchins. [1]
The following extant species are listed in this genus by the World Register of Marine Species: [1] [2]

The Ophidiasteridae are a family of sea stars with about 30 genera. Occurring both in the Indo-Pacific and Atlantic Oceans, ophidiasterids are greatest in diversity in the Indo-Pacific. Many of the genera in this family exhibit brilliant colors and patterns, which sometimes can be attributed to aposematism and crypsis to protect themselves from predators. Some ophidiasterids possess remarkable powers of regeneration, enabling them to either reproduce asexually or to survive serious damage made by predators or forces of nature. Some species belonging to Linckia, Ophidiaster and Phataria shed single arms that regenerate the disc and the remaining rays to form a complete individual. Some of these also reproduce asexually by parthenogenesis.

Lytechinus variegatus, commonly called the green sea urchin or the variegated sea urchin, is a species of sea urchin that can be found in the warm waters of the western Atlantic Ocean and Caribbean Sea.

Ophiopholis is a genus of brittle stars (Ophiuroidea) found in oceans worldwide from tropics to temperate regions.

Goniasteridae constitute the largest family of sea stars, included in the order Valvatida. They are mostly deep-dwelling species, but the family also include several colorful shallow tropical species.

Coelopleurus is an extant genus of echinoids with fossil records dating back to the Eocene, with remains found in Europe and North America.

Cidaridae is a family of sea urchins in the order Cidaroida.

Spatangus is a genus of heart urchins in the Spatangidae family. The genus is synonymous with the previously recognised genera Prospatangus Lambert, 1902 and Spatagus. There are nine recognised species. The type species is Spatangus purpureus Müller, 1776 by subsequent designation.

Toxopneustidae is a family of globular sea urchins in the class Echinoidea.

Luidia is a genus of starfish in the family Luidiidae in which it is the only genus. Species of the family have a cosmopolitan distribution.

Clypeaster, common name "cake urchins" or "sea biscuits", is a genus of echinoderms belonging to the family Clypeasteridae.
Gymnechinus, is a genus of sea urchin.

The Freyellidae are a family of deep-sea-dwelling starfish. It is one of two families in the order Brisingida. The majority of species in this family are found in Antarctic waters and near Australia. Other species have been found near New Zealand and the United States.

Ophiactis is a genus of brittle stars (Ophiuroidea).
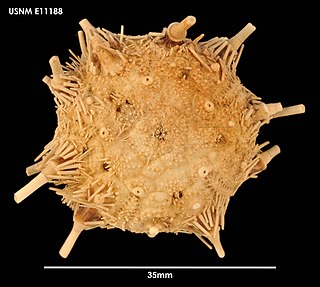
Aporocidaris is a genus of sea urchins in the family Ctenocidaridae. Several species are found in deep water in circum-Antarctic locations.

Mediaster is a genus of starfish in the family Goniasteridae. It was circumscribed in 1857 by William Stimpson for M. aequalis, the genus's type species. Its junior synonym is the genus Isaster, which was circumscribed in 1894 by Addison Emery Verrill for the species now known as M. bairdi. Verrill himself synonymized the two genus names in 1899.

Aporometridae is a monotypic family of crinoids, the only genus being Aporometra, which contains three species, all endemic to the seas around Australia.

Caenopedina is a genus of sea urchins of the family Pedinidae.

Fibularia is a genus of echinoderms belonging to the family Fibulariidae. The genus has almost a cosmopolitan distribution.
Dichrometra is a genus of echinoderms belonging to the family Mariametridae.