
Magna Carta Libertatum, commonly called Magna Carta, is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by Archbishop of Canterbury Stephen Langton to make peace between the unpopular king and a group of rebel barons, it promised the protection of church rights, protection for the barons from illegal imprisonment, access to swift justice, and limitations on feudal payments to the Crown, to be implemented through a council of 25 barons. Neither side stood behind their commitments, and the charter was annulled by Pope Innocent III, leading to the First Barons' War.

In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. The term is similar to the idea of a senate, synod or congress, and is commonly used in countries that are current or former monarchies, a form of government with a monarch as the head. Some contexts restrict the use of the word parliament to parliamentary systems, although it is also used to describe the legislature in some presidential systems, even where it is not in the official name.

Canberra is the capital city of Australia. Founded following the federation of the colonies of Australia as the seat of government for the new nation, it is Australia's largest inland city and the eighth-largest city overall. Unusual among Australian cities, it is an entirely planned city. The city is located at the northern end of the Australian Capital Territory at the northern tip of the Australian Alps, the country's highest mountain range. As of June 2019, Canberra's estimated population was 426,704.

Government House, commonly referred to as Yarralumla, is the official residence of the Governor-General of Australia. It is located in the suburb of Yarralumla, in the City of Canberra, in the Australian Capital Territory. The house is set amid 54 hectares of parkland. The house and associated grounds were added to the Commonwealth Heritage List on 22 June 2004.

Parliament House is the meeting place of the Parliament of Australia, located in Canberra, the capital of Australia. The building was designed by Mitchell/Giurgola & Thorp Architects and built by a Concrete Constructions and John Holland joint venture. It was opened on 9 May 1988 by Elizabeth II, Queen of Australia. It cost more than A$1.1 billion to build.

Yarralumla is a large inner south suburb of Canberra, the capital city of Australia. Located approximately 3.5 kilometres (2.2 mi) south-west of the city, Yarralumla extends along the south-west bank of Lake Burley Griffin from Scrivener Dam to Commonwealth Avenue.

Barton is a suburb of Canberra, Australian Capital Territory, Australia. At the 2016 census, Barton had a population of 1,439 people.

Runnymede is a water-meadow alongside the River Thames in the English county of Surrey, and just over 20 miles (32 km) west of central London. It is notable for its association with the sealing of Magna Carta, and as a consequence is, with its adjoining hillside, the site of memorials. Runnymede Borough is named after the area, Runnymede being at its northernmost point.

Old Parliament House, formerly known as the Provisional Parliament House, was the seat of the Parliament of Australia from 1927 to 1988. The building began operation on 9 May 1927 after Parliament's relocation from Melbourne to the new capital, Canberra. In 1988, the Commonwealth Parliament transferred to the new Parliament House on Capital Hill. It also serves as a venue for temporary exhibitions, lectures and concerts.

North Terrace is one of the four terraces that bound the central business and residential district of Adelaide, the capital city of South Australia. It runs east–west, along the northern edge of "the square mile". The western end continues on to Port Road, and the eastern end continues across the Adelaide Parklands as Botanic Road.
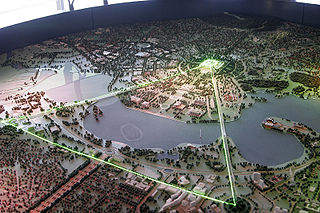
The National Triangle, which is referred to as the Parliamentary Triangle, is the ceremonial precinct of Canberra, containing some of Australia's most significant buildings. The National Triangle is formed by Commonwealth, Kings and Constitution Avenues. Buildings within the National Triangle have been located and designed intentionally for visual effect, and those of national significance are popular tourist attractions.

Commonwealth Place is located on the southern shore of Lake Burley Griffin, Canberra. It lies along the ‘water axis’ running along the lake from Black Mountain. Commonwealth Place is the location of the Gallery of Australian Design, Reconciliation Place, a restaurant and Speakers Square. Walter Burley Griffin, the architect who designed Canberra, envisaged that the area would be the site of a "water gate" which would have a terrace above it, providing a "forum for the people". Griffin's vision was for a long time left unrecognised but as of 2005 the area was being developed to reflect the original plan.

Lennox Gardens, a park in Canberra, Australia, lying on the south side of Lake Burley Griffin, close to Commonwealth Avenue Bridge and Albert Hall in the suburb of Yarralumla. Before the construction of Lake Burley Griffin a road ran through the present garden, this road being one of two main crossing points across the Molonglo River. The name of the road was Lennox Crossing from which the present garden takes its name. The northern segment of the road is still present on Acton peninsula. The garden was officially named in 1963. Lennox Crossing was named after David Lennox, an early bridge builder in NSW and Victoria.

The National Rose Gardens are a heritage-listed rose gardens located in Parkes, a suburb of Canberra, in the Australian Capital Territory of Australia. The rose gardens were added to the Australian Commonwealth Heritage List on 22 June 2004.

Kings Avenue is a road in Canberra which goes between New Parliament House, across Lake Burley Griffin at the Kings Avenue Bridge, to Russell near the Australian-American Monument..

Constitution Place is a park in Canberra, the capital of Australia. The area was named in February 1998 by Prime Minister of Australia John Howard during the course of the Fourth Constitutional Convention on the options for an Australian republic. The park is located to the south-east of Old Parliament House and adjoining the Old Parliament House Gardens and nearby to the National Archives of Australia. It is semicircular in shape, with curved road frontages on King George Terrace, Walpole Crescent and Queen Victoria Terrace. There is also a windbreak of trees, which were planted by Charles Weston as superintendent of parks and gardens in Canberra.

A bill of rights, sometimes called a declaration of rights or a charter of rights, is a list of the most important rights to the citizens of a country. The purpose is to protect those rights against infringement from public officials and private citizens.
The National Capital Authority (NCA) is a statutory authority of the Australian Government that was established to manage the Commonwealth's interest in the planning and development of Canberra as the capital city of Australia.
The Centenary of Women's Suffrage Fountain is located in the grounds of Old Parliament House in Canberra, Australian Capital Territory, Australia. It commemorates the passing of the Commonwealth Franchise Act 1902, which granted the right to vote to white Australian women over 21 years of age.

The King George V Memorial has been located outside Old Parliament House, Canberra since the 1940s. Commissioned in 1936 and largely completed by 1941, it took until 1953 to officially unveil the monument due to delays to the final elements of its construction which resulted from the Second World War. The Memorial was originally located directly in front of the-then Parliament House, but was moved to its current location in 1968.



















