Related Research Articles

Mu-metal is a nickel–iron soft ferromagnetic alloy with very high permeability, which is used for shielding sensitive electronic equipment against static or low-frequency magnetic fields. It has several compositions. One such composition is approximately 77% nickel, 16% iron, 5% copper, and 2% chromium or molybdenum. More recently, mu-metal is considered to be ASTM A753 Alloy 4 and is composed of approximately 80% nickel, 5% molybdenum, small amounts of various other elements such as silicon, and the remaining 12 to 15% iron. The name came from the Greek letter mu (μ) which represents permeability in physics and engineering formulas. A number of different proprietary formulations of the alloy are sold under trade names such as MuMETAL, Mumetall, and Mumetal2.

A naval mine is a self-contained explosive device placed in water to damage or destroy surface ships or submarines. Unlike depth charges, mines are deposited and left to wait until they are triggered by the approach of, or contact with, any vessel or a particular vessel type, akin to anti-infantry vs. anti-vehicle mines. Naval mines can be used offensively, to hamper enemy shipping movements or lock vessels into a harbour; or defensively, to protect friendly vessels and create "safe" zones. Mines allow the minelaying force commander to concentrate warships or defensive assets in mine-free areas giving the adversary three choices: undertake an expensive and time-consuming minesweeping effort, accept the casualties of challenging the minefield, or use the unmined waters where the greatest concentration of enemy firepower will be encountered.

An unguided bomb, also known as a free-fall bomb, gravity bomb, dumb bomb, or iron bomb, is a conventional or nuclear aircraft-delivered bomb that does not contain a guidance system and hence, simply follows a ballistic trajectory. This described all aircraft bombs in general service until the latter half of World War II, and the vast majority until the late 1980s.
The GATOR mine system is a United States military system of air-dropped anti-tank and anti-personnel mines developed in the 1980s to be compatible with existing cluster dispensers. It is used with two dispenser systems—the Navy 230 kg (500 lb) CBU-78/B and the Air Force 450 kg (1,000 lb) CBU-89/B. Additionally the mines are used with the land- and helicopter-based Volcano mine system.
The Mark 84 or BLU-117 is an American general-purpose bomb. It is the largest of the Mark 80 series of weapons. Entering service during the Vietnam War, it became a commonly used US heavy unguided bomb to be dropped. At the time, it was the third largest bomb by weight in the US inventory behind the 15,000-pound (6,800 kg) BLU-82 "Daisy Cutter" and the 3,000-pound (1,400 kg) M118 "demolition" bomb. It is currently sixth in size due to the addition of the 5,000 lb (2,300 kg) GBU-28 in 1991, the 22,600 lb (10,300 kg) GBU-43/B Massive Ordnance Air Blast bomb (MOAB) in 2003, and the 30,000 lb (14,000 kg) Massive Ordnance Penetrator.

A proximity fuze is a fuze that detonates an explosive device automatically when the distance to the target becomes smaller than a predetermined value. Proximity fuzes are designed for targets such as planes, missiles, ships at sea, and ground forces. They provide a more sophisticated trigger mechanism than the common contact fuze or timed fuze. It is estimated that it increases the lethality by 5 to 10 times, compared to these other fuzes.
A booby trap is a device or setup that is intended to kill, harm, or surprise a human or another animal. It is triggered by the presence or actions of the victim and sometimes has some form of bait designed to lure the victim towards it. The trap may be set to act upon trespassers that enter restricted areas, and it can be triggered when the victim performs an action. It can also be triggered by vehicles driving along a road, as in the case of improvised explosive devices (IEDs).
A guidance system is a virtual or physical device, or a group of devices implementing a controlling the movement of a ship, aircraft, missile, rocket, satellite, or any other moving object. Guidance is the process of calculating the changes in position, velocity, altitude, and/or rotation rates of a moving object required to follow a certain trajectory and/or altitude profile based on information about the object's state of motion.

Missile guidance refers to a variety of methods of guiding a missile or a guided bomb to its intended target. The missile's target accuracy is a critical factor for its effectiveness. Guidance systems improve missile accuracy by improving its Probability of Guidance (Pg).

In an explosive, pyrotechnic device, or military munition, a fuse is the part of the device that initiates function. In common usage, the word fuse is used indiscriminately. However, when being specific, the term fuse describes a simple pyrotechnic initiating device, like the cord on a firecracker whereas the term fuze is used when referring to a more sophisticated ignition device incorporating mechanical and/or electronic components, such as a proximity fuze for an M107 artillery shell, magnetic or acoustic fuze on a sea mine, spring-loaded grenade fuze, pencil detonator, or anti-handling device.

The CBU-97 Sensor Fuzed Weapon is a United States Air Force 1,000-pound (450 kg)-class freefall Cluster Bomb Unit. It was developed and produced by Textron Defense Systems. A CBU-97 used in conjunction with the Wind Corrected Munitions Dispenser guidance tail kit is converted to a precision-guided weapon, and the combination is designated CBU-105.

A guided bomb is a precision-guided munition designed to achieve a smaller circular error probable (CEP).

An anti-handling device is an attachment to or an integral part of a landmine or other munition such as some fuze types found in general-purpose air-dropped bombs, cluster bombs and sea mines. It is designed to prevent tampering or disabling, or to target bomb disposal personnel. When the protected device is disturbed, it detonates, killing or injuring anyone within the blast area. There is a strong functional overlap of booby traps and anti-handling devices.

A proximity sensor is a sensor able to detect the presence of nearby objects without any physical contact.
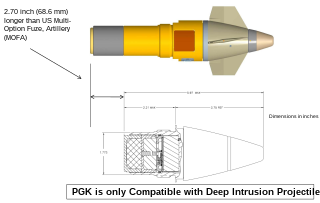
The M1156 Precision Guidance Kit (PGK), formerly XM1156, is a U.S. Army-designed precision guidance system to turn existing 155 mm artillery shells into smart weapons. The prime contractor was Alliant Techsystems – later merging with Orbital Sciences Corporation to form Orbital ATK, in turn being taken over by Northrop Grumman and renamed Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems – and the industry team includes Interstate Electronics Corporation. By April 2018, more than 25,000 PGKs had been produced.

Ammunition is the material fired, scattered, dropped or detonated from any weapon or weapon system. Ammunition is both expendable weapons and the component parts of other weapons that create the effect on a target.
In military munitions, a fuze is the part of the device that initiates function. In some applications, such as torpedoes, a fuze may be identified by function as the exploder. The relative complexity of even the earliest fuze designs can be seen in cutaway diagrams.

A grenade is an explosive weapon typically thrown by hand, but can also refer to a shell shot from the muzzle of a rifle or a grenade launcher. A modern hand grenade generally consists of an explosive charge ("filler"), a detonator mechanism, an internal striker to trigger the detonator, and a safety lever secured by a cotter pin. The user removes the safety pin before throwing, and once the grenade leaves the hand the safety lever gets released, allowing the striker to trigger a primer that ignites a fuze, which burns down to the detonator and explodes the main charge.

An artillery fuze or fuse is the type of munition fuze used with artillery munitions, typically projectiles fired by guns, howitzers and mortars. A fuze is a device that initiates an explosive function in a munition, most commonly causing it to detonate or release its contents, when its activation conditions are met. This action typically occurs a preset time after firing, or on physical contact with or detected proximity to the ground, a structure or other target. Fuze, a variant of fuse, is the official NATO spelling.

In the field of weaponry, terminal guidance refers to any guidance system that is primarily or solely active during the "terminal phase", just before the weapon impacts its target. The term is generally used in reference to missile guidance systems, and specifically to missiles that use more than one guidance system through the missile's flight.
References
- ↑ "Magnetic fuse" (PDF).
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2011-06-12. Retrieved 2010-04-26.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)