Related Research Articles

Victoria Island is a large island in the Arctic Archipelago that straddles the boundary between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories of Canada. It is the eighth-largest island in the world, and at 217,291 km2 (83,897 sq mi) in area, it is Canada's second-largest island. It is nearly double the size of Newfoundland (111,390 km2 [43,010 sq mi]), and is slightly larger than the island of Great Britain (209,331 km2 [80,823 sq mi]) but smaller than Honshu (225,800 km2 [87,200 sq mi]). The western third of the island lies in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories; the remainder is part of Nunavut's Kitikmeot Region. The population of 2,168 is divided among two settlements, the larger of which is in Nunavut and the other of which is in the Northwest Territories.

The Dixon Entrance is a strait about 80 kilometers (50 mi) long and wide in the Pacific Ocean at the Canada–United States border, between the U.S. state of Alaska and the province of British Columbia in Canada. The Dixon Entrance is part of the Inside Passage shipping route. It forms part of the maritime boundary between the U.S. and Canada, although the location of that boundary here is disputed.

The Burrard Peninsula is a peninsula in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia, Canada, bounded by the Burrard Inlet to the north, the Georgia Strait to the west, the North Arm of Fraser River to the south, and the Pitt River and Douglas Island to the east. The City of Vancouver occupies almost all of the western half of the peninsula, and the Cities of Burnaby and New Westminster occupy more than half of the eastern half. At its northeastern end, the peninsula is connected to the Eagle Mountain and Mount Burke of the Coast Mountains via a small isthmus at the center of the Tri-Cities.

Desolation Sound is a deep water sound at the northern end of the Salish Sea and of the Sunshine Coast in British Columbia, Canada.

Copeland Islands Marine Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada, located in Desolation Sound to the northwest of Lund on the northern Sunshine Coast off the west coast of the Malaspina Peninsula.
Malaspina Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada, located on the northeast side of the Malaspina Peninsula facing Desolation Sound in the northernmost area of that province's Sunshine Coast region.

Dionisio Alcalá Galiano was a Spanish naval officer, cartographer, and explorer. He mapped various coastlines in Europe and the Americas with unprecedented accuracy using new technology such as chronometers. He commanded an expedition that explored and mapped the Strait of Juan de Fuca and the Strait of Georgia, and made the first European circumnavigation of Vancouver Island. He reached the rank of brigadier and died during the Battle of Trafalgar.

Manuel Quimper Benítez del Pino was a Spanish Peruvian explorer, cartographer, naval officer, and colonial official. He participated in charting the Strait of Juan de Fuca and the Sandwich Islands in the late 18th century. He was later appointed a colonial governor in his native Peru at the beginning of the fight for independence there. He retired to Spain, but was able to return to Peru where he served as a naval officer in the new republic and pursued a literary career, publishing over 20 books about his experiences before his death there in Lima.
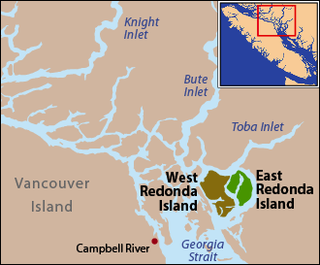
East Redonda Island is a coastal island in British Columbia, Canada, part of the Discovery Islands archipelago. It lies just to the north of Desolation Sound Marine Park, which is located off the north end of the Malaspina Peninsula at the mouth of Toba Inlet within Electoral Area C of the Strathcona Regional District.

During the Age of Discovery, the Spanish Empire undertook several expeditions to the Pacific Northwest of North America. Spanish claims to the region date to the papal bull of 1493, and the Treaty of Tordesillas signed in 1494. In 1513, this claim was reinforced by Spanish explorer Vasco Núñez de Balboa, the first European to sight the Pacific Ocean, when he claimed all lands adjoining this ocean for the Spanish Crown. Spain only started to colonize the claimed territory north of present-day Mexico in the 18th century, when it settled the northern coast of Las Californias.

Alberni Inlet is a long, narrow inlet in Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada, that stretches from the Pacific Ocean at Barkley Sound about 40 km (25 mi) inland terminating at Port Alberni. It was named by the Spanish explorer Francisco de Eliza after Pedro de Alberní y Teixidor, Captain of the Free Company of Volunteers of Catalonia who was appointed in the Spanish fort in Nootka Sound from 1790 to 1792. The inlet includes traditional territories of the Ucluelet, Uchucklesaht, Huu-ay-aht, Hupacasath, and Tseshaht peoples, who are part of the Nuu-chah-nulth Tribal Council people.
The Sechelt Peninsula is located on the Sunshine Coast of British Columbia, just northwest of Vancouver. It is bounded to the west by Malaspina Strait, to the north by Agamemnon Channel and Jervis Inlet, to the east by Sechelt Inlet, and to the south by the Strait of Georgia (separating it from Vancouver Island. Its approximately 350 km2 is a mixture of drier and wetter temperate rain forest. The Caren Range extends north–south along the shore of Sechelt Inlet. The peninsula is a popular outdoor recreation destination, containing many lakes and opportunities for shoreline and woodland hiking, including to the renowned Skookumchuk Narrows. There are several parks, the largest of which is Spipiyus Provincial Park in the interior of the peninsula.

West Redonda Island is an island in British Columbia, Canada. It is part of the Discovery Islands, an archipelago between Vancouver Island and the mainland, and between the Strait of Georgia and Johnstone Strait.
Bliss Landing, formerly Bishop Landing or Bishops Landing, was a cannery town on the South Coast of British Columbia, Canada, located on the northwest side of the Malaspina Peninsula on the upper Sunshine Coast, north of the town of Lund and across the mouth of Desolation Sound from Cortes Bay and Manson's Landing on Cortes Island.
Malaspina Strait is a strait in the northern Gulf of Georgia-Sunshine Coast region of British Columbia, Canada. It separates Texada Island from the upper Sunshine Coast-Malaspina Peninsula area on the adjacent mainland.
Malaspina Inlet is an inlet on the east side of Desolation Sound in the South Coast region of British Columbia, Canada, located between Malaspina and Gifford Peninsulas. Sidewaters include Thors Cove and, via it, Theodosia Inlet, where the locality of Theodosia Arm is located. The upper, southeastern, end of Malaspina Inlet near the City of Powell River is called Okeover Inlet. on the east side of which the steamer landing Larsons Landing is located. Grace Harbour is located on north side of Malaspina Inlet on the southwest side of Gifford Peninsula.
The Gifford Peninsula is a peninsula on the east side of Desolation Sound in the Sunshine Coast region of the South Coast of British Columbia, Canada, located immediately north of the Malaspina Peninsula and separated from it by Malaspina Inlet. On its east side is Lancelot Inlet and its arm Theodosia Inlet
The Coode Peninsula is a small peninsula on the inner side of the larger Malaspina Peninsula in the Sunshine Coast area of the South Coast of British Columbia, Canada, projecting into Malaspina Inlet just south of Okeover Inlet.
Drury inlet is an inlet in the Queen Charlotte Strait region of the Central Coast of British Columbia, Canada, extending west from Wells Passage to the northwest of North Broughton Island, northwest of the town of Port Hardy. Branching off to the northeast from the north side of the head of the inlet is Actaeon Sound.

Checleset Bay is a bay on the northwest coast of Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. It is located southeast of Brooks Peninsula and northwest of Kyuquot Sound. Much of the land around the bay is part of Brooks Peninsula Provincial Park. Checleset Bay has three large inlets, Nasparti Inlet, Ououkinsh Inlet, and Malksope Inlet.
References
- ↑ Walbran, John T. (1909). British Columbia coast names, 1592-1906 : to which are added a few names in adjacent United States territory, their origin and history. Ottawa Government Printing Bureau. pp. 313–314. OCLC 317633225. Archived from the original on 2012-03-07. Retrieved 2010-02-06.
50°01′00″N124°46′00″W / 50.01667°N 124.76667°W