
Cnidaria is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in freshwater and marine environments, predominantly the latter.

Entoprocta, or Kamptozoa, is a phylum of mostly sessile aquatic animals, ranging from 0.1 to 7 millimetres long. Mature individuals are goblet-shaped, on relatively long stalks. They have a "crown" of solid tentacles whose cilia generate water currents that draw food particles towards the mouth, and both the mouth and anus lie inside the "crown". The superficially similar Bryozoa (Ectoprocta) have the anus outside a "crown" of hollow tentacles. Most families of entoprocts are colonial, and all but 2 of the 150 species are marine. A few solitary species can move slowly.

Adansonia is a genus made up of eight species of medium-to-large deciduous trees known as baobabs. They are placed in the Malvaceae family, subfamily Bombacoideae. They are native to Madagascar, mainland Africa, and Australia. The trees have also been introduced to other regions such as Asia. The generic name honours Michel Adanson, the French naturalist and explorer who described Adansonia digitata. The baobab is also known as the "upside down tree", a name that originates from several myths. They are among the most long-lived of vascular plants and have large flowers that are reproductive for a maximum of 15 hours. The flowers open around dusk, opening so quickly that movement can be detected by the naked eye, and are faded by the next morning. The fruits are large, oval to round and berry-like and hold kidney-shaped seeds in a dry, pulpy matrix.

Medusozoa is a clade in the phylum Cnidaria, and is often considered a subphylum. It includes the classes Hydrozoa, Scyphozoa, Staurozoa and Cubozoa, and possibly the parasitic Polypodiozoa. Medusozoans are distinguished by having a medusa stage in their often complex life cycle, a medusa typically being an umbrella-shaped body with stinging tentacles around the edge. With the exception of some Hydrozoa, all are called jellyfish in their free-swimming medusa phase.

Stauromedusae are the stalked jellyfishes. They are the sole living members of the class Staurozoa and belong to the medusozoa subphylum of Cnidaria. They are unique among medusa jellyfish in that they do not have an alternation of polyp and medusa life cycle phases, but are instead interpreted as an attached medusa stage. With a lifestyle more resembling that of polypoid forms. They have a generally trumpet-shaped body, oriented upside-down in comparison with other jellyfish, with the tentacles projecting upwards, and the stalk located in the centre of the umbrella.

Staurozoa is a class of Medusozoa, jellyfishes and hydrozoans. It has one extant order: Stauromedusae with a total of 50 known species. A fossil group called Conulariida has been proposed as a second order, although this is highly speculative. The extinct order is largely unknown and described as a possibly cnidarian clade of marine life with shell-like structures, the Conulariida. Staurozoans are small animals that live in marine environments, usually attached to seaweeds, rocks, or gravel. They have a large antitropical distribution, a majority found in boreal or polar, near-shore, and shallow waters. Few staurozoans are found in warmer tropical and subtropical water environments of the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Ocean basins, but most are known from the Northern Hemisphere. Over the years the number of discovered species has increased, with an estimated 50 species currently recognized. Information on Staurozoa is sparse, and it is one of the least studied groups within Cnidaria. While often neglected, correctly recognizing the characteristics of this class is crucial for understanding cnidarian evolution.
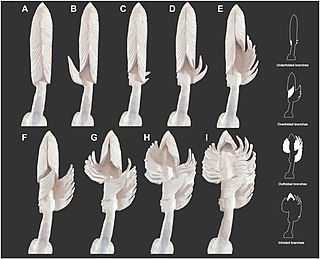
Charniodiscus is an Ediacaran fossil that in life was probably a stationary filter feeder that lived anchored to a sandy sea bed. The organism had a holdfast, stalk and frond. The holdfast was bulbous shaped, and the stalk was flexible. The frond was segmented and had a pointed tip. There were two growth forms: one with a short stem and a wide frond, and another with a long stalk, elevating a smaller frond about 50 centimetres (20 in) above the holdfast. While the organism superficially resembles the sea pens (cnidaria), it is probably not a crown-group animal.

Otholobium is a genus of flowering plants in the pea family with over 50 named species, but several also remain undescribed sofar. Species may be herbaceous perennials, subshrubs, shrubs or small trees. The alternately set leaves are accompanied by stipules and mostly consist of three leaflets, sometimes just one. The inflorescences are on short or long stalks in the axils of the leaves. Within the inflorescences, the pea-like flowers occur in groups of three, rarely of two, subtended by a bract, and each individual flower also is subtended by a narrow bract. The petals may be white, pink, purple or blue, often with a differently colored nectar guide, that may sometimes even be yellow. The seedpods contain just one, black, dark or light brown seed. Most species are restricted to the Cape provinces of South Africa, but some occur at higher elevations in eastern Africa. Charles Stirton erected the genus in 1981. The species in South America will probably be segregated, because these are not sufficiently related to the African species.

Calvadosia corbini is a stalked jellyfish species in the family Kishinouyeidae from the tropical western Atlantic. The species is named after Peter Corbin, a marine biologist noted for his extensive work on Atlantic Stauromedusae.

Haliclystus is a genus of stalked jellyfish that contains 11 species and one nomen nudum. It is the largest genus in the order Stauromedusae. Members of this genus are found in the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic, and Southern oceans. Two members of this genus, Haliclystus kerguelensis and Haliclystus antarcticus, are found in the Southern hemisphere only. The remaining 9 members are found in the Northern hemisphere only.

Haliclystus auricula is a stalked jellyfish found in the Northern hemisphere. It is the type species for its genus.
Lucernaria janetae is an exceptionally large stalked jellyfish discovered on deep-sea hydrothermal vents on the East Pacific Rise in 2003 and described in 2005.

Haliclystus antarcticus is a stalked jellyfish which lives on rocky shore lines in the Southern hemisphere.

Haliclystidae is a family of stalked jellyfish in the order Stauromedusae.
Kyopoda is a genus of stalked jellyfish, It has only one species in the genus, Kyopoda lamberti, and is in turn the only genus in the family Kyopodiidiae.

Haliclystus octoradiatus, common name spotted kaleidoscope jellyfish, is a stalked jellyfish in the family Lucernariidae.

Manania are a genus of stalked jellyfish in the family Haliclystidae.

Manania handi is a species of stalked jellyfish found in the Pacific Ocean along the west coast of North America. This species can be found in shallow waters at low tide on soft substrates such as seagrass (Phyllospadix), but the related M. gwilliami have also been recovered at depths of >10 metres. This may reflect that intertidal specimens represent the fringes of a population that is typically more commonly found in the subtidal zone.

Haliclystus sanjuanensis is a species of small (~4 cm) stalked jellyfish found in the Pacific Ocean along the west coast of North America. This species can be found in shallow waters at low tide on soft substrates such as seagrass (Phyllospadix). A variety of colour morphs can be found ranging from yellow-green to red. Haliclystus sanjuanensis remains undescribed officially, despite sequence data establishing it as a distinct taxon.
Sabicea amomii is a species of woodvine in the family Rubiaceae, which is native to Cameroon. There are no synonyms.














