Sus is the genus of wild and domestic pigs, within the even-toed ungulate family Suidae. Sus include domestic pigs and their ancestor, the common Eurasian wild boar, along with other species. Sus species, like all suids, are native to the Eurasian and African continents, ranging from Europe to the Pacific islands. Suids other than the pig are the babirusa of Indonesia, the pygmy hog of South Asia, the warthogs of Africa, and other pig genera from Africa. The suids are a sister clade to peccaries.

The wild boar, also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species is now one of the widest-ranging mammals in the world, as well as the most widespread suiform. It has been assessed as least concern on the IUCN Red List due to its wide range, high numbers, and adaptability to a diversity of habitats. It has become an invasive species in part of its introduced range. Wild boars probably originated in Southeast Asia during the Early Pleistocene and outcompeted other suid species as they spread throughout the Old World.

The onager, also known as hemione or Asiatic wild ass, is a species of the family Equidae native to Asia. A member of the subgenus Asinus, the onager was described and given its binomial name by German zoologist Peter Simon Pallas in 1775. Five subspecies have been recognized, one of which is extinct.

Breeding back is a form of artificial selection by the deliberate selective breeding of domestic animals, in an attempt to achieve an animal breed with a phenotype that resembles a wild type ancestor, usually one that has gone extinct. Breeding back is not to be confused with dedomestication.

The pig, often called swine, hog, or domesticpig when distinguishing from other members of the genus Sus, is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is variously considered a subspecies of Sus scrofa or a distinct species. The pig's head-plus-body length ranges from 0.9 to 1.8 m, and adult pigs typically weigh between 50 and 350 kg, with well-fed individuals even exceeding this range. The size and weight of hogs largely depends on their breed. Compared to other artiodactyls, a pig's head is relatively long and pointed. Most even-toed ungulates are herbivorous, but pigs are omnivores, like their wild relative. Pigs grunt and make snorting sounds.
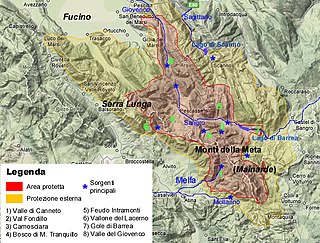
Abruzzo, Lazio and Molise National Park is an Italian national park established in 1923. The majority of the park is located in the Abruzzo region, with smaller parts in Lazio and Molise. It is sometimes called by its former name Abruzzo National Park. The park headquarters are in Pescasseroli in the Province of L'Aquila. The park's area is 496.80 km2 (191.82 sq mi).

The Italian wolf, also known as the Apennine wolf, is a subspecies of the grey wolf native to the Italian Peninsula. It inhabits the Apennine Mountains and the Western Alps, though it is undergoing expansion towards the north and east. As of 2022 the wolf population within Italy is estimated to be 3,307 individuals. Although not universally recognised as a distinct subspecies, it nonetheless possesses a unique mtDNA haplotype and a distinct skull morphology.

Neotinea ustulata, the burnt orchid or burnt-tip orchid, is a European terrestrial orchid native to mountains in central and southern Europe, growing at up to 2,400 m (7,900 ft) elevation. The plant is considered Endangered in Great Britain and Least Concern internationally based on IUCN Red List criteria. The burnt-tip orchid was voted the county flower of Wiltshire in 2002 following a poll by the wild flora conservation charity Plantlife.

The Iberian wolf, is a subspecies of grey wolf. It inhabits the northwest of the Iberian Peninsula, which includes northwestern Spain and northern Portugal. It is home to 2,200-2,700 wolves which have been isolated from mixing with other wolf populations for over a century. They form the largest wolf population in Western Europe.

The Central European Football League (CEFL) is a European organization of American football which hosts two international competitions, CEFL Championship and CEFL Cup. The final game of the CEFL Championship playoffs is dubbed CEFL Bowl.

Boar hunting is the practice of hunting wild boar, feral pigs, warthogs, and peccaries. Boar hunting was historically a dangerous exercise due to the tusked animal's ambush tactics as well as its thick hide and dense bones rendering them difficult to kill with premodern weapons.

Boar–pig hybrid is a hybridized offspring of a cross between the Eurasian wild boar and any domestic pig. Feral hybrids exist throughout Eurasia, the Americas, Australia, and in other places where European settlers imported wild boars to use as game animals. In many areas, a variable mixture of these hybrids and feral pigs of all-domesticated original stock have become invasive species. Their status as pest animals has reached crisis proportions in Australia, parts of Brazil, and parts of the United States, and the animals are often freely hunted in hopes of eradicating them or at least reducing them to a controllable population.
The wild boar and boar's head are common charges in heraldry.

Rispescia, or Santa Maria di Rispescia, is a small town in southern Tuscany, a frazione of the comune of Grosseto, situated about 10 km south-east of the capital, right outside the Natural Park of Maremma, near the frazione of Alberese.

Circeo National Park is an Italian national park founded in 1934. It occupies a strip of coastal land from Anzio to Terracina, including also a sector of forest in the mainland of San Felice Circeo, and the island of Zannone.

The Indian boar, also known as the Andamanese pig or Moupin pig, is a subspecies of wild boar native to India, Nepal, Myanmar, western Thailand and Sri Lanka

The Japanese boar, also known as the white-moustached pig, nihon-inoshishi (ニホンイノシシ), or yama kujira, is a subspecies of wild boar native to all of Japan, save for Hokkaido and the Ryukyu Islands.

The Central European boar is a subspecies of wild boar, currently distributed across almost all of mainland Europe, with the exception of some northern areas in both Scandinavia and European Russia and the southernmost parts of Greece. It is a medium-sized, dark to rusty-brown haired subspecies with long and relatively narrow lacrimal bones. In Northern Italy, artificially introduced S. s. scrofa have extensively interbred with the smaller sized indigenous S. s. majori populations since the 1950s.

The Central Asian boar is a small long maned subspecies of wild boar indigenous to Southeastern Iran, Pakistan and Northwest India.
Oscar de Beaux was an Italian mammalogist. His studies of mammals primarily concerned the Italian colonies of Africa. De Beaux was also a conservationist, authoring one of the first papers to argue the ethics of conservation, "Biological ethics: an attempt to arouse a naturalistic conscience".