
The Maritime Alps are a mountain range in the southwestern part of the Alps. They form the border between the French region of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur and the Italian regions of Piedmont and Liguria. They are the southernmost part of the Alps.
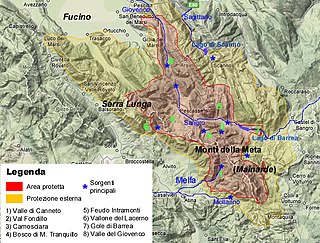
Abruzzo, Lazio and Molise National Park is an Italian national park established in 1923. The majority of the park is located in the Abruzzo region, with smaller parts in Lazio and Molise. It is sometimes called by its former name Abruzzo National Park. The park headquarters are in Pescasseroli in the Province of L'Aquila. The park's area is 496.80 km2 (191.82 sq mi).

Entracque is a small town in the Valle Gesso of the Maritime Alps of north-west Italy, about 20 kilometres (12 mi) southwest of Cuneo and close to the French border. It is the principal settlement and capoluogo of the comune or municipality of the same name in the Piedmontese Province of Cuneo.

The Parco Nazionale delle Foreste Casentinesi, Monte Falterona, Campigna is a national park in Italy. Created in 1993, it covers an area of about 368 square kilometres (142 sq mi), on the two sides of the Apennine watershed between Romagna and Tuscany, and is divided between the provinces of Forlì Cesena, Arezzo and Florence.
The Monti Simbruini are a mountain range in central Italy, a part of Apennines mountain system.
Pollino National Park is an Italian national park in the southern peninsula, in the provinces of Cosenza, Matera and Potenza. Its named from the homonymous mountain massif Pollino. The park is home of the oldest European tree, a Heldreich's pine estimated 1,230 years old and the symbol of the park is the rare Bosnian pine tree. Since November 2015, with the inclusion in the global list of geoparks by UNESCO, the Pollino Park is considered a World Heritage Site. Encompassing a total of 88,650 ha in the Lucanian side and 103,915 in the Calabrian one is the largest park in the country covering 1,925.65 square kilometers and among the 50 largest in the world. The common beech is the park's most prevalent tree and the park is also home to a variety of important medicinal herbs.

Monte Frontè is a mountain in Liguria, northern Italy, part of the Alps. It is located in the province of province of Imperia. It lies at an altitude of 2,152 metres. After Monte Saccarello it is the second highest peak in the Ligurian region.

Monte Saccarello (Italian) or Mont Saccarel (French) is a mountain located on the French-Italian border between Liguria, Piedmont and Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur.

The Natural Regional Park of Serre is a protected natural area of Calabria, Italy created in 2004.

The Regional Natural Park of the Ligurian Alps is a natural park in Province of Imperia. It was established in 2007 by the legge regionale nr.34 of 15/11/2007.

The Dolomiti Bellunesi National Park is a national park in the province of Belluno, Veneto, in the northern Italy.

The Cima della Fascia is a mountain of the Ligurian Alps located in Piedmont.

The Natural Park of Marguareis(in Italian Parco Naturale del Marguareis) is a regional natural park of the Ligurian Alps located in the Province of Cuneo.

The Bergamasque Alps Regional Park is a nature reserve in Lombardy, Italy. Established in 1989, it encompasses the Bergamasque Alps, known in Italy as Alpi Orobie; with an area of nearly 70,000 hectares, it is the largest natural park in Lombardy.

The Northern Grigna Regional Park is a nature reserve in Lombardy, Italy. Established in 2005, it encompasses most of the Grigna massif, located in the province of Lecco, in the Bergamasque Alps).

The Orsiera-Rocciavrè Natural Park is a nature reserve in Piedmont, Italy. Established in 1980, it covers a vast Alpine area between the Val Susa and the Val Chisone, in the Graian Alps and the Cottian Alps. The Site of Community Importance of Orsiera-Rocciavrè is part of the park, whose highest point is the peak of Monte Orsiera, 2,890 meters above sea level. The Colle delle Finestre, the Fenestrelle Fort and the Montebenedetto Charterhouse are also located inside the park.

The Gran Bosco di Salbertrand Natural Park is a nature reserve in Piedmont, Italy. Established in 1980, it protects the Site of Community Importance of the Great Woods of Salbertrand, in the Val Susa, south of the Dora Riparia, between 1,000 and 2,700 meters above sea level. The woods, which cover an area of about eight hundred acres, consist of a mix of silver firs and Norway spruces, rarely found in the Western Alps.

The Campo dei Fiori Regional Park is a nature reserve in Lombardy, Italy. Established in 1984 and enlarged in 2009, it comprises the Campo dei Fiori and Martica massifs in the Varese Prealps, between the Valganna, the Valcuvia and the city of Varese.

The Paneveggio-Pale di San Martino Natural Park is a nature reserve in Trentino, Italy. Established in 1967, it stretches over nearly 20,000 ha in the Dolomites, encompassing the Pale di San Martino massif, the Paneveggio forest, and the easternmost part of the Lagorai range, between the valleys of Fiemme, Fassa, Primiero, and Vanoi.

The Ampezzo Dolomites Natural Park is a nature reserve in Veneto, Italy. Established in 1990, it is entirely located in the territory of Cortina d’Ampezzo, in the Province of Belluno, and encompasses some of the most famous Dolomitic groups, such as the Tofane, Monte Cristallo, the Croda Rossa d'Ampezzo, Lagazuoi, Pomagagnon and Col Bechei. Together with the adjacent Naturpark Fanes-Sennes-Prags in the Province of Bolzano, it forms a protected area of 37,000 hectares in the heart of the Dolomites. The park has been designated as a Site of Community Importance, and about one quarter of its territory is afforded further protection through twenty smaller reserves.


















