
In Freemasonry, a Mason at sight, or Mason on sight, is a non-Mason who has been initiated into Freemasonry and raised to the degree of Master Mason through a special application of the power of a Grand Master.

In Freemasonry, a Mason at sight, or Mason on sight, is a non-Mason who has been initiated into Freemasonry and raised to the degree of Master Mason through a special application of the power of a Grand Master.
The process of making a Mason at sight was listed by Albert Mackey as the eighth of his "Twenty-Five Landmarks of Freemasonry". [1]
The customary method for raising a person to Master Mason through the rare process of recognizing him a Mason at sight has the Grand Master creating a new lodge for the single purpose of initiating the candidate. [2] This "occasional lodge" is then dissolved when the reason for its creation - the initiation of the candidate - has been completed. [2] However, while the process of recognizing a Mason at sight usually involves this procedure, Masonic historian Louis L. Williams has observed that "using his unique and unquestionable power, the Grand Master could pretty well proceed as he might see fit" such as simply decreeing the individual to be a Master Mason. [3]
Early instances in the history of speculative Masonry, in which a man has been made a Mason at sight, include the raising of Francis Stephen, Duke of Lorraine, in 1731 at Houghton Hall, fourteen years before his accession as Holy Roman Emperor, and of Frederick, Prince of Wales in 1737. [4]
Joseph Smith, founder of the LDS Church, was raised at sight in March of 1842, completing the three degrees of Freemasonry within the atypically short timespan of two days. [5] [6]
Other notable persons in the United States who have been made a Mason at sight include General Douglas MacArthur on January 17, 1936, in the presence of over six hundred Master Masons, [7] General George C. Marshall, who was raised by the Grand Master of the Grand Lodge of the District of Columbia in December 1941, [8] and Don King, [9] who was raised by Grand Master Odes J. Kyle Jr. of the Most Worshipful Prince Hall Grand Lodge of Ohio in 1987.
William Howard Taft was recognized as a Mason at sight by an occasional lodge created for that purpose on February 18, 1909, a few weeks prior to his inauguration as the 27th President of the United States. [10] [11] [3] The lodge was convened at about 4:00 p.m. at the Scottish Rite Cathedral in Cincinnati by Charles Hoskinson, the Grand Master of Ohio, and consisted of him and William B. Mellish. [11] He dissolved it after 6:00 p.m. [11]
Joe Biden was declared a Master Mason at sight by the Prince Hall Grand Lodge of South Carolina on January 19, 2025. [12] [13] [14] The Pillar, however, have noted that "Biden would have to himself accept, even passively by not rejecting the designation, the conferred membership — the masons don’t have the power to make someone a member without consent, anymore than one person can marry another without their consent." [13] They further question if this actually occurred, casting some doubt on his Masonic membership. Others have raised questions of Biden's legitimacy as a Master Mason given that the Prince Hall Grand Lodge of South Carolina "is not recognized as regular by any so-called mainstream U.S. grand lodge, the United Grand Lodge of England, or any other major regular, recognized Masonic jurisdiction." [14]

Freemasonry or simply Masonry includes various fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of stonemasons that, from the end of the 14th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities and clients. Freemasonry is the oldest fraternity in the world and among the oldest continued organizations in history.

A Masonic lodge, also called a private lodge or constituent lodge, is the basic organisational unit of Freemasonry.
In Freemasonry, regularity is one of the factors by which individual Grand Lodges judge whether to recognise one another for the purposes of allowing formal interaction at the Grand Lodge level and visitation by members of other jurisdictions. Each individual Grand Lodge determines which other Grand Lodges it considers Regular.
The relationship between Mormonism and Freemasonry began early in the life of Joseph Smith, founder of the Latter Day Saint movement. Smith's older brother, Hyrum, and possibly his father, Joseph, Sr. were Freemasons while the family lived near Palmyra, New York. In the late 1820s, the western New York region was swept with anti-Masonic fervor.

The United Grand Lodge of England (UGLE) is the governing Masonic lodge for the majority of freemasons in England, Wales, and the Commonwealth of Nations. Claiming descent from the Masonic Grand Lodge formed 24 June 1717 at the Goose & Gridiron Tavern in London, it is considered to be the oldest Masonic Grand Lodge in the world, together with the Grand Lodge of Scotland, and the Grand Lodge of Ireland.
Prince Hall Freemasonry is a branch of North American Freemasonry created for African Americans founded by Prince Hall on September 29, 1784. Prince Hall Freemasonry is the oldest and largest predominantly African-American fraternity in the United States.
While many Christian denominations either allow or take no stance on their members joining Freemasonry, others discourage or prohibit their members from joining the fraternity.
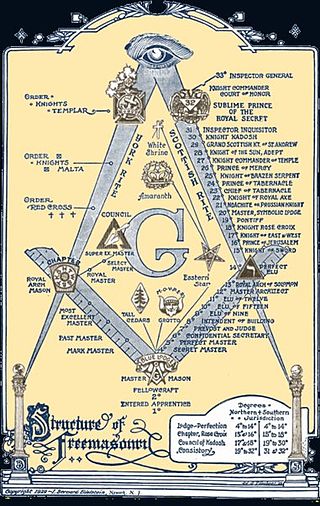
There are many organisations and orders which form part of the widespread fraternity of Freemasonry, each having its own structure and terminology. Collectively these may be referred to as Masonic bodies, Masonic orders, Concordant bodies or appendant bodies of Freemasonry.
Masonic landmarks are a set of principles that many Freemasons claim to be ancient and unchangeable precepts of Masonry. Issues of the "regularity" of a Freemasonic Lodge, Grand Lodge or Grand Orient are judged in the context of the landmarks. Because each Grand Lodge is self-governing, with no single body exercising authority over the whole of Freemasonry, the interpretations of these principles can and do vary, leading to controversies of recognition. Different Masonic jurisdictions have different landmarks.

Freemasonry has had a complex relationship with women for centuries. A few women were involved in Freemasonry before the 18th century, despite de jure prohibitions in the Premier Grand Lodge of England.

This is a chronology of the formation of "regular" or "mainstream" Masonic Grand Lodges in North America, descending from the Premier Grand Lodge of England or its rival, the Antient Grand Lodge of England. A Grand Lodge is the governing body that supervises "Craft" Freemasonry in a particular jurisdiction or geographical area.

The Grand Lodge of Free & Accepted Masons of Indiana is one of two statewide organizations that oversee Masonic lodges in the state of Indiana. It was established on January 13, 1818. In 2016 the number of Freemasons in the Grand Lodge of Indiana was 55,553 amongst its 394 separate lodges, currently making it the sixth largest Masonic jurisdiction in the U.S. The Grand Lodge of Indiana's offices and archives are located in the Indianapolis Masonic Temple. The historically black Most Worshipful Prince Hall Grand Lodge of Indiana F&AM is the second regular Masonic grand lodge in the state, and it was originally established in 1856 as the Independent Union Grand Lodge of Free and Accepted Masons of the State of Indiana. The two grand lodges agreed to mutual recognition in May 1998, and they jointly share sovereignty over the Masonic fraternity in Indiana.

The Grand Lodge of Ohio, formally known as the Grand Lodge of Free & Accepted Masons of Ohio, is the governing body of the largest group of Masonic lodges in Ohio. The Grand Lodge of Ohio follows the Anglo-American tradition of Freemasonry that is common in the United States. In 2023, the Grand Lodge reported a total membership of 75,000 Master Masons.
The Most Worshipful National Grand Lodge Free & Accepted Ancient York Masons Prince Hall Origin National Compact USA is a body of Masonry in the United States of America composed predominantly of African American Freemasons. It governs Grand Lodges within the United States and the Commonwealth of The Bahamas.
The Grand Lodge of New Jersey Free & Accepted Masons is the official governing body of New Jersey Masonic Lodges as recognized by other Grand Jurisdictions throughout the world. As early as 1730, New Jersey was one of the first states with active Freemasonry. The Grand Lodge of NJ was formally established in 1787. The Most Worshipful Prince Hall Grand Lodge of State of New Jersey and The Most Worshipful Grand Lodge of New Jersey recognize each other as Masonic Grand Lodges.

The Grand Lodge of Free & Accepted Masons of California, commonly called the Grand Lodge of California, is one of the two Masonic Grand Lodges in the state recognized by the United Grand Lodge of England, the other being the Most Worshipful Prince Hall Grand Lodge of California Free & Accepted Masons. The Grand Lodge of California is headquartered in San Francisco, California.

The Grand Lodge of Ancient, Free And Accepted Masons of New Mexico is the oldest and largest of the two regular Masonic Grand Lodges in the State of New Mexico. It was founded on August 7, 1877, in Santa Fe, New Mexico.