
Trema is a genus of about 15 species of evergreen trees closely related to the hackberries (Celtis), occurring in subtropical and tropical regions of southern Asia, northern Australasia, Africa, South and Central America, and parts of North America. They are generally small trees, reaching 10–20 m (33–66 ft) tall.

Antidesma is a genus of tropical plant in the family Phyllanthaceae formally described by Linnaeus in 1753. It is native to tropical Africa, S + E + SE Asia, Australia, and various oceanic islands. The greatest diversity occurs in Southeast Asia.
Canarium luzonicum, commonly known as elemi, is a tree native to the Philippines. The oleoresin harvested from it is also known as elemi.

The genus Mitrephora, of family Annonaceae, comprises around 50 species of trees and shrubs found in tropical Asia and northern Australasia. The area of distribution extends from China in the North down to Queensland, Australia in the South. The genus is widely found in southern India and Southeast Asia. It reaches a maximum of diversity in Borneo and the Philippines.

Litsea is a genus of evergreen or deciduous trees or shrubs belonging to the laurel family, Lauraceae. The genus includes a large number of accepted species in tropical and subtropical areas of North America and Asia.

Dysoxylum is a genus of rainforest trees and shrubs in the flowering plant family Meliaceae. About 34 species are recognised in the genus, distributed from India and southern China, through southeast Asia to New Guinea, Solomon Islands, and Australia. The name Dysoxylum derives from the Greek word ‘Dys’ meaning "bad" referring to "ill-smelling" and ‘Xylon’ meaning "wood".

Hydnocarpus is a genus of medium to large trees in the Family Achariaceae; the genus was previously placed in the now defunct family Flacourtiaceae. Species have been recorded from Indochina, Indonesia, Malaysia and the Philippines.

Chionanthus, common name: fringetrees, is a genus of about 140 species of flowering plants in the family Oleaceae.

Tetrastigma is a genus of plants in the grape family, Vitaceae. The plants are lianas that climb with tendrils and have palmately compound leaves. Plants are dioecious, with separate male and female plants; female flowers are characterized by their four-lobed stigmas. The species are found in subtropical and tropical regions of Asia, Malaysia, and Australia, where they grow in primary rainforest, gallery forest and monsoon forest and moister woodland. Species of this genus are notable as being the sole hosts of parasitic plants in the family Rafflesiaceae, one of which, Rafflesia arnoldii, produces the largest single flower in the world. Tetrastigma is the donor species for horizontal gene transfer to Sapria and Rafflesia due to multiple gene theft events.

Actinodaphne is an Asian genus of flowering plants in the laurel family (Lauraceae). It contains approximately 125 species of dioecious evergreen trees and shrubs.

Leea is a genus of plants in the family Vitaceae, subfamily Leeoideae, that are native to parts of central Africa, tropical Asia, Australia and Melanesia. It was previously placed in its own family, Leeaceae, based on morphological differences between it and other Vitaceae genera. These differences include ovule number per locule, carpel number, and the absence or presence of a staminoidal tube and floral disc. Pollen structure has also been examined for taxonomic demarcation, though studies have concluded that the pollen of Leeaceae and Vitaceae suggests the families should remain separate while other studies conclude that Leea should be included in Vitaceae.

Pinanga is a genus of flowering plant of the palm family in the subtribe Arecinae. It is native to eastern and southern Asia across to New Guinea.

Gomphandra is a genus of plant in family Stemonuraceae. They are dioecious trees or shrubs. The genus includes 44 accepted species, which range from India through Indochina to southern China and Taiwan, and through Malaysia, Indonesia, and the Philippines to New Guinea, Queensland, and the Solomon Islands.

Mastixia is a genus of about 19 species of resinous evergreen trees, usually placed in the family Cornaceae. Its range extends from India through Southeast Asia and New Guinea to the Solomon Islands. Mastixia species have alternate or opposite simple broad leaves, many-flowered inflorescences, and blue to purple drupaceous fruits.

Memecylon is a plant group in Melastomataceae. It consists of 350-400 species of small to medium-sized trees and shrubs occurring in the Old World tropics. Memecylon is a monophyletic group basal to the Melastomataceae clade. Memecylon taxa have more than 600 published basionyms. Diversity of this group is concentrated in tropical Africa, Madagascar, Sri Lanka, India and Malaysia.

Polyalthia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Annonaceae. There are approximately 90 species distributed from Africa to Asia and the Pacific.

Pseuduvaria is a genus of the plant family Annonaceae and tribe Miliuseae: with a native range is Tropical Asia.
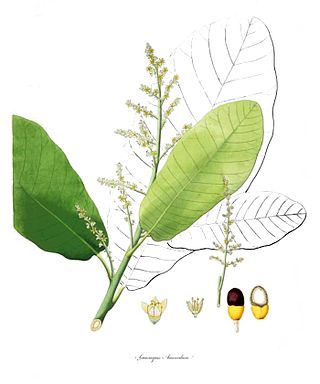
Semecarpus is a genus of plants in the family Anacardiaceae. It includes 87 species native to the Indian subcontinent, Indochina, Malesia, Taiwan, Papuasia, Queensland, and the South Pacific.

Colona is a genus of flowering plant in the Malvaceae sensu lato or Tiliaceae: now placed in the subfamily Grewioideae. It is found in south-east Asia.
Oreocnide is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Urticaceae.

















