
The Neotropical realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting Earth's land surface. Physically, it includes the tropical terrestrial ecoregions of the Americas and the entire South American temperate zone.

Industrialisation (UK) or industrialization (US) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive reorganisation of an economy for the purpose of manufacturing. Industrialisation is associated with increase of polluting industries heavily dependent on fossil fuels. With the increasing focus on sustainable development and green industrial policy practices, industrialisation increasingly includes technological leapfrogging, with direct investment in more advanced, cleaner technologies.

The humerus is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes. The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes, and 3 fossae. As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons.

Horses can use various gaits during locomotion across solid ground, either naturally or as a result of specialized training by humans.

Backstroke or back crawl is one of the four swimming styles used in competitive events regulated by FINA, and the only one of these styles swum on the back. This swimming style has the advantage of easy breathing, but the disadvantage of swimmers not being able to see where they are going. It also has a different start from the other three competition swimming styles. The swimming style is similar to an upside down front crawl or freestyle. Both backstroke and front crawl are long-axis strokes. In individual medley backstroke is the second style swum; in the medley relay it is the first style swum.

The trot is a two-beat diagonal horse gait where the diagonal pairs of legs move forward at the same time with a moment of suspension between each beat. It has a wide variation in possible speeds, but averages about 13 kilometres per hour (8.1 mph). A very slow trot is sometimes referred to as a jog. An extremely fast trot has no special name, but in harness racing, the trot of a Standardbred is faster than the gallop of the average non-racehorse, and has been clocked at over 30 miles per hour (48 km/h).
Hand signals are agreed gestures that people make with their hands or body to communicate in a non-verbal way. When used in traffic, hand signals are often used to convey driver's intention of their next movement. In some countries, hand signals can apply to any vehicle whose signal lights are missing or damaged. Hand signals are commonly used and applies to cyclists and motorists. Hand signals are commonly used to signal a left turn, right turn, overtaking, slowing or stopping.
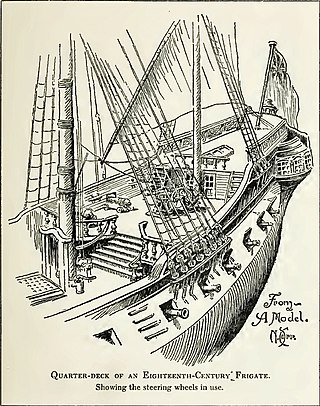
The quarterdeck is a raised deck behind the main mast of a sailing ship. Traditionally it was where the captain commanded his vessel and where the ship's colours were kept. This led to its use as the main ceremonial and reception area on board, and the word is still used to refer to such an area on a ship or even in naval establishments on land. Many such facilities have areas decorated like shipboard quarterdecks.

The Palazzo Barberini is a 17th-century palace in Rome, facing the Piazza Barberini in Rione Trevi. Today, it houses the Galleria Nazionale d'Arte Antica, the main national collection of older paintings in Rome.
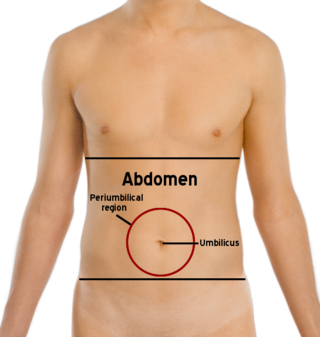
The abdomen is the front part of the torso between the thorax (chest) and pelvis in humans and in other vertebrates. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity. In arthropods, it is the posterior tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax.

In vertebrates, the pubis or pubic bone forms the lower and anterior part of each side of the hip bone. The pubis is the most forward-facing of the three bones that make up the hip bone. The left and right pubic bones are each made up of three sections; a superior ramus, an inferior ramus, and a body.

The Auchenorrhyncha suborder of the Hemiptera contains most of the familiar members of what was called the "Homoptera" – groups such as cicadas, leafhoppers, treehoppers, planthoppers, and spittlebugs. The aphids and scale insects are the other well-known "Homoptera", and they are in the suborder Sternorrhyncha.

The lateral parts of the occipital bone are situated at the sides of the foramen magnum; on their under surfaces are the condyles for articulation with the superior facets of the atlas.

Balanced rudders are used by both ships and aircraft. Both may indicate a portion of the rudder surface ahead of the hinge, placed to lower the control loads needed to turn the rudder. For aircraft the method can also be applied to elevators and ailerons; all three aircraft control surfaces may also be mass balanced, chiefly to avoid aerodynamic flutter.

The superfamily Membracoidea of sap-sucking true-bugs includes two of the largest families within what used to be called the "Homoptera": the leafhoppers (Cicadellidae) and the treehoppers (Membracidae). The other families in this group are quite small, and have, at various points, generally been included as members within other families, though they are all presently considered to be valid, monophyletic groups. The relict family Myerslopiidae is restricted to New Zealand and South America while the Melizoderidae consist of two genera restricted to South America. The great diversity of Neotropical taxa suggests that the group originated in that region.

There are two basic positions of the arms in ballet. In one, the dancer keeps the fingers of both arms fully touching to form an oval shape, either almost touching the hips, or at navel level, or raised above the dancer's head. In the other, the arms are extended to the sides with the elbows slightly bent. These positions may be combined to give other positions.

The Dominion Cinema is an independent cinema located in the Morningside area of Edinburgh, Scotland. Designed in the Art Deco style by the architect Thomas Bowhill Gibson, it was opened in 1938. The Dominion is now a Category B listed building.

Arisarum vulgare, common name the friar's cowl or larus, is an herbaceous, perennial, rhizomatous plant in the genus Arisarum belonging to the family Araceae.

Munididae is a family of squat lobsters, taxonomically separated from the family Galatheidae in 2010.

The LeFerriere House is a historic house at 171-173 Intervale Avenue in Burlington, Vermont. Built about 1888 as worker housing in the city's Old North End, it is architecturally a distinctive vernacular interpretation of Queen Anne architecture. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2008 as the LeFarriere House.


















