Northern root-knot nematode is a species of vegetable pathogens which produces tiny galls on around 550 crop and weed species. They invade root tissue after birth. Females are able to lay up to 1,000 eggs at a time in a large egg mass. By surviving harsh winters, they can survive in cold climates.

Root-knot nematodes are plant-parasitic nematodes from the genus Meloidogyne. They exist in soil in areas with hot climates or short winters. About 2000 plants worldwide are susceptible to infection by root-knot nematodes and they cause approximately 5% of global crop loss. Root-knot nematode larvae infect plant roots, causing the development of root-knot galls that drain the plant's photosynthate and nutrients. Infection of young plants may be lethal, while infection of mature plants causes decreased yield.

Meloidogyne incognita, also known as the "southern root-nematode" or "cotton root-knot nematode" is a plant-parasitic roundworm in the family Heteroderidae. This nematode is one of the four most common species worldwide and has numerous hosts. It typically incites large, usually irregular galls on roots as a result of parasitism.
Belonolaimus longicaudatus is a common parasite of grasses and other plant crops and products. It is the most destructive nematode pest of turf grass, and it also attacks a wide range of fruit, vegetable, and fiber crops such as citrus, cotton, ornamentals, and forage. The sting nematode is a migratory ectoparasite of roots. It is well established in many golf courses and presents a problem in turf management. The sting nematode is only present in very sandy soils. It cannot reproduce in heavier or clay soils.

Rotylenchulus reniformis, the reniform nematode, is a species of parasitic nematode of plants with a worldwide distribution in the tropical and subtropical regions.

Meloidogyne arenaria is a species of plant pathogenic nematodes. This nematode is also known as the peanut root knot nematode. The word "Meloidogyne" is derived from two Greek words that mean "apple-shaped" and "female". The peanut root knot nematode, M. arenaria is one of the "major" Meloidogyne species because of its worldwide economic importance. M. arenaria is a predominant nematode species in the United States attacking peanut in Alabama, Florida, Georgia, and Texas. The most damaging nematode species for peanut in the USA is M. arenaria race 1 and losses can exceed 50% in severely infested fields. Among the several Meloidogyne species that have been characterized, M. arenaria is the most variable both morphologically and cytologically. In 1949, two races of this nematode had been identified, race 1 which reproduces on peanut and race 2 which cannot do so. However, in a recent study, three races were described. López-Pérez et al (2011) had also studied populations of M. arenaria race 2, which reproduces on tomato plants carrying the Mi gene and race 3, which reproduces on both resistant pepper and tomato.

Meloidogyne javanica is a species of plant-pathogenic nematodes. It is one of the tropical root-knot nematodes and a major agricultural pest in many countries. It has many hosts. Meloidogyne javanica reproduces by obligatory mitotic parthenogenesis (apomixis).

Meloidogyne chitwoodi is a plant pathogenic root-knot nematode that is a crop pest of potatoes, carrots, and black salsify. Root-knot nematodes such as M. chitwoodi cause the production of root-knot galls when their larvae infect the plant's roots and capture nutrients stored in the roots.
Pratylenchus brachyurus is a plant parasitic nematode.
Heterodera carotae is a plant pathogenic nematode commonly known as the carrot root nematode or carrot cyst nematode. It is found in Europe, Cyprus and India and is considered an invasive species in the United States. It causes damage to carrot crops and is very specific in its choice of hosts, only infecting Daucus carota and Daucus pulcherrima.
Meloidogyne acronea, the African cotton root-knot nematode or African cotton root nematode, is a plant pathogenic nematode affecting pigeonpeas. It is also an invasive species. The roots and surrounding soils of cereals, grasses, and Gossypium spp. provide habitat for this organism. M. acronea was confirmed as a potentially problematic pest of cotton, Gossypium hirsutum cv. Makoka, which was proven through pot experiments.
Xiphinema americanum, the American dagger nematode, is a species of plant pathogenic nematodes. It is one of many species that belongs to the genus Xiphinema. It was first described by N. A. Cobb in 1913, who found it on both sides of the United States on the roots of grass, corn, and citrus trees. Not only is Xiphinema americanum known to vector plant viruses, but also X. americanum has been referred to as "the most destructive plant parasitic nematode in America", and one of the four major nematode pests in the Southeastern United States.
There are many plant-parasitic species in the root-knot nematode genus (Meloidogyne) that attack coffee such as M. incognita, M. arenaria, M. exigua, M. javanica and M. coffeicola. Study has already shown interspecific variability coffee, in which show how this species can be adapting to new hosts and environments.
Heterodera sacchari, the sugarcane cyst nematode, mitotic parthenogenic sedentary endoparasitic nematode. This plant-parasitic nematode infects the roots of sugarcane, and the female nematode eventually becomes a thick-walled cyst filled with eggs. Aboveground symptoms are species specific and are similar to those caused by other Heterodera species. Symptoms include: stunted and chlorotic plants, and reduced root growth. Seedlings may be killed in heavily infested soils.
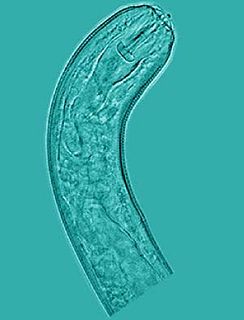
Pratylenchus is a genus of nematodes known commonly as lesion nematodes. They are parasitic on plants and are responsible for root lesion disease on many taxa of host plants in temperate regions around the world. Lesion nematodes are migratory endoparasites that feed and reproduce in the root and move around, unlike the cyst or root-knot nematodes, which may stay in one place. They usually only feed on the cortex of the root. Species are distinguished primarily by the morphology of the stylets.
Meloidogyne enterolobii was originally described from a population collected from the pacara earpod tree in China in 1983. In 2001 it was reported for the first time in the continental USA in Florida. M. enterolobii is now considered one of the most important root-knot nematode species because of its ability of reproducing on root-knot nematode-resistant bell pepper and other economically important crops.
Globodera tabacum, commonly known as a tobacco cyst nematode, is a plant parasitic nematode that mainly infests the tobacco plant, but also plants in family Solanaceae.
Mononchoides fortidens, of the order Diplogasterida, is a free-living predacious nematode that feeds on both nematodes and bacteria . The predatory behavior of this nematode presents the opportunity to use it as a bio-control agent against other plant parasitic nematodes. It has been shown to have a preference for the second stage juveniles of Meloidogyne incognita.
Holotrichia disparilis is a species of chafer found in Sri Lanka.
Prof. Waceke Wanjohi is a professor at Kenyatta University who works in plant nematology, research, teaching, networking, and graduate education. Dedicated to boosting Africa's competitiveness in the global arena by improving agricultural output in smallholder farming systems in Sub-Saharan Africa.





