
Cupressaceae or the cypress family is a family of conifers. The family includes 27–30 genera, which include the junipers and redwoods, with about 130–140 species in total. They are monoecious, subdioecious or (rarely) dioecious trees and shrubs up to 116 m (381 ft) tall. The bark of mature trees is commonly orange- to red-brown and of stringy texture, often flaking or peeling in vertical strips, but smooth, scaly or hard and square-cracked in some species. The family reached its peak of diversity during the mesozoic era.

Chamaecyparis, common names cypress or false cypress, is a genus of conifers in the cypress family Cupressaceae, native to eastern Asia and to the western and eastern margins of the United States. The name is derived from the Greek khamai (χαμαί), meaning "on the earth", and kuparissos (κυπάρισσος) for "cypress".

Cunninghamia is a genus of one or two living species of evergreen coniferous trees in the cypress family Cupressaceae. They are native to China, northern Vietnam and Laos, and perhaps also Cambodia. They may reach 50 m (160 ft) in height. In vernacular use, it is most often known as Cunninghamia, but is also sometimes called "China-fir". The genus name Cunninghamia honours Dr. James Cunningham, a British doctor who introduced this species into cultivation in 1702 and botanist Allan Cunningham.

Athrotaxis is a genus of two to three species of conifers in the cypress family, Cupressaceae. The genus is endemic to western Tasmania, where they grow in high-elevation temperate rainforests.
Mycobacterium houstonense is a member of the Mycobacterium fortuitum third biovariant complex. The specific epithet houstonense refers to Houston, Texas, where the first isolate of the M. fortuitum third biovariant (sorbitol-positive) was identified.
The Chloroflexota are a phylum of bacteria containing isolates with a diversity of phenotypes, including members that are aerobic thermophiles, which use oxygen and grow well in high temperatures; anoxygenic phototrophs, which use light for photosynthesis ; and anaerobic halorespirers, which uses halogenated organics as electron acceptors.
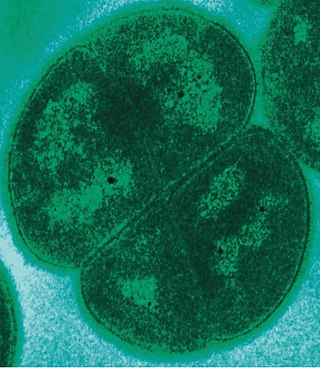
Deinococcus is in the monotypic family Deinococcaceae, and one genus of three in the order Deinococcales of the bacterial phylum Deinococcota highly resistant to environmental hazards. These bacteria have thick cell walls that give them Gram-positive stains, but they also include a second membrane and are therefore closer in structure to Gram-negative bacteria. Deinococcus survive when their DNA is exposed to high doses of gamma and UV radiation. Whereas other bacteria change their structure in the presence of radiation, such as by forming endospores, Deinococcus tolerate it without changing their cellular form and do not retreat into a hardened structure. They are also characterized by the presence of the carotenoid pigment deinoxanthin that give them their pink color. They are usually isolated according to these two criteria. In August 2020, scientists reported that bacteria from Earth, particularly Deinococcus bacteria, were found to survive for three years in outer space, based on studies conducted on the International Space Station. These findings support the notion of panspermia, the hypothesis that life exists throughout the Universe, distributed in various ways, including space dust, meteoroids, asteroids, comets, planetoids or contaminated spacecraft.

Sequoioideae, commonly referred to as redwoods, is a subfamily of coniferous trees within the family Cupressaceae, that range in the northern hemisphere. It includes the largest and tallest trees in the world. The trees in the subfamily are amongst the most notable trees in the world and are common ornamental trees. The subfamily reached its peak diversity in the early cenozoic.
Chamaecyparis eureka is an extinct species of conifer in the family Cupressaceae. It is known from fossil foliage found in the Buchanan Lake Formation deposits, dated to the middle Eocene Lutetian stage, from western Axel Heiberg Island, located in the Arctic Ocean in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. C. eureka is the oldest confirmed member of the genus Chamaecyparis, which includes five to six living species, depending on circumscription, which are native to Eastern Asia, Japan, and North America.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 2011.
Polynucleobacter is a genus of bacteria, originally established by Heckmann and Schmidt (1987) to exclusively harbor obligate endosymbionts of ciliates belonging to the genus Euplotes.

The Allenby formation is a sedimentary rock formation in British Columbia which was deposited during the Ypresian stage of the Early Eocene. It consists of conglomerates, sandstones with interbedded shales and coal. The shales contain an abundance of insect, fish and plant fossils known from 1877 and onward, while the Princeton Chert was first indented in the 1950s and is known from anatomically preserved plants.

Glyptostrobus europaeus is an extinct conifer species of the family Cupressaceae that is found as fossils throughout the Northern Hemisphere. The sole living species of Glyptostrobus was described from China in 1926. The name of the genus comes from the Greek "glypto" meaning grooved or carved, and "strobilus" meaning cone. The species name "europaeus" refers to the fact that it was first described from Europe.
This article contains papers in paleobotany that were published in 2016.
This article records new taxa of plants that were described during the year 2014, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleobotany that occurred in the year 2014.
Hughmillerites is a fossil cypress, found in the Late Jurassic of Scotland and Early Cretaceous of Canada.
The paleoflora of the Eocene Okanagan Highlands includes all plant and fungi fossils preserved in the Eocene Okanagan Highlands Lagerstätten. The highlands are a series of Early Eocene geological formations which span an 1,000 km (620 mi) transect of British Columbia, Canada and Washington state, United States and are known for the diverse and detailed plant fossils which represent an upland temperate ecosystem immediately after the Paleocene-Eocene thermal maximum, and before the increased cooling of the middle and late Eocene to Oligocene. The fossiliferous deposits of the region were noted as early as 1873, with small amounts of systematic work happening in the 1880-90s on British Columbian sites, and 1920-30s for Washington sites. A returned focus and more detailed descriptive work on the Okanagan Highlands sites revived in the 1970s. The noted richness of agricultural plant families in Republic and Princeton floras resulted in the term "Eocene orchards" being used for the paleofloras.
This article records new taxa of fossil plants that are scheduled to be described during the year 2021, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleobotany that are scheduled to occur in the year 2021.
This paleobotany list records new fossil plant taxa that were to be described during the year 2022, as well as notes other significant paleobotany discoveries and events which occurred during 2022.
This paleobotany list records new fossil plant taxa that were to be described during the year 2012, as well as notes other significant paleobotany discoveries and events which occurred during 2012.








