The Menapii were a Belgic tribe dwelling near the North Sea, around present-day Cassel, during the Iron Age and the Roman period.

Touggourt is a city and commune, former sultanate and capital of Touggourt District, in Touggourt Province, Algeria, built next to an oasis in the Sahara. As of the 2008 census, the commune had a population of 39,409 people, up from 32,940 in 1998, and an annual growth rate of 1.8%. Touggourt's urban area includes the communes of Nezla, Tebesbest and Zaouia El Abidia, for a total population of 146,108.

Cirta, also known by various other names in antiquity, was the ancient Berber, Punic and Roman settlement which later became Constantine, Algeria.

Médéa is the capital city of Médéa Province, Algeria. It is located roughly 68 km south of Algiers. The present-day city is situated on the site of an ancient Roman military post and has a history dating back to the 10th century. The town is French in character, with a rectangular city plan, red tile-roofed buildings, and beautiful public gardens. The hills surrounding Médéa are covered with vineyards, orchards, and farms that yield abundant grain. Médéa's chief products are wines, irrigation equipment, and various handicrafts.

Mauretania Caesariensis was a Roman province located in present-day Algeria. The full name refers to its capital Caesarea Mauretaniae.
The Delmatae, alternatively Dalmatae, during the Roman period, were a group of Illyrian tribes in Dalmatia, contemporary southern Croatia and western Bosnia and Herzegovina. The region of Dalmatia takes its name from the tribe.

Alpine skiing at the 2006 Winter Olympics consisted of ten events, held at Sestriere and Cesana-San Sicario, Italy. The races were held 12–25 February 2006.

Chlef is the capital of Chlef Province, Algeria. Located in the north of Algeria, 200 kilometres (120 mi) west of the capital, Algiers, it was founded in 1843, as Orléansville, on the ruins of Roman Castellum Tingitanum. In 1962, it was renamed al-Asnam, but after the devastating earthquake on October 10, 1980, it has borne its present name, Chlef, which is derived from the name of the Chelif River, the longest river in Algeria.

Relizane or Ghilizan (Arabic: غلیزان; is a city in Algeria. It is the capital city of Relizane Province.

Celemantia was a Roman castellum and settlement on the territory of the present-day municipality Iža, some 4 km to the east of Komárno in Slovakia. It is the biggest known Roman castellum in present-day Slovakia. It was a part of the Roman limes, the frontier-zone of the Empire.

Fectio, known as Vechten in Old Dutch, was a Roman castellum in the province Germania Inferior established in the year 4 or 5 AD. It was located at the place where the river Vecht (Fectio) branched off from the Rhine, leading to Lake Flevo, which was later to become the Zuiderzee. This was near the modern hamlet of Vechten in the municipality Bunnik, Utrecht, Netherlands.

Tadmit is a small town and commune in Djelfa Province, Algeria. According to the 1998 census it has a population of 6,172. Tadmit is something of a secluded town, although it is located several kilometres southwest of Djelfa. It is accessed via a small road off the N1 Trans-Saharan Highway.
The Tariotes or Tariotae were an Illyrian tribe that lived on the Adriatic coast of Dalmatia, in modern-day Croatia. They are considered part of the Dalmatae. The Tariotes are mentioned in the Classical literature by Roman author Pliny the Elder alone. In Pliny's Natural History the territory of the Tariotes is called Tariota and is mentioned as an ancient region, while their city is called Tariona, and described as a castellum, i.e. a stronghold. Tariona was located between the Krka River in the north and Cape Ploča in the south, along the coastal area. Tariote territory is also testified by two boundary inscriptions dating back to Roman Imperial times, which were found in the area of Marina. Those inscriptions refer to the boundaries of pastures used by the tribe of the Tariotes. A passage in the Libri Coloniarum of the Gromatici Veteres, probably dating back to the 5th century AD, is also considered to report the name of the tribe, along with that of the Sardeates.
Medjedel is a town and commune in M'Sila Province, Algeria. According to the 1998 census it has a population of 18,616.

Tibiscum was a Dacian town mentioned by Ptolemy, later a Roman fort and municipium. The ruins of the ancient settlement are located in Jupa, near Caransebeș, Caraș-Severin County, Romania. The Roman settlement here was one of the most important vestiges of classical antiquity in Banat.

Gemellae was a Roman fort and associated camp on the fringe of the Sahara Desert in what is today part of Algeria. It is now an archaeological site, 25 km south and 19 km west of Biskra, and 5 km southwest of the present-day village of M'Lili with which it probably shares an original Berber name. It was connected by military Roman road to Castellum Dimmidi and Capsa.

Auzia was a Roman-Berber colonia in present-day Sour El-Ghozlane, Algeria. The area was located around 150 km south-east of Algiers, in the ancient province of Mauretania Caesariensis.
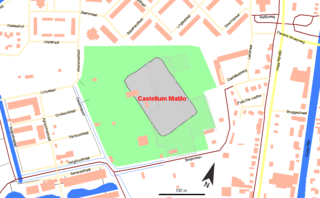
Matilo or Matilone was once a Roman fort (castellum) in modern-day Leiden. Positioned on the southern banks of the Oude Rijn, it served to protect the Roman borders in the province of Germania Inferior. On the Peutinger map, it lies between the encampments of Albaniana and Praetorium Agrippinae (Valkenburg). The seventh-century Ravenna Cosmography cites the name in the accusative case as Matellionem.

Thibilis was a Roman and Byzantine era town in what was Numidia but is today northeast Algeria. The site has extensive Roman and Byzantine ruins.
Castellum Ripae or Hadjar-Ouaghef is a locality and archeological site in Algeria, North Africa.