
Trematoda is a class of flatworms known as flukes or trematodes. They are obligate internal parasites with a complex life cycle requiring at least two hosts. The intermediate host, in which asexual reproduction occurs, is usually a snail. The definitive host, where the flukes sexually reproduce, is a vertebrate. Infection by trematodes can cause disease in all five traditional vertebrate classes: mammals, birds, amphibians, reptiles, and fish.
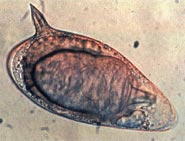
Schistosoma is a genus of trematodes, commonly known as blood flukes. They are parasitic flatworms responsible for a highly significant group of infections in humans termed schistosomiasis, which is considered by the World Health Organization as the second-most socioeconomically devastating parasitic disease, with hundreds of millions infected worldwide.

Clonorchis sinensis, the Chinese liver fluke, is a liver fluke belonging to the class Trematoda, phylum Platyhelminthes. It infects fish-eating mammals, including humans. In humans, it infects the common bile duct and gall bladder, feeding on bile. It was discovered by British physician James McConnell at the Medical College Hospital in Calcutta (Kolkata) in 1874. The first description was given by Thomas Spencer Cobbold, who named it Distoma sinense. The fluke passes its lifecycle in three different hosts, namely freshwater snail as first intermediate hosts, freshwater fish as second intermediate host, and mammals as definitive hosts.

Praziquantel (PZQ), sold under the brandname Biltricide among others, is a medication used to treat a number of types of parasitic worm infections in mammals, birds, amphibians, reptiles, and fish. In humans specifically, it is used to treat schistosomiasis, clonorchiasis, opisthorchiasis, tapeworm infections, cysticercosis, echinococcosis, paragonimiasis, fasciolopsiasis, and fasciolosis. It should not be used for worm infections of the eye. It is taken by mouth.
Opisthorchis viverrini, common name Southeast Asian liver fluke, is a food-borne trematode parasite from the family Opisthorchiidae that infects the bile duct. People are infected after eating raw or undercooked fish. Infection with the parasite is called opisthorchiasis. O. viverrini infection also increases the risk of cholangiocarcinoma, a cancer of the bile ducts.

Theodor Maximilian Bilharz was a German physician who made pioneering discoveries in the field of parasitology. His contributions led to the foundation of tropical medicine. He is best remembered as the discoverer of the blood fluke Schistosoma haematobium, the causative parasite of bloody urine (haematuria) known since ancient times in Egypt. The parasite, as the cause of bladder cancer, is declared by the International Agency for Research on Cancer as Group 1 carcinogen. The infection is known by an eponymous term bilharzia or bilharziasis, as well as by schistosomiasis.
Metagonimoides oregonensis is a trematode, or fluke worm, in the family Heterophyidae. This North American parasite is found primarily in the intestines of raccoons, American minks, frogs in the genus Rana, and freshwater snails in the genus Goniobasis. It was first described in 1931 by E. W. Price. The parasite has a large distribution, from Oregon to North Carolina. Adult flukes vary in host range and morphology dependent on the geographical location. This results in different life cycles, as well as intermediate hosts, across the United States. On the west coast, the intermediate host is freshwater snails (Goniobasis), while on the east coast the intermediate host is salamanders (Desmognathus). The parasites on the west coast are generally much larger than on the east coast. For example, the pharynx as well as the body of the parasite are distinctly larger in Oregon than in North Carolina. The reverse pattern is observed on the east coast for uterine eggs, which are larger on the west coast. In snails, there is also a higher rate of infection in female snails than in males. Research on the life history traits of the parasites have been performed with hamsters and frogs as model species.

Heterophyes heterophyes, or the intestinal fish fluke, was discovered by Theodor Maximaillian Bilharz in 1851. This parasite was found during an autopsy of an Egyptian mummy. H. heterophyes is found in the Middle East, West Europe and Africa. They use different species to complete their complex lifestyle. Humans and other mammals are the definitive host, first intermediate host are snails, and second intermediate are fish. Mammals that come in contact with the parasite are dogs, humans, and cats. Snails that are affected by this parasite are the Cerithideopsilla conica. Fish that come in contact with this parasite are Mugil cephalus, Tilapia milotica, Aphanius fasciatus, and Acanthgobius sp. Humans and mammals will come in contact with this parasite by the consumption of contaminated or raw fish. This parasite is one of the smallest endoparasite to infect humans. It can cause intestinal infection called heterophyiasis.

Heterophyidae is a family of intestinal trematodes in the order Plagiorchiida.

Haplorchis is a genus of intestinal flukes in the family Heterophyidae.

Haplorchis taichui is a species of intestinal fluke in the family Heterophyidae. It is a human parasite.

Cryptocotyle is a genus of trematodes from the family Heterophyidae. The definitive hosts of the parasites are fish-eating birds and mammals. The metacercariae are visible in the skin of infected fish as "black spots".

Semisulcospira libertina is a species of freshwater snail with an operculum, an aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Semisulcospiridae. Widespread in east Asia, it lives in China, Taiwan, Korea, Japan, and the Philippines. In some countries it is harvested as a food source. It is medically important as a vector of clonorchiasis, paragonimiasis, metagonimiasis and others.

Metagonimus yokogawai, or the Yokogawa fluke, is a species of a trematode, or fluke worm, in the family Heterophyidae.

Semisulcospira reiniana is a species of freshwater snail with an operculum, an aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Semisulcospiridae.
Metagonimus miyatai is a species of a trematode, or fluke worm, in the family Heterophyidae.
Metagonimus takahashii is a species of a trematode, or fluke worm, in the family Heterophyidae.
Carcinogenic parasites are parasitic organisms that depend on other organisms for their survival, and cause cancer in such hosts. Three species of flukes (trematodes) are medically-proven carcinogenic parasites, namely the urinary blood fluke, the Southeast Asian liver fluke and the Chinese liver fluke. S. haematobium is prevalent in Africa and the Middle East, and is the leading cause of bladder cancer. O. viverrini and C. sinensis are both found in eastern and southeastern Asia, and are responsible for cholangiocarcinoma. The International Agency for Research on Cancer declared them in 2009 as a Group 1 biological carcinogens in humans.
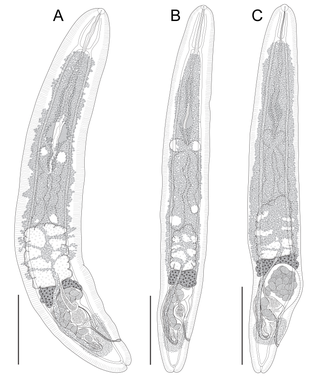
Aporocotylidae is a family of trematodes within the order Diplostomida, which contains species commonly known as fish blood flukes. It contains more than 40 genera, the largest being Cardicola. Species in this family parasite fish in both fresh and marine water.

Gastropod-borne parasitic diseases (GPDs) are a group of infectious diseases that require a gastropod species to serve as an intermediate host for a parasitic organism that can infect humans upon ingesting the parasite or coming into contact with contaminated water sources. These diseases can cause a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe, life-threatening conditions, with them being prevalent in many parts of the world, particularly in developing regions. Preventive measures such as proper sanitation and hygiene practices, avoiding contact with infected gastropods and cooking or boiling food properly can help to reduce the risk of these diseases.













