
Methylchloroisothiazolinone, also referred to as MCI, is a preservative with antibacterial and antifungal effects within the group of isothiazolinones. These compounds have an active sulphur moiety that is able to oxidize thiol-containing residues, thereby effectively killing most aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Methylchloroisothiazolinone is effective against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, yeast, and fungi.

Thiomersal (INN), or thimerosal, is an organomercury compound. This compound is a well-established antiseptic and antifungal agent.
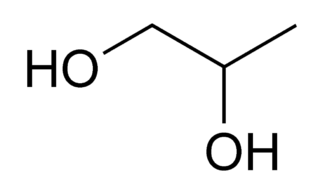
Propylene glycol (IUPAC name: propane-1,2-diol), according to the National Library of Medicine and Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, is a synthetic liquid substance that absorbs water. It is labeled an organic compound in chemistry due to its carbon attributes. Its chemical formula is CH3CH(OH)CH2OH. It is a viscous, colorless liquid, which is nearly odorless but possesses a faintly sweet taste. Containing two alcohol groups, it is classed as a diol. It is miscible with a broad range of solvents, including water, acetone, and chloroform. In general, glycols are non-irritating, have very low volatility and very low toxicity.

Methylisothiazolinone, MIT, or MI,, is a powerful synthetic biocide and preservative within the group of isothiazolinones, which is used in numerous personal care products and a wide range of industrial applications.

Contact dermatitis is a type of inflammation of the skin.

Latex allergy is a medical term encompassing a range of allergic reactions to the proteins present in natural rubber latex. Latex allergy generally develops after repeated exposure to products containing natural rubber latex. When latex-containing medical devices or supplies come in contact with mucous membranes, the membranes may absorb latex proteins. The immune system of some susceptible individuals produces antibodies that react immunologically with these antigenic proteins. As many items contain or are made from natural rubber, including shoe soles, elastic bands, rubber gloves, condoms, baby-bottle nipples, and balloons, there are many possible routes of exposure that may trigger a reaction. People with latex allergies may also have or develop allergic reactions to some fruits, such as bananas.
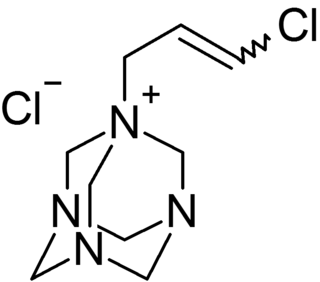
Quaternium-15 is a quaternary ammonium salt used as a surfactant and preservative in many cosmetics and industrial substances. It acts as an antimicrobial agent because it acts as a formaldehyde releaser, though doing so can also cause contact dermatitis, a symptom of an allergic reaction, especially in those with sensitive skin.
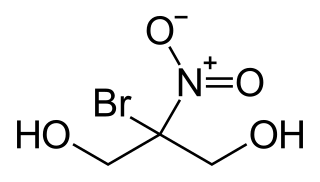
Bronopol is an organic compound that is used as an antimicrobial. It is a white solid although commercial samples appear yellow.

A patch test is a method used to determine whether a specific substance causes allergic inflammation of a patient's skin. Any individual suspected of having allergic contact dermatitis or atopic dermatitis needs patch testing.
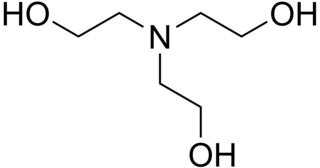
Triethanolamine, or TEA is a viscous organic compound that is both a tertiary amine and a triol. A triol is a molecule with three alcohol groups. Approximately 150,000 tonnes were produced in 1999. It is a colourless compound although samples may appear yellow because of impurities.

Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a form of contact dermatitis that is the manifestation of an allergic response caused by contact with a substance; the other type being irritant contact dermatitis (ICD).

Balsam of Peru, also known and marketed by many other names, is a balsam derived from a tree known as Myroxylon balsamum var. pereirae; it is found in El Salvador, where it is an endemic species.

Benzisothiazolinone (BIT) is a widely used biocide and belongs to the group of isothiazolinones.

Diazolidinyl urea is an antimicrobial preservative used in cosmetics. It is chemically related to imidazolidinyl urea which is used in the same way. Diazolidinyl urea acts as a formaldehyde releaser.

A formaldehyde releaser, formaldehyde donor or formaldehyde-releasing preservative is a chemical compound that slowly releases formaldehyde.
Amidoamines are a class of chemical compounds that are formed from fatty acids and diamines. They are used as intermediates in the synthesis of surfactants, such as cocamidopropyl betaine (CAPB), some of which are used in personal care products including soaps, shampoos, and cosmetics. Amidoamines can also serve as curing agents for epoxy resins.

DMDM hydantoin is an antimicrobial formaldehyde releaser preservative with the trade name Glydant. DMDM hydantoin is an organic compound belonging to a class of compounds known as hydantoins. It is used in the cosmetics industry and found in products like shampoos, hair conditioners, hair gels, Rite Aid Liquid Lubricant, and skin care products.
Perfume intolerance or perfume allergy is a controversial condition wherein people exhibit sensitivity or allergic reactions to ingredients in some perfumes and some other fragrances. It is a form of multiple chemical sensitivity, a more general phenomenon for this diagnosis.

Iodopropynyl Butyl Carbamate (IPBC) is a water-soluble preservative used globally in the paints & coatings, wood preservatives, personal care, and cosmetics industries. IPBC is a member of the carbamate family of biocides. IPBC was invented in the 1970s and has a long history of effective use as an antifungal technology.

Nickel allergy or nickel allergic contact dermatitis (Ni-ACD) is a form of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) caused by exposure to the chemical element nickel.

















