Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula CO(NH2)2. This amide has two –NH2 groups joined by a carbonyl (C=O) functional group.

Formaldehyde ( fər-MAL-də-hide, alsofor-) (systematic name methanal) is a naturally occurring organic compound with the formula CH2O (H−CHO). The pure compound is a pungent-smelling colorless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde (refer to section Forms below), hence it is stored as an aqueous solution (formalin). It is the simplest of the aldehydes (R−CHO). The common name of this substance comes from its similarity and relation to formic acid.
Hexamethylenetetramine, also known as methenamine, hexamine, or urotropin, is a heterocyclic organic compound with the formula (CH2)6N4. This white crystalline compound is highly soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It has a cage-like structure similar to adamantane. It is useful in the synthesis of other organic compounds, including plastics, pharmaceuticals, and rubber additives. It sublimes in vacuum at 280 °C.

Phenol formaldehyde resins (PF) or phenolic resins are synthetic polymers obtained by the reaction of phenol or substituted phenol with formaldehyde. Used as the basis for Bakelite, PFs were the first commercial synthetic resins (plastics). They have been widely used for the production of molded products including billiard balls, laboratory countertops, and as coatings and adhesives. They were at one time the primary material used for the production of circuit boards but have been largely replaced with epoxy resins and fiberglass cloth, as with fire-resistant FR-4 circuit board materials.
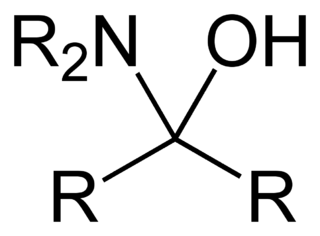
A hemiaminal (also carbinolamine) is a functional group or type of chemical compound that has a hydroxyl group and an amine attached to the same carbon atom: -C(OH)(NR2)-. R can be hydrogen or an alkyl group. Hemiaminals are intermediates in imine formation from an amine and a carbonyl by alkylimino-de-oxo-bisubstitution. Hemiaminals can be viewed as a blend of aminals and geminal diol. They are a special case of amino alcohols.
Urea-formaldehyde (UF), also known as urea-methanal, so named for its common synthesis pathway and overall structure, is a nontransparent thermosetting resin or polymer. It is produced from urea and formaldehyde. These resins are used in adhesives, plywood, particle board, medium-density fibreboard (MDF), and molded objects.

Biuret is a chemical compound with the chemical formula HN(CONH2)2. It is a white solid that is soluble in hot water. The term "biuret" also describes a family of organic compounds with the chemical formula R1R2N−C(=O)−N(R3)−C(=O)−NR4R5. Thus, dimethyl biuret is H(CH3)N−C(=O)−N(H)−C(=O)−N(CH3)H. A variety of organic derivatives are known. Also known as carbamylurea, it results from the condensation of two equivalents of urea. As such, it is an undesirable impurity in urea-based fertilizers. As biuret is toxic to plants, its percentage in fertilizers must be kept low.

Crotonaldehyde is a chemical compound with the formula CH3CH=CHCHO. The compound is usually sold as a mixture of the E- and Z-isomers, which differ with respect to the relative position of the methyl and formyl groups. The E-isomer is more common (data given in Table is for the E-isomer). This lachrymatory liquid is moderately soluble in water and miscible in organic solvents. As an unsaturated aldehyde, crotonaldehyde is a versatile intermediate in organic synthesis. It occurs in a variety of foodstuffs, e.g. soybean oils.
A controlled-release fertiliser (CRF) is a granulated fertiliser that releases nutrients gradually into the soil. Controlled-release fertilizer is also known as controlled-availability fertilizer, delayed-release fertilizer, metered-release fertilizer, or slow-acting fertilizer. Usually CRF refers to nitrogen-based fertilizers. Slow- and controlled-release involve only 0.15% of the fertilizer market (1995).
Methanediol, also known as formaldehyde monohydrate or methylene glycol, is an organic compound with chemical formula CH2(OH)2. It is the simplest geminal diol. In aqueous solutions it coexists with oligomers (short polymers). The compound is closely related and convertable to the industrially significant derivatives paraformaldehyde ((CH2O)n), formaldehyde (H2C=O), and 1,3,5-trioxane ((CH2O)3).

A formaldehyde releaser, formaldehyde donor or formaldehyde-releasing preservative is a chemical compound that slowly releases formaldehyde.
A thermoset polymer matrix is a synthetic polymer reinforcement where polymers act as binder or matrix to secure in place incorporated particulates, fibres or other reinforcements. They were first developed for structural applications, such as glass-reinforced plastic radar domes on aircraft and graphite-epoxy payload bay doors on the space shuttle.

Dimethylol ethyleneurea is an organic compound derived from formaldehyde and urea. It is a colourless solid that is used for treating cellulose-based heavy fabrics to inhibit wrinkle formation. Dimethylol ethylene urea (DMEU) bonds with the hydroxyl groups present in long cellulose chains and prevents the formation hydrogen bonding between the chains, the primary cause of wrinkling. This treatment produces permanently wrinkle-resistant fabrics and is different from the effects achieved from using fabric softeners.
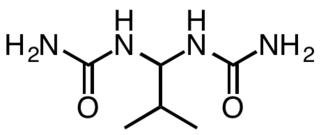
Isobutylidenediurea (abbreviated IBDU) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2CHCH{NHC(O)NH2}2. It is a derivative of urea (OC(NH2)2), which itself is highly soluble in water, but IBDU is not. It functions as a controlled-release fertiliser owing to its low solubility, which limits the rate of its hydrolysis to urea, which is a fast-acting fertiliser.

In chemistry, ureas are a class of organic compounds with the formula (R2N)2CO where R = H, alkyl, aryl, etc. Thus, in addition to describing a specific chemical compound (H2N)2CO), urea is the name of a functional group that is found in many compounds and materials of both practical and theoretical interest. Generally ureas are colorless crystalline solids, which, owing to the presence of fewer hydrogen bonds, exhibit melting points lower than that of urea itself.

Bis(hydroxymethyl)urea is an organic compound with the formula OC(NHCH2OH)2. This white water-soluble solid is an intermediate in the formation of urea-formaldehyde resins. It forms upon treatment of urea with an excess of formaldehyde.
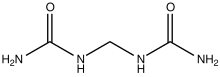
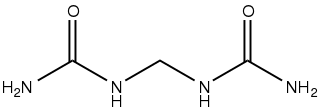
Dimethylene triurea (DMTU) is the organic compound with the formula (H2NC(O)NHCH2NH)2CO. It is a white water-soluble solid. The compound is formed by the condensation of formaldehyde with urea. Both branched and linear isomers exist.

Crotonylidene diurea (CDU) is an organic compound formed by the condensation of crotonaldehyde with two equivalents of urea. It is a white, water-soluble solid. CDU is a component of some controlled-release fertilizers.

Methylol urea is the organic compound with the formula H2NC(O)NHCH2OH. It is a white, water-soluble solid that decomposes near 110 °C.
Hydroxymethylation is a chemical reaction that installs the CH2OH group. The transformation can be implemented in many ways and applies to both industrial and biochemical processes.