
Boops boops, commonly called the bogue, is a species of seabream native to the eastern Atlantic.

Microcotyle is a genus which belongs to the phylum Platyhelminthes and class Monogenea. Species of Microcotyle are ectoparasites that affect their host by attaching themselves as larvae on the gills of the fish and grow into adult stage. This larval stage is called oncomiracidium, and is characterized as free swimming and ciliated.

Ophidion barbatum, the snake blenny, is a fish species in the family Ophidiidae. It is widespread in the eastern Atlantic from southern England to Senegal in West Africa, and the northern Mediterranean. It is a marine subtropical demersal fish, up to 25 centimetres (9.8 in) long.

Cichlidogyrus is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans in the family Ancyrocephalidae. The type-species of the genus is Cichlidogyrus arthracanthusPaperna, 1960, by original designation. All the species of the genus are parasites on the gills of fish, namely African Cichlidae, Nandidae and Cyprinodontidae.
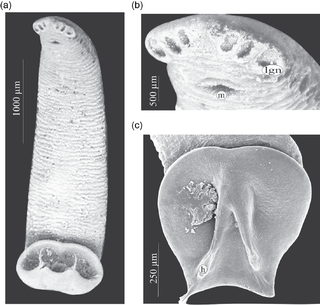
Monocotylidae is a family of monogenean flatworms.

The Diplectanidae are a family of monopisthocotylean monogeneans. They are all parasitic on the gills of fish. Diplectanids are small animals, generally around 1 mm in length. As parasites, they can be extremely numerous, up to several thousand on an individual fish.

Louis Euzet was a French parasitologist.

Echinoplectanum is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans in the family Diplectanidae. All its species are parasites on the gills of fish; hosts recorded to date are all groupers, including coralgroupers and the Dusky grouper. So far, species of Echinoplectanum have been recorded only from fish caught off Australia, New Caledonia and in the Mediterranean Sea.
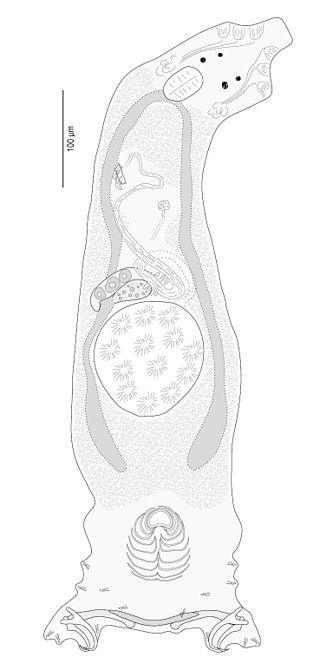
Lamellodiscus is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans in the family Diplectanidae; all species of Lamellodiscus are small worms, parasitic on the gills of teleost fish.
Cardiocephaloides longicollis is a species of flukes. The life cycle of C. longicollis is asexual as well as complex. Its asexual stage resides in the body of whelks where it replicates many times, and eventually its eggs are dispersed in the water through feces. C.longicollis begin their early life as free swimming miracidia larvae in the water. They go on to infect snails, and a variety of fishes, usually second intermediate host, in the form of a cercariae. While C.longicollis has previously been recorded in 19 fish species, researchers have found 12 other species which are viable hosts for C.longicollis making for a grand total of 31 aquatic species. The final host for this parasite are the gulls that eat the infected fish in which the parasite has formed cysts in.

Microcotylidae is a family of polyopisthocotylean monogeneans. All the species in this family are parasitic on fish.

Microcotyle algeriensis is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
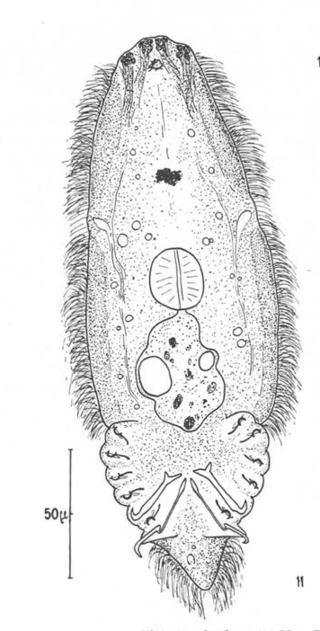
An oncomiracidium is the ciliated and free-living larva of a monogenean, a type of parasitic flatworm commonly found on fish. It is similar to the miracidium of Trematoda, but has sclerotised (hardened) hooklets not found in the latter.
Microcotyle victoriae is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.

Microcotyle sebastis is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.

Microcotyle pomatomi is a species of monogenean that is parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.

Microcotyle visa is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Microcotyle danielcarrioni is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.

Pseudaxine trachuri is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Gastrocotylidae.
Microcotyle isyebi is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
















