
Structural engineering is a sub-discipline of civil engineering in which structural engineers are trained to design the 'bones and muscles' that create the form and shape of man-made structures. Structural engineers also must understand and calculate the stability, strength, rigidity and earthquake-susceptibility of built structures for buildings and nonbuilding structures. The structural designs are integrated with those of other designers such as architects and building services engineer and often supervise the construction of projects by contractors on site. They can also be involved in the design of machinery, medical equipment, and vehicles where structural integrity affects functioning and safety. See glossary of structural engineering.
Structural engineers analyze, design, plan, and research structural components and structural systems to achieve design goals and ensure the safety and comfort of users or occupants. Their work takes account mainly of safety, technical, economic, and environmental concerns, but they may also consider aesthetic and social factors.
Structural analysis is the determination of the effects of loads on physical structures and their components. Structures subject to this type of analysis include all that must withstand loads, such as buildings, bridges, aircraft and ships. Structural analysis employs the fields of applied mechanics, materials science and applied mathematics to compute a structure's deformations, internal forces, stresses, support reactions, accelerations, and stability. The results of the analysis are used to verify a structure's fitness for use, often precluding physical tests. Structural analysis is thus a key part of the engineering design of structures.
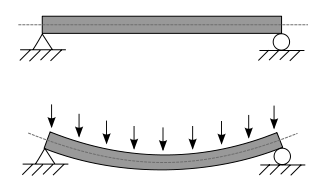
A beam is a structural element that primarily resists loads applied laterally to the beam's axis. Its mode of deflection is primarily by bending. The loads applied to the beam result in reaction forces at the beam's support points. The total effect of all the forces acting on the beam is to produce shear forces and bending moments within the beams, that in turn induce internal stresses, strains and deflections of the beam. Beams are characterized by their manner of support, profile, equilibrium conditions, length, and their material.

Prestressed concrete is a form of concrete used in construction. It is substantially "prestressed" (compressed) during production, in a manner that strengthens it against tensile forces which will exist when in service.

Earthquake engineering is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering that designs and analyzes structures, such as buildings and bridges, with earthquakes in mind. Its overall goal is to make such structures more resistant to earthquakes. An earthquake engineer aims to construct structures that will not be damaged in minor shaking and will avoid serious damage or collapse in a major earthquake. Earthquake engineering is the scientific field concerned with protecting society, the natural environment, and the man-made environment from earthquakes by limiting the seismic risk to socio-economically acceptable levels. Traditionally, it has been narrowly defined as the study of the behavior of structures and geo-structures subject to seismic loading; it is considered as a subset of structural engineering, geotechnical engineering, mechanical engineering, chemical engineering, applied physics, etc. However, the tremendous costs experienced in recent earthquakes have led to an expansion of its scope to encompass disciplines from the wider field of civil engineering, mechanical engineering, nuclear engineering, and from the social sciences, especially sociology, political science, economics, and finance.
Structural health monitoring (SHM) involves the observation and analysis of a system over time using periodically sampled response measurements to monitor changes to the material and geometric properties of engineering structures such as bridges and buildings.
An extradosed bridge employs a structure that combines the main elements of both a prestressed box girder bridge and a cable-stayed bridge. The name comes from the word extrados, the exterior or upper curve of an arch, and refers to how the "stay cables" on an extradosed bridge are not considered as such in the design, but are instead treated as external prestressing tendons deviating upward from the deck. In this concept, they remain part of the main bridge superstructure.

Abaqus FEA is a software suite for finite element analysis and computer-aided engineering, originally released in 1978. The name and logo of this software are based on the abacus calculation tool. The Abaqus product suite consists of five core software products:
- Abaqus/CAE, or "Complete Abaqus Environment". It is a software application used for both the modeling and analysis of mechanical components and assemblies (pre-processing) and visualizing the finite element analysis result. A subset of Abaqus/CAE including only the post-processing module can be launched independently in the Abaqus/Viewer product.
- Abaqus/Standard, a general-purpose Finite-Element analyzer that employs implicit integration scheme (traditional).
- Abaqus/Explicit, a special-purpose Finite-Element analyzer that employs explicit integration scheme to solve highly nonlinear systems with many complex contacts under transient loads.
- Abaqus/CFD, a Computational Fluid Dynamics software application which provides advanced computational fluid dynamics capabilities with extensive support for preprocessing and postprocessing provided in Abaqus/CAE.
- Abaqus/Electromagnetic, a Computational electromagnetics software application which solves advanced computational electromagnetic problems.

The history of structural engineering dates back to at least 2700 BC when the step pyramid for Pharaoh Djoser was built by Imhotep, the first architect in history known by name. Pyramids were the most common major structures built by ancient civilizations because it is a structural form which is inherently stable and can be almost infinitely scaled.
GRAITEC AdvanCAD / CAE software package developed by GRAITEC that includes three complementary software applications:
STAAD or (STAAD.Pro) is a structural analysis and design software application originally developed by Research Engineers International in 1997. In late 2005, Research Engineers International was bought by Bentley Systems.
Extreme Loading for Structures (ELS) is commercial structural-analysis software based on the applied element method (AEM) for the automatic tracking and propagation of cracks, separation of elements, element collision, and collapse of structures under extreme loads. AEM combines features of Finite element method and Discrete element method simulation with its own solver capabilities for the generation of PC-based structural analysis.

Applied Science International, LLC, aka ASI is a United States-based company headquartered in Raleigh, North Carolina, that provides advanced engineering design and analysis software and services to the DHS, United States Department of Defense, Engineering Firms, Demolition Contractors, and Universities.
ADINA is a commercial engineering simulation software program that is developed and distributed worldwide by ADINA R & D, Inc. The company was founded in 1986 by Dr. Klaus-Jürgen Bathe, and is headquartered in Watertown, Massachusetts, United States.
Simulation modeling is the process of creating and analyzing a digital prototype of a physical model to predict its performance in the real world. Simulation modeling is used to help designers and engineers understand whether, under what conditions, and in which ways a part could fail and what loads it can withstand. Simulation modeling can also help to predict fluid flow and heat transfer patterns. It analyses the approximate working conditions by applying the simulation software.
The PLPAK developers, BE4E, describe it as "The PLPAK is special purpose software package for structural analysis of building slabs and foundations based on the Boundary Element Method". The PLPAK uses the shear-deformable plate bending theory according to Reissner.

VisualFEA is a finite element analysis program running on MS Windows and Mac OS X platforms. The program is being developed and distributed by Intuition Software, Inc. in South Korea, and is used chiefly for structural and geotechnical analysis. The strongest point of the program is its intuitive and user-friendly usage based on graphical pre- and postprocessing capabilities. VisualFEA has educational functions for teaching and learning structural mechanics and finite element analysis through graphical simulation. Thus, this program is widely used in college courses related to structural mechanics and finite element method.

RFEM is a 3D finite element analysis software working under Microsoft Windows computer operating systems. RFEM can be used for structural analysis and design of steel, concrete, timber, glass, membrane and tensile structures as well as for plant and mechanical engineering or dynamic analysis.

Vectorworks, Inc. is a U.S.-based software development company that focuses on CAD and BIM software for the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC), landscape, and entertainment industries. Vectorworks is owned by the Nemetschek Group, a German company.
midas Civil. (2021, March 5). In midasoft.com. https://www.midasoft.com/bridge-library/civil/products/midascivil









