
Carl Wilhelm von Nägeli was a Swiss botanist. He studied cell division and pollination but became known as the man who discouraged Gregor Mendel from further work on genetics. He rejected natural selection as a mechanism of evolution, favouring orthogenesis driven by a supposed "inner perfecting principle".

Sphaeropleales is an order of green algae that used to be called Chlorococcales. The order includes some of the most common freshwater planktonic algae such as Scenedesmus and Pediastrum. The Sphaeropleales includes vegetatively non-motile unicellular, colonial, or filamentous taxa. They have biflagellate zoospores with flagella that are directly opposed in direction : Sphaeroplea, Atractomorpha, Neochloris, Hydrodictyon, and Pediastrum. All of these taxa have basal body core connections. Motile cells generally lack cell walls or have only a very fine layer surrounding the cell membrane. Other common characteristics include a robust vegetative cell wall, cup-shaped chloroplasts with large pyrenoids, and relatively large nuclei.

Pilosella is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae. Some sources include it within the genus Hieracium.
Oocystaceae is a family of green algae, in the order Chlorellales. The type genus is Oocystis.

The Desmidiaceae are one of four families of charophyte green algae in the order Desmidiales (desmids).

The Corallinaceae are one of the two extant Coralline families of red algae; they are differentiated from the morphologically similar Sporolithaceae by their formation of grouped sporangial chambers, clustered into sori. The Corallinoideae is monophyletic; the other subfamilies form another monophyletic group.

The Acarosporaceae are a family of fungi in the order Acarosporales. Members of this family have a widespread distribution, and are mostly lichenized with green algae. According to a 2021 estimate, the family contains 11 genera and about 260 species. The family is characterised by a hamathecium formed of paraphysoids.

Graecoanatolica is a genus of small freshwater snails, aquatic gastropod mollusks in the family Hydrobiidae.
Euryarthron is a genus in the beetle family Cicindelidae. There are more than 20 described species in Euryarthron, found in Africa.

Wrangeliaceae is a red alga family in the order Ceramiales. It was published by J.Agardh in 1851 in his book Species, genera et ordines algarum : seu descriptiones succinctae specierum.

Heppia is a genus of olive, brownish, gray, or blackish squamulose, crustose, or peltate like lichens. Heppia was once the type genus of the family Heppiaceae, but that family was folded into synonymy with Lichinaceae.
Nosema bombycis is a species of Microsporidia of the genus Nosema infecting silkworms, responsible for pébrine. This species was the first microsporidium described, when pebrine decimated silkworms in farms in the mid-19th century. This description was made by Carl Nägeli. Louis Pasteur, taking up an idea of Osimo which had not been successful, showed breeders a practical way to select uninfected individuals to recreate new healthy farms.
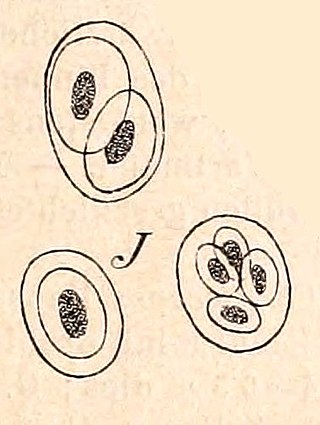
Gloeothece is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Aphanothecaceae.

Aphanothece is a polyphyletic genus with 63 accepted species. The name is derived from the Greek words, ‘aphanes’ and ‘theke’ which mean “invisible" and “box or sheath” respectively. This genera is cosmopolitan, found in soils, thermal springs and other benthic, freshwater, marine, hypersaline, and moist terrestrial environments. Morphology can vary, with both microscopic and macroscopic colonies large enough to be collected and preserved in herbarium records.

Apiocystis is a genus of algae belonging to the family Tetrasporaceae. It is found attached to freshwater aquatic algae or plants. The species of this genus are found in Europe and Northern America, and are widespread but generally uncommon.
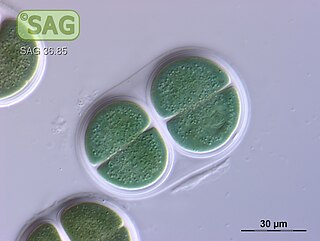
Chroococcus is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Chroococcaceae.

Coelosphaerium is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Merismopediaceae.

Mesotaenium is a genus of algae belonging to the family Mesotaeniaceae.

Netrium is a genus of algae belonging to the family Mesotaeniaceae.
Caeruleum is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Acarosporaceae. Two species are currently recognized, C. heppii and C. immersum. Caeruleum is generally similar to the related genus Acarospora.















