Related Research Articles

The rights of lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) people in the U.S. state of Utah have significantly evolved in the 21st century. Protective laws have become increasingly enacted since 2014, despite the state's reputation as socially conservative and highly religious. Utah's anti-sodomy law was invalidated in 2003 by Lawrence v. Texas, and fully repealed by the state legislature in 2019. Same-sex marriage has been legal since the state's ban was ruled unconstitutional by federal courts in 2014. In addition, statewide anti-discrimination laws now cover sexual orientation and gender identity in employment and housing, and the use of conversion therapy on minors is prohibited. In spite of this, there are still a few differences between the treatment of LGBTQ people and the rest of the population, and the rights of transgender youth are restricted.
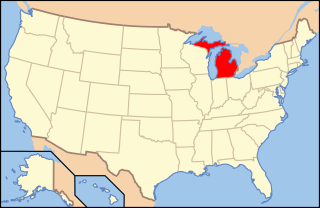
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBTQ) people in the U.S. state of Michigan enjoy the same rights as non-LGBTQ people. Michigan in June 2024 was ranked "the most welcoming U.S. state for LGBT individuals". Same-sex sexual activity is legal in Michigan under the U.S. Supreme Court case Lawrence v. Texas, although the state legislature has not repealed its sodomy law. Same-sex marriage was legalised in accordance with 2015's Obergefell v. Hodges decision. Discrimination on the basis of both sexual orientation and gender identity is unlawful since July 2022, was re-affirmed by the Michigan Supreme Court - under and by a 1976 statewide law, that explicitly bans discrimination "on the basis of sex". The Michigan Civil Rights Commission have also ensured that members of the LGBT community are not discriminated against and are protected in the eyes of the law since 2018 and also legally upheld by the Michigan Supreme Court in 2022. In March 2023, a bill passed the Michigan Legislature by a majority vote - to formally codify both "sexual orientation and gender identity" anti-discrimination protections embedded within Michigan legislation. Michigan Governor Gretchen Whitmer signed the bill on March 16, 2023. In 2024, Michigan repealed “the last ban on commercial surrogacy within the US” - for individuals and couples and reformed the parentage laws, that acknowledges same sex couples and their families with children.
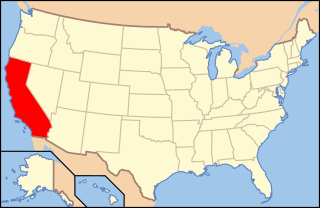
California is seen as one of the most liberal states in the U.S. in regard to lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) rights, which have received nationwide recognition since the 1970s. Same-sex sexual activity has been legal in the state since 1976. Discrimination protections regarding sexual orientation and gender identity or expression were adopted statewide in 2003. Transgender people are also permitted to change their legal gender on official documents without any medical interventions, and mental health providers are prohibited from engaging in conversion therapy on minors.

The state of Washington is seen as one of the most progressive states in the U.S. in regard to lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and queer (LGBTQ) rights; with jurisprudence having evolved significantly since the late 20th century. Same-sex sexual activity was legalized in 1976. LGBTQ people are fully protected from discrimination in the areas of employment, housing and public accommodations; the state enacting comprehensive anti-discrimination legislation regarding sexual orientation and gender identity in 2006. Same-sex marriage has been legal since 2012, and same-sex couples are allowed to adopt. Conversion therapy on minors has also been illegal since 2018.
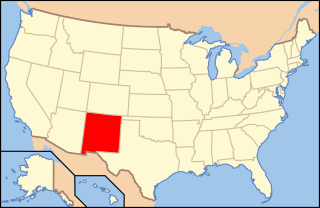
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) people in the U.S. state of New Mexico enjoy the same rights as non-LGBTQ people. New Mexico has seen prominent advances in gay and lesbian rights in recent decades. Same-sex sexual activity has been legal since 1975. Same-sex marriage is legal statewide in New Mexico, as is adoption and access to fertility treatments for lesbian couples. Same-sex couples have had the same rights as heterosexual married couples since 2013. Discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation and gender identity is banned statewide in the areas of employment, housing and public accommodations. Additionally, conversion therapy on minors is prohibited in the state.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) people in the U.S. state of Kentucky still face some legal challenges not experienced by other people. Same-sex sexual activity in Kentucky has been legally permitted since 1992, although the state legislature has not repealed its sodomy statute for same-sex couples. Same-sex marriage is legal in Kentucky under the U.S. Supreme Court ruling in Obergefell v. Hodges. The decision, which struck down Kentucky's statutory and constitutional bans on same-sex marriages and all other same-sex marriage bans elsewhere in the country, was handed down on June 26, 2015.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) people in the U.S. state of Mississippi face legal challenges and discrimination not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. LGBT rights in Mississippi are limited in comparison to other states. Same-sex sexual activity is legal in Mississippi as a result of the U.S. Supreme Court decision in Lawrence v. Texas. Same-sex marriage has been recognized since June 2015 in accordance with the Supreme Court's decision in Obergefell v. Hodges. State statutes do not address discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation and gender identity; however, the U.S. Supreme Court's ruling in Bostock v. Clayton County established that employment discrimination against LGBTQ people is illegal under federal law. The state capital Jackson and a number of other cities provide protections in housing and public accommodations as well.
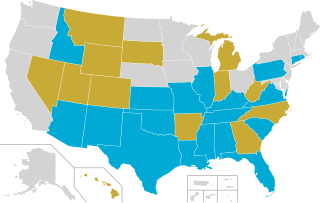
State Religious Freedom Restoration Acts are state laws based on the Religious Freedom Restoration Act (RFRA), a federal law that was passed almost unanimously by the U.S. Congress in 1993 and signed into law by President Bill Clinton. The laws mandate that religious liberty of individuals can only be limited by the "least restrictive means of furthering a compelling government interest". Originally, the federal law was intended to apply to federal, state, and local governments. In 1997, the U.S. Supreme Court in City of Boerne v. Flores held that the Religious Freedom Restoration Act only applies to the federal government but not states and other local municipalities within them. As a result, 21 states have passed their own RFRAs that apply to their individual state and local governments.
Kansas House Bill 2453, also known as the Religious Freedom Act, is a piece of legislation proposed in the state of Kansas that would allow people to refuse to provide services in any way related to any relationship under the name "marriage, domestic partnership, civil union or similar arrangement" if their objection to doing so is based on their religious beliefs. Representative Charles Macheers (R-Shawnee) introduced the legislation on January 16, 2014. It passed in the House but was not taken up by the Kansas Senate.
Arizona SB 1062 was an Arizona bill to amend an existing law to give any individual or legal entity an exemption from any state law if it substantially burdened their exercise of religion, including Arizona law requiring public accommodation.
Indiana Senate Bill 101, titled the Religious Freedom Restoration Act (RFRA), is a law in the U.S. state of Indiana, which allows individuals and companies to assert as a defense in legal proceedings that their exercise of religion has been, or is likely to be, substantially burdened.
Arkansas HB 1228, also known as the Conscience Protection Act and the Religious Freedom Restoration Act, is a law in the state of Arkansas that aims to increase "judicial scrutiny" in cases involving religious beliefs. Opponents of the law say that it will allow for lawful discrimination of LGBT people. The law was passed by the Arkansas Senate on March 31, 2015. The next day, Governor Asa Hutchinson announced he would not sign the bill as written, instructing the legislature to make changes to its language. The final version was passed and signed into law as Act 975.
The state of North Dakota has improved in its treatment of lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender residents in the late 1990s and into the 21st Century, when the LGBT community began to openly establish events, organizations and outlets for fellow LGBT residents and allies, and increase in political and community awareness.
The First Amendment Defense Act was a bill introduced into the United States House of Representatives and United States Senate on June 17, 2015. The Senate sponsor of the bill was Mike Lee (R-Utah), and the House sponsor was Raúl Labrador (R-Idaho). The bill aimed to prevent the federal government from taking action against a person on the basis that such person believes or acts in accordance with a religious belief or moral conviction that: (1) marriage is or should be recognized as the union of one man and one woman, or (2) sexual relations are properly reserved to such a marriage.

Mississippi House Bill 1523, also called the Religious Liberty Accommodations Act or Protecting Freedom of Conscience from Government Discrimination Act, is 2016 state legislation passed in direct response to federal rulings in support of same-sex marriage. MS H.B. 1523 provides protections for persons, religious organizations, and private associations who choose to provide or withhold services discriminatorily in accordance to the three "deeply held religious beliefs or moral convictions" which are specifically outlined in the bill. These protected beliefs are 1) that marriage is and should be an exclusively heterosexual union, 2) sex should not occur outside of marriage, and 3) that biologically-assigned sex is objective and immutably linked to gender.
The Mississippi Student Religious Liberties Act of 2013 is a 2013 act which protects the views of students in any educational institution from being reprimanded for their religious views. Under the bill, a school may not discipline a student for expressing anti-LGBT views either verbally or through written assignments.
Senate Bill 297 is a 2015 Utah anti-LGBT act that allows for an exemption for individuals, religious officials, religious organizations, and government officers and employees who object to participating to issuing marriage licenses for marriages they object to based on "deeply held beliefs about marriage, family, and sexuality."
Senate Bill 149, officially called An Act to provide certain protections to faith-based or religious child-placement agencies, is a 2017 anti-LGBT law that was enacted in the state of South Dakota that permits taxpayer-funded agencies to deny services on the basis of religious exemptions.
Child Placing Agency Inclusion Act is a 2017 anti-LGBT law that was enacted in the U.S. state of Alabama that permits taxpayer-funded adoption agencies to deny services on the basis of religious exemptions.
Utah Senate Bill 296 is a law passed by the Utah State Legislature and signed into law by Governor Gary Herbert in 2015. SB 296 amended the 1997 Utah Antidiscrimination Act to add sexual orientation and gender identity as protected classes under state law when it comes to housing and employment. The law was described by various news outlets and commentators as the "Utah Compromise".
References
- 1 2 Mississippi Legislature 2014 Regular Session Senate Bill 2681 Archived 2014-02-21 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "Mississippi Passed Its Anti-Gay Segregation Bill". Slate. 2 April 2014. Retrieved April 4, 2014.
- ↑ "So-Called "Religious Freedom" Bill Passes Mississippi State Legislature". Archived from the original on 2016-03-11. Retrieved 2016-04-06.
- ↑ Evans, Woody (December 12, 2019). "'Faith' is Inadequate and Dangerous Cover for Racism". Jackson Free Press .