
Pemba Island is a Tanzanian island forming part of the Zanzibar Archipelago, lying within the Swahili Coast in the Indian Ocean.

The Tongoni Ruins are a 15th century Swahili ruins of a mosque and forty tombs located in Tongoni ward in Tanga District inside Tanga Region of Tanzania. The largest and possibly most significant Swahili site in Tanzania is Tongoni, which is located 25 km north of the Pangani River. Overlooking Mtangata Bay, about forty standing tombs and a Friday mosque of the "northern" style occupy a third of a hectare. People from the area continue to worship there spiritually. They bury their departed family members to the south of the historic tombs. The area was a different place four to five centuries ago. Contrary to its almost unnoticed presence today, it was a prosperous and a respected Swahili trading centre during the 15th century. Most of the ruins are still not yet been uncovered. The site is a registered National Historic Site.

Tumbatu is a historic Swahili settlement located on Tumbatu Island, Kaskazini A District of Unguja North Region in Tanzania. This site is a significant archaeological site that contains a large number of collapsed coral stone structures including private houses and several mosques, the largest of which is located on the shore facing the village of Mkokotoni on Unguja. Pearce initially looked into the ruins in 1915 and wrote about the mosques, palace, and other stone homes.
Chambani is a historic site and village located in Mkoani District of Pemba South Region. Its one of several National Historic sites on the island of Pemba. The site is located nine kilometres south of Chake-Chake, close to several sets of ruins, notably the Pujini Ruins, a 15th-century citadel, located close to the village of Pujini, two kilometres to the north.
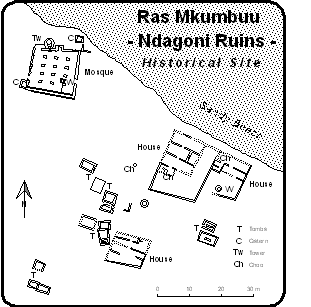
Ras Mkumbuu Ruins are located in Chake Chake district of South Pemba Region. They lie close to the village of Ndagoni at the end of a long narrow peninsula known as Ras Mkumbuu, which lies to the northwest of the town of Chake-Chake. The ruins mainly date from the 9th century CE and were abandoned in the 16th century, though there are indications that they were built over older foundations. Notable among these ruins are those of a large mosque which was for some time the largest structure of its type in sub-Saharan Africa. James Kirkman, the first archeologist to excavate here in the 1950s, proposed to connect his findings with the "Qanbalu" mentioned by the Arab explorer Al-Masudi around 900 but could not identify remnants earlier than the 13th century . A possible identification of Pemba Island as a whole and especially Ras Mkumbuu with Qanbalu is still discussed.

Pemba Island is a large coral island off the coast of Tanzania. Inhabited by Bantu settlers from the Tanga coast since 600 AD, the island has a rich trading, agricultural, and religious history that has contributed to the studies of the Swahili Coast trade throughout the Indian Ocean.

National Historic Sites of Tanzania is an official list of places in Tanzania that have been designated as National Historic Sites as per the Ministry of Natural Resources and Tourism of Tanzania under the Antiquities Division. The list is not complete and is currently being updated.

Mkama Ndume Ruins was a medieval Swahili settlement palace ruins located in Chake Chake District of Pemba South Region that was abandoned in the 16th Century prior to Portuguese arrival and is known for its fortification. The site is located 10 km (6.2 mi) east of the town of Chake-Chake. The settlement was ruled by a leader named Mohammed bin Abdul Rahman, who was known for his cruelty towards his subjects thus earned his infamous nickname Mkama Ndume meaning milker of men in old Swahili. The settlement ruins bear this nickname.
Sanje ya Kati is a protected, uninhabited historic site located on Sanje ya Kati Island in Pande Mikoma ward in Kilwa District, Lindi Region of Tanzania's Indian Ocean coast. The site is home to medieval Swahili ruins that have yet to be fully excavated.

Pujini Ruins is a Medieval historic site next to the village of Pujini located in Chake Chake District of Pemba South Region. There used to be a fortified palace at the site, only ruins of the walls remain. The palace is believed to have been of Mkame Mdume. Its one of several National Historic Sites on the island of Pemba including Chambani and Ras Mkumbuu.

Chwaka is a medieval Swahili historic site next to the village of Chwaka located in Micheweni District of Pemba North Region, Tanzania. There is an excavated Swahili mosque on the site. The location of these ruins is 6 km (3.7 mi) from the small town of Konde, at the end of a trail that extends 900 m (3,000 ft) in the direction of the village of Tumbe on the way to the village of Myumoni.
Mtambwe Kuu or Mtambwe Mkuu is a Medieval Swahili historic site located in Chake Chake District of Pemba North Region. A town wall, a mosque, tombs, and residences are among the several stone constructions at the Mtambwe Mkuu site in northwest Pemba. The oldest indications of occupation date from the eleventh century and persisted successfully and unbrokenly until the fifteenth century. It was once again occupied in the nineteenth century. A cache of over 2,000 gold and silver coins from the 10 and eleventh centuries were found during an excavation at the location, demonstrating Pemba's Swahili involvement in the regional trade networks at the time.
Tumbe is an early Medieval Swahili historic site next to the village of Tumbe located in Micheweni District of Pemba North Region. Between 600 and 1000 AD, the city of Tumbe served as the island's primary location. There is sufficient evidence that this city served as a major commerce hub for the Indian Ocean. Smaller sites from the eighth to tenth centuries AD were grouped together around the major metropolis.
Shamiani is a protected historic site located inside Mkoani District of Pemba South Region in Tanzania. The site is home to partially excavated, abandoned medieval Swahili ruins with a brief occupation period from about 14th to 16th century.

Msuka Mjini Ruins is a protected historic site located inside Micheweni District of Pemba North Region in Tanzania. Msuka Mjini has a Swahili mosque from the fifteenth century preserved in ruins on the Kigomasha peninsula on the island. The date 816AH is carved on the interior of the circular mirhab.
Kichokochwe is protected historic site located inside Wete District of Pemba North Region in Tanzania. The site is home to partially excavated abandoned late medieval Swahili ruins, with a mosque and tombs.
Mduuni Ruins is a protected historic site located inside Micheweni District of Pemba North Region in Tanzania. The settlement was established around 1100 CE.

Kunduchi is a Medieval Swahili National Historic Site located in Kunduchi ward, located in Kinondoni District of Dar es Salaam Region in Tanzania. There is an excavated 15th-century mosque on the site. An 18th-century cemetery with the biggest collection of pillared tombs in East Africa, situated in a baobab woodland, and embellished with Ming era's porcelain plates. The pottery discovered here demonstrates the medieval town's affluence and trading connections with imperial China.

Mbuamaji or sometimes spelled Mbwamaji is a Medieval Swahili, National Historic Site located in Somangila ward of Kigamboni District in Dar es Salaam Region of Tanzania. Despite years of neglect that resulted in vandalism, the Tanzanian government is aiming to start restoration efforts as soon as possible.












