Tuskegee Airmen National Historic Site, at Moton Field in Tuskegee, Alabama, commemorates the contributions of African-American airmen in World War II. Moton Field was the site of primary flight training for the pioneering pilots known as the Tuskegee Airmen, and is now operated by the National Park Service to interpret their history and achievements. It was constructed in 1941 as a new training base. The field was named after former Tuskegee Institute principal Robert Russa Moton, who died the previous year.

Tuscaloosa National Airport is 3.5 miles northwest of Tuscaloosa, in Tuscaloosa County, Alabama. The airport is owned and operated by the City of Tuscaloosa. The FAA's National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2019–2023 categorized the airport as a general aviation facility. The City of Tuscaloosa changed the name of the airport that had formerly operated under the name Tuscaloosa Regional Airport, in March 2019, to reflect the FAA's official designation as a national airport, one of only 89 in the nation.

Sharpe Field is a private use airport located six nautical miles (11 km) northwest of the central business district of Tuskegee, a city in Macon County, Alabama, United States. This airport is privately owned by the Bradbury Family Partnership.

Gila Bend Air Force Auxiliary Field is a United States Air Force auxiliary airfield used as an emergency landing facility by Luke Air Force Base and Davis-Monthan Air Force Base aircraft and units from other nearby bases using the Barry M. Goldwater Air Force Range complex. The airfield is located 3.5 miles south of Interstate 8 and the central business district of Gila Bend, in Maricopa County, Arizona, United States.

Cross City Air Force Station is a former United States Air Force facility, located 1.6 miles (2.6 km) east of Cross City, Florida.
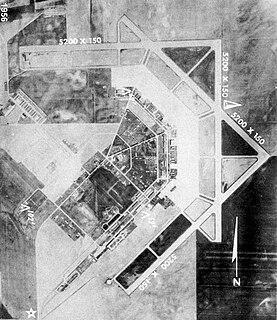
George Field is a former World War II military airfield, located 5 miles east-northeast of Lawrenceville, Illinois. It operated as an advanced pilot training school for the United States Army Air Forces from 1942 until 1945.
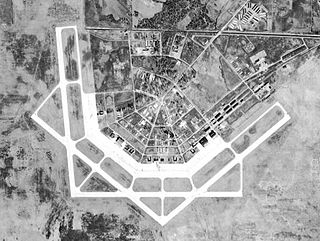
Courtland Army Airfield is a former United States Army facility located two nautical miles northeast of the central business district of Courtland, a town in Lawrence County, Alabama, United States.

Taylor Field is a closed military airfield located 11 miles east-southeast of Montgomery, Alabama. It was one of thirty-two Air Service training camps established after the United States entry into World War I in April 1917.
Danville Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Danville, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Courtland Army Air Field, it was turned into Danville Airport following the war, and was eventually closed between 1986 and 1989. No trace of the airfield remains.
Trinity Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Trinity, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Courtland Army Air Field, it was turned back into farmland after the war.
Bay Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Courtland, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Courtland Army Air Field, it was converted back into farmland after the war.
Leighton Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Leighton, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Courtland Army Air Field, it was turned back into farmland after the war.
Furniss Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Orrville, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Craig Field, it was turned back into farmland after the war.
Autaugaville Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Autaugaville, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Craig and Maxwell Fields, it was turned back into farmland after the war.
McLemore Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Montgomery, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Craig Field, it was turned back into farmland after the war.
Elmore Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Montgomery, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Gunter Field, it was redeveloped into Wetumpka Municipal Airport after the war.
Mount Meigs Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Montgomery, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Gunter Field, it was turned back into farmland after the war.
Deatsville Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Montgomery, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Gunter Field, it was turned back into farmland after the war.
Passmore Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Prattville, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Maxwell Field, it was turned back into farmland after the war.
Troy Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Troy, Alabama. Constructed after 1942 as an auxiliary to the nearby Maxwell Field, it was turned into Troy Municipal Airport after the war.