
Pteridospermatophyta, also called "pteridosperms" or "seed ferns" are a polyphyletic grouping of extinct seed-producing plants. The earliest fossil evidence for plants of this type are the lyginopterids of late Devonian age. They flourished particularly during the Carboniferous and Permian periods. Pteridosperms declined during the Mesozoic Era and had mostly disappeared by the end of the Cretaceous Period, though Komlopteris seem to have survived into Eocene times, based on fossil finds in Tasmania.

The euphyllophytes are a clade of plants within the tracheophytes. The group may be treated as an unranked clade, a division under the name Euphyllophyta or a subdivision under the name Euphyllophytina. The euphyllophytes are characterized by the possession of true leaves ("megaphylls"), and comprise one of two major lineages of extant vascular plants. As shown in the cladogram below, the euphyllophytes have a sister relationship to the lycopodiophytes or lycopsids. Unlike the lycopodiophytes, which consist of relatively few presently living or extant taxa, the euphyllophytes comprise the vast majority of vascular plant lineages that have evolved since both groups shared a common ancestor more than 400 million years ago. The euphyllophytes consist of two lineages, the spermatophytes or seed plants such as flowering plants (angiosperms) and gymnosperms, and the Polypodiophytes or ferns, as well as a number of extinct fossil groups.

Caytonia is an extinct genus of seed ferns.

Sagenopteris is a genus of extinct seed ferns from the Triassic to late Early Cretaceous.

A seed plant or spermatophyte, also known as a phanerogam or a phaenogam, is any plant that produces seeds. It is a category of embryophyte that includes most of the familiar land plants, including the flowering plants and the gymnosperms, but not ferns, mosses, or algae.
The Westphalian is a regional stage or age in the regional stratigraphy of northwest Europe, with an age between roughly 315 and 307 Ma. It is a subdivision of the Carboniferous System or Period and the regional Silesian Series. The Westphalian is named for the region of Westphalia in western Germany where strata of this age occur. The Coal Measures of England and Wales are also largely of Westphalian age, though they also extend into the succeeding Stephanian.

Dicroidium is an extinct genus of fork-leaved seed plants. It is the archetypal genus of the corystosperms, an extinct group of seed plants, often called "seed ferns", assigned to the order Corystospermales or Umkomasiales. Species of Dicroidium were widely distributed and dominant over Gondwana during the Triassic. Their fossils are known from South Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, Australia, New Zealand, South America, Madagascar, the Indian subcontinent and Antarctica.
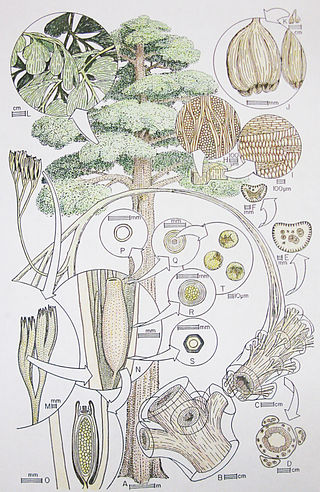
Callistophytales is an extinct order of spermatophytes which lived from the Pennsylvanian to Permian periods. They were mainly scrambling and lianescent (vine-like) plants found in the wetland "coal swamps" of Euramerica and Cathaysia. Like many other early spermatophytes, they could be described as "seed ferns", combining ovule-based reproduction with pinnate leaves superficially similar to modern ferns.

The Callistophytaceae was a family of seed ferns (pteridosperms) from the Carboniferous and Permian periods. They first appeared in late Middle Pennsylvanian (Moscovian) times, 306.5–311.7 million years ago (Ma) in the tropical coal forests of Euramerica, and became an important component of Late Pennsylvanian vegetation of clastic soils and some peat soils. The best known callistophyte was documented from Late Pennsylvanian coal ball petrifactions in North America.
Emplectopteridaceae is an extinct family of pteridosperms known mainly from Permian floras of the Cathaysian Realm. They were mostly shrubby plants with a scrambling or upright habit, and favoured a range of habitats from arid to moist or even aquatic.

Umkomasia is a genus of seed bearing organs produced by corystosperm seed ferns, first based on fossils collected by Hamshaw Thomas from the Burnera Waterfall locality near the Umkomaas River of South Africa. He recognized on the basis of cuticular similarities that the same plant produced pollen organs Pteruchus and the leaves Dicroidium. Various other corystosperm seed bearing organs from the Jurassic and Cretaceous have been assigned to this genus, but recently have been given distinct genera, with Umkomasia being restricted to the Triassic.

Umkomasia macleanii is an ovulate structure of a seed fern (Pteridospermatophyta and the nominate genus of Family Umkomasiaceae. It was first described by Hamshaw Thomas from the Umkomaas locality of South Africa.

Pteruchus africanus is a pollen organ of a seed fern (Pteridospermatophyta). It was first described by Hamshaw Thomas from the Umkomaas locality of South Africa.

Pteruchus is a form genus for pollen organs of the seed fern (Pteridospermatophyta family Umkomasiaceae. It was first described by Hamshaw Thomas from the Umkomaas locality of South Africa. It is associated with the seed bearing organs Umkomasia and Dicroidium leaves.
Lyginopteridaceae is an extinct family of plants (Pteridospermatophyta) in North America and European Carboniferous coal measures.

Caytonia nathorstii is an extinct species of seed ferns.

Dictyopteridiaceae are an extinct family of glossopterid plants known from the Permian period. It generally refers to reproductive organs, which are associated with Glossopteris leaves.
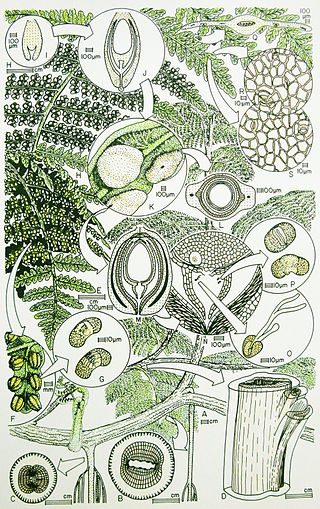
Stamnostoma is an extinct genus of seed ferns based on cupules with seeds. These are among the earliest known seed plants and of earliest Carboniferous (Tournaisian) age.

Dictyopteridium is an extinct genus of plants belonging to Glossopteridaceae, but the name is used only for compression fossils of elongate multiovulate reproductive structures adnate to Glossopteris leaves. Permineralized remains identical to Dictyopteridium have been referred to the organ genus Homevaleia

Lagenostoma is a genus of seed ferns (Pteridospermatophyta), based on ovules preserved in coal balls from the Six Inch Coal of the Hough Hill Colliery near Stalybridge, England. Distinctive stalked glands enabled Oliver and Scott to attribute these seeds to fernlike foliage of Sphenopteris hoeningshauseni in the same coal balls. This was the first recognition that some Carboniferous fernlike leaves had seeds, and so were not pteridophytes, but rather Pteridospermatophyta, or seed ferns. The realization that seed plants as well as spore plants had fernlike leaves was a major contribution to the evolutionary history of plants.












