
Paleobotany, also spelled as palaeobotany, is the branch of botany dealing with the recovery and identification of plant remains from geological contexts, and their use for the biological reconstruction of past environments (paleogeography), and the evolutionary history of plants, with a bearing upon the evolution of life in general. A synonym is paleophytology. It is a component of paleontology and paleobiology. The prefix palaeo- or paleo- means "ancient, old", and is derived from the Greek adjective παλαιός, palaios. Paleobotany includes the study of terrestrial plant fossils, as well as the study of prehistoric marine photoautotrophs, such as photosynthetic algae, seaweeds or kelp. A closely related field is palynology, which is the study of fossilized and extant spores and pollen.

In seed plants, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells. It consists of three parts: the integument, forming its outer layer, the nucellus, and the female gametophyte in its center. The female gametophyte — specifically termed a megagametophyte — is also called the embryo sac in angiosperms. The megagametophyte produces an egg cell for the purpose of fertilization. The ovule is a small structure present in the ovary. It is attached to the placenta by a stalk called a funicle. The funicle provides nourishment to the ovule. On the basis of the relative position of micropyle, body of the ovule, chalaza and funicle, there are six types of ovules.

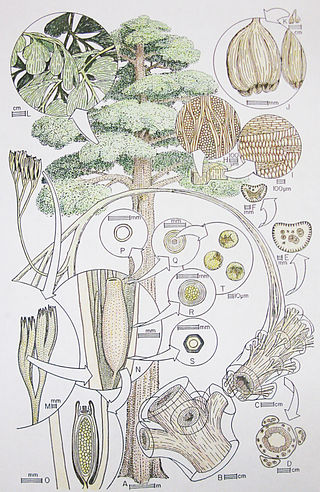
Pteridospermatophyta, also called "pteridosperms" or "seed ferns" are a polyphyletic grouping of extinct seed-producing plants. The earliest fossil evidence for plants of this type are the lyginopterids of late Devonian age. They flourished particularly during the Carboniferous and Permian periods. Pteridosperms declined during the Mesozoic Era and had mostly disappeared by the end of the Cretaceous Period, though Komlopteris seem to have survived into Eocene times, based on fossil finds in Tasmania.

The Caytoniales are an extinct order of seed plants known from fossils collected throughout the Mesozoic Era, around 252 to 66 million years ago. They are regarded as seed ferns because they are seed-bearing plants with fern-like leaves. Although at one time considered angiosperms because of their berry-like cupules, that hypothesis was later disproven. Nevertheless, some authorities consider them likely ancestors or close relatives of angiosperms. The origin of angiosperms remains unclear, and they cannot be linked with any known seed plants groups with certainty.

Caytonia is an extinct genus of seed ferns.

Sagenopteris is a genus of extinct seed ferns from the Triassic to late Early Cretaceous.

The Medullosales is an extinct order of pteridospermous seed plants characterised by large ovules with circular cross-section and a vascularised nucellus, complex pollen-organs, stems and rachides with a dissected stele, and frond-like leaves. Their nearest still-living relatives are the cycads.

The Lyginopteridales are an extinct group of seed plants known from the Paleozoic. They were the first plant fossils to be described as pteridosperms and, thus, the group on which the concept of pteridosperms was first developed; they are the stratigraphically oldest-known pteridosperms, occurring first in late Devonian strata; and they have the most primitive features, most notably in the structure of their ovules. They probably evolved from a group of Late Devonian progymnosperms known as the Aneurophytales, which had large, compound frond-like leaves. The Lyginopteridales became the most abundant group of pteridosperms during Mississippian times, and included both trees and smaller plants. During early and most of middle Pennsylvanian times the Medullosales took over as the more important of the larger pteridosperms but the Lyginopteridales continued to flourish as climbing (lianescent) and scrambling plants. However, later in Middle Pennsylvanian times the Lyginopteridales went into serious decline, probably being out-competed by the Callistophytales that occupied similar ecological niches but had more sophisticated reproductive strategies. A few species continued into Late Pennsylvanian times, and in Cathaysia and east equatorial Gondwana they persisted into the Late Permian, but subsequently became extinct. Most evidence of the Lyginopteridales suggests that they grew in tropical latitudes of the time, in North America, Europe and China.

Dicroidium is an extinct genus of fork-leaved seed plants. It is the archetypal genus of the corystosperms, an extinct group of seed plants, often called "seed ferns", assigned to the order Corystospermales or Umkomasiales. Species of Dicroidium were widely distributed and dominant over Gondwana during the Triassic. Their fossils are known from South Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, Australia, New Zealand, South America, Madagascar, the Indian subcontinent and Antarctica.
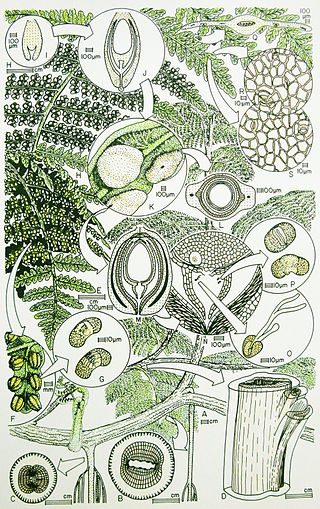
The Callistophytaceae was a family of seed ferns (pteridosperms) from the Carboniferous and Permian periods. They first appeared in late Middle Pennsylvanian (Moscovian) times, 306.5–311.7 million years ago (Ma) in the tropical coal forests of Euramerica, and became an important component of Late Pennsylvanian vegetation of clastic soils and some peat soils. The best known callistophyte was documented from Late Pennsylvanian coal ball petrifactions in North America.

Lepidopteris is a form genus for leaves of Peltaspermaceae, an extinct family of seed plants, which lived from around 260 to 190 million years ago, from the Late Permian to Early Jurassic. Fossils of the genus have been found across both hemispheres. Nine species are currently recognized.Lepidopteris was a common and widespread seed fern, which survived the Permian-Triassic extinction event but was largely wiped out by the Triassic-Jurassic extinction event. Lepidopteris callipteroides is especially common between the first two episodes of the Permian-Triassic extinction event, and L. ottonis forms a comparable acme zone immediately before the Triassic-Jurassic extinction event. Lepidopteris would persist into the Early Jurassic in Patagonia, represented by the species Lepidopteris scassoi.

Umkomasia is a genus of seed bearing organs produced by corystosperm seed ferns, first based on fossils collected by Hamshaw Thomas from the Burnera Waterfall locality near the Umkomaas River of South Africa. He recognized on the basis of cuticular similarities that the same plant produced pollen organs Pteruchus and the leaves Dicroidium. Various other corystosperm seed bearing organs from the Jurassic and Cretaceous have been assigned to this genus, but recently have been given distinct genera, with Umkomasia being restricted to the Triassic.

Umkomasia macleanii is an ovulate structure of a seed fern (Pteridospermatophyta and the nominate genus of Family Umkomasiaceae. It was first described by Hamshaw Thomas from the Umkomaas locality of South Africa.

Pteruchus africanus is a pollen organ of a seed fern (Pteridospermatophyta). It was first described by Hamshaw Thomas from the Umkomaas locality of South Africa.

Pteruchus is a form genus for pollen organs of the seed fern (Pteridospermatophyta family Umkomasiaceae. It was first described by Hamshaw Thomas from the Umkomaas locality of South Africa. It is associated with the seed bearing organs Umkomasia and Dicroidium leaves.
Moresnetiaceae is a natural family of seed ferns in the Division Pteridospermatophyta that appears in the North American and European Devonian to Carboniferous coal measures.

Caytonia nathorstii is an extinct species of seed ferns.

Dictyopteridium is an extinct genus of plants belonging to Glossopteridaceae, but the name is used only for compression fossils of elongate multiovulate reproductive structures adnate to Glossopteris leaves. Permineralized remains identical to Dictyopteridium have been referred to the organ genus Homevaleia

Lagenostoma is a genus of seed ferns (Pteridospermatophyta), based on ovules preserved in coal balls from the Six Inch Coal of the Hough Hill Colliery near Stalybridge, England. Distinctive stalked glands enabled Oliver and Scott to attribute these seeds to fernlike foliage of Sphenopteris hoeningshauseni in the same coal balls. This was the first recognition that some Carboniferous fernlike leaves had seeds, and so were not pteridophytes, but rather Pteridospermatophyta, or seed ferns. The realization that seed plants as well as spore plants had fernlike leaves was a major contribution to the evolutionary history of plants.

Komlopteris is an extinct genus of "seed fern" with possible corystosperm affinities. Fossils have been found across both hemispheres, dating from the latest Triassic to the early Eocene (Ypresian), making it the youngest "seed fern" in the fossil record.



















