Related Research Articles

The Motorola 68000 is a 16/32-bit complex instruction set computer (CISC) microprocessor, introduced in 1979 by Motorola Semiconductor Products Sector.

The Motorola 68020 is a 32-bit microprocessor from Motorola, released in 1984. A lower-cost version was also made available, known as the 68EC020. In keeping with naming practices common to Motorola designs, the 68020 is usually referred to as the "020", pronounced "oh-two-oh" or "oh-twenty".

The 68HC11 is an 8-bit microcontroller family introduced by Motorola Semiconductor in 1984. It descended from the Motorola 6800 microprocessor by way of the 6801. The 68HC11 devices are more powerful and more expensive than the 68HC08 microcontrollers and are used in automotive applications, barcode readers, hotel card key writers, amateur robotics, and various other embedded systems. The MC68HC11A8 was the first microcontroller to include CMOS EEPROM.
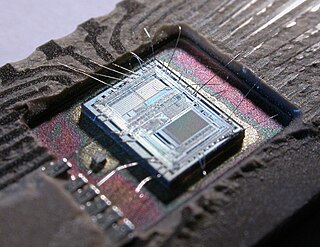
A microcontroller or microcontroller unit (MCU) is a small computer on a single integrated circuit. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Program memory in the form of NOR flash, OTP ROM, or ferroelectric RAM is also often included on the chip, as well as a small amount of RAM. Microcontrollers are designed for embedded applications, in contrast to the microprocessors used in personal computers or other general-purpose applications consisting of various discrete chips.

PowerPC is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) created by the 1991 Apple–IBM–Motorola alliance, known as AIM. PowerPC, as an evolving instruction set, has been named Power ISA since 2006, while the old name lives on as a trademark for some implementations of Power Architecture–based processors.

The Motorola DSP56000 is a family of digital signal processor (DSP) chips produced by Motorola Semiconductor starting in 1986 with later models are still being produced in the 2020s. The 56k series was intended mainly for embedded systems doing signal processing, but was also quite popular for a time in a number of computers, including the NeXT, Atari Falcon030 and SGI Indigo workstations all using the 56001. Upgraded 56k versions are still used today in audio equipment, radar systems, communications devices and various other embedded DSP applications. The 56000 was also used as the basis for the updated 96000, which was not commercially successful.
PowerPC G4 is a designation formerly used by Apple to describe a fourth generation of 32-bit PowerPC microprocessors. Apple has applied this name to various processor models from Freescale, a former part of Motorola. Motorola and Freescale's proper name of this family of processors is PowerPC 74xx.

The 68HC12 is a microcontroller family from Motorola Semiconductor. Originally introduced in the mid-1990s, the architecture is an enhancement of the Freescale 68HC11. Programs written for the HC11 are usually compatible with the HC12, which has a few extra instructions. The first 68HC12 derivatives had a maximum bus speed of 8 MHz and flash memory sizes up to 128 KB.

The M6800 Microcomputer System was a series of 8-bit microprocessors and microcontrollers from Motorola that began with the 6800 CPU. The architecture also inspired the MOS Technology 6502, and that company started in the microprocessor business producing 6800 replacements.
ARM9 is a group of 32-bit RISC ARM processor cores licensed by ARM Holdings for microcontroller use. The ARM9 core family consists of ARM9TDMI, ARM940T, ARM9E-S, ARM966E-S, ARM920T, ARM922T, ARM946E-S, ARM9EJ-S, ARM926EJ-S, ARM968E-S, ARM996HS. Since ARM9 cores were released from 1998 to 2006, they are no longer recommended for new IC designs, instead ARM Cortex-A, ARM Cortex-M, ARM Cortex-R cores are preferred.

PSoC is a family of microcontroller integrated circuits by Cypress Semiconductor. These chips include a CPU core and mixed-signal arrays of configurable integrated analog and digital peripherals.
RS08 is a family of 8-bit microcontrollers by NXP Semiconductors. Originally released by Freescale in 2006, the RS08 architecture is a reduced-resource version of the Freescale MC68HCS08 central processing unit (CPU), a member of the 6800 microprocessor family. It has been implemented in several microcontroller devices for embedded systems.
Background debug mode (BDM) interface is an electronic interface that allows debugging of embedded systems. Specifically, it provides in-circuit debugging functionality in microcontrollers. It requires a single wire and specialized electronics in the system being debugged. It appears in many Freescale Semiconductor products. Background commands are categorized into two types: Non-intrusive commands and Active background commands. Non-intrusive commands can be issued while the user program is running, which include memory access commands.
The 68HC08 is a broad family of 8-bit microcontrollers from Motorola Semiconductor.
In computer architecture, 16-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 16 bits wide. Also, 16-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on registers, address buses, or data buses of that size. 16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.

The ARM Cortex-M is a group of 32-bit RISC ARM processor cores licensed by ARM Limited. These cores are optimized for low-cost and energy-efficient integrated circuits, which have been embedded in tens of billions of consumer devices. Though they are most often the main component of microcontroller chips, sometimes they are embedded inside other types of chips too. The Cortex-M family consists of Cortex-M0, Cortex-M0+, Cortex-M1, Cortex-M3, Cortex-M4, Cortex-M7, Cortex-M23, Cortex-M33, Cortex-M35P, Cortex-M52, Cortex-M55, Cortex-M85. A floating-point unit (FPU) option is available for Cortex-M4 / M7 / M33 / M35P / M52 / M55 / M85 cores, and when included in the silicon these cores are sometimes known as "Cortex-MxF", where 'x' is the core variant.
Communications Processor Module (CPM) is a component of Motorola 68000 family (QUICC) or Motorola/Freescale Semiconductor PowerPC/Power ISA (PowerQUICC) microprocessors designed to provide features related to imaging and communications. A microprocessor can delegate most of the input/output processing to the Communications Processor Module and the microprocessor does not have to perform those functions itself. Some input/output functions require quick response from the processor, for example due to precise timing requirements during data transmission. With CPM performing those operations, the main microprocessor is free to perform other tasks.
References
- ↑ Freescale Semiconductor, Inc., M68HC16 Family CPU16 Reference Manual. "M68HC16 Family CPU16 Reference Manual" (PDF).
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ↑ o, Internet archive (1993). "components :: motorola :: 68HC16 :: Motorola 68HC16Y1 Users Manual 1993".
- ↑ o, Analog devices. "68HC16MODULE".