
A bean is the seed of several plants in the family Fabaceae, which are used as vegetables for human or animal food. They can be cooked in many different ways, including boiling, frying, and baking, and are used in many traditional dishes throughout the world.

Dopamine is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine constitutes about 80% of the catecholamine content in the brain. It is an amine synthesized by removing a carboxyl group from a molecule of its precursor chemical, L-DOPA, which is synthesized in the brain and kidneys. Dopamine is also synthesized in plants and most animals. In the brain, dopamine functions as a neurotransmitter—a chemical released by neurons to send signals to other nerve cells. Neurotransmitters are synthesized in specific regions of the brain, but affect many regions systemically. The brain includes several distinct dopamine pathways, one of which plays a major role in the motivational component of reward-motivated behavior. The anticipation of most types of rewards increases the level of dopamine in the brain, and many addictive drugs increase dopamine release or block its reuptake into neurons following release. Other brain dopamine pathways are involved in motor control and in controlling the release of various hormones. These pathways and cell groups form a dopamine system which is neuromodulatory.
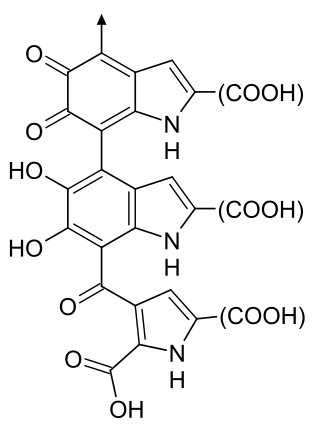
Melanin is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. The melanin pigments are produced in a specialized group of cells known as melanocytes.

Vicia faba, commonly known as the broad bean, fava bean, or faba bean, is a species of vetch, a flowering plant in the pea and bean family Fabaceae. It is widely cultivated as a crop for human consumption, and also as a cover crop. Varieties with smaller, harder seeds that are fed to horses or other animals are called field bean, tic bean or tick bean. Horse bean, Vicia faba var. equinaPers., is a variety recognized as an accepted name. This legume is very common in Southern European, Northern European, East Asian, Latin American and North African cuisines.

Phaseolus vulgaris, the common bean is a herbaceous annual plant grown worldwide for its edible dry seeds or green, unripe pods. Its leaf is also occasionally used as a vegetable and the straw as fodder. Its botanical classification, along with other Phaseolus species, is as a member of the legume family Fabaceae. Like most members of this family, common beans acquire the nitrogen they require through an association with rhizobia, which are nitrogen-fixing bacteria.

Macrotyloma uniflorum is a legume native to tropical southern Asia, known for its distinct taste and texture, widely used legume in many cuisines. It is also known for human consumption for its rich nutrients and reputed medicinal properties. It is commonly grown for horse feed, hence the name “horse gram”. Horse gram grown in parts of India, as well as Nepal, Malaysia, Sri Lanka, and is introduced to the West Indies. It is consumed whole, sprouted, or ground. It is consumed in many parts of India and is also known as a superfood. Horse gram is also allowed to be eaten on some Hindu fasting days. Medical uses of these legumes have been discussed and is described in the Ayurveda.
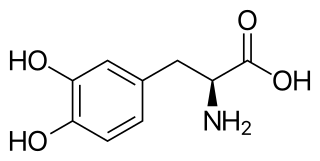
l-DOPA, also known as levodopa and l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine, is made and used as part of the normal biology of some plants and animals, including humans. Humans, as well as a portion of the other animals that utilize l-DOPA, make it via biosynthesis from the amino acid l-tyrosine. l-DOPA is the precursor to the neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), which are collectively known as catecholamines. Furthermore, l-DOPA itself mediates neurotrophic factor release by the brain and CNS. l-DOPA can be manufactured and in its pure form is sold as a psychoactive drug with the INN levodopa; trade names include Sinemet, Pharmacopa, Atamet, and Stalevo. As a drug, it is used in the clinical treatment of Parkinson's disease and dopamine-responsive dystonia.

Mucuna is a genus of around 114 accepted species of climbing lianas (vines) and shrubs of the family Fabaceae: tribe Phaseoleae, typically found in tropical and subtropical forests in the Americas, sub-Saharan Africa, southern, southeastern, and eastern Asia, New Guinea, Australia, and the Pacific Islands.

Vigna aconitifolia is a drought-resistant legume, commonly grown in arid and semi-arid regions of India. It is commonly called mat bean, moth bean, matki or dew bean. The pods, sprouts and protein-rich seeds of this crop are commonly consumed in India. Moth bean can be grown on many soil types, and can also act as a pasture legume.

Mucuna pruriens is a tropical legume native to Africa and tropical Asia and widely naturalized and cultivated. Its English common names include monkey tamarind, velvet bean, Bengal velvet bean, Florida velvet bean, Mauritius velvet bean, Yokohama velvet bean, cowage, cowitch, lacuna bean, and Lyon bean.

Ormosia is a genus of legumes. 131 living species, mostly trees or large shrubs, are native to the tropical Americas, from southwestern Mexico to Bolivia and southern Brazil, to southern, southeastern, and eastern Asia, and to New Guinea and Queensland. Most are tropical, while some extend into temperate temperate regions of China. A few species are threatened by habitat destruction, while the Hainan ormosia is probably extinct already.

Cynometra lenticellata is a flowering tropical tree in the family Fabaceae. It is native to tropical semi-deciduous rainforest and gallery forests in northern Queensland, some of the Torres Strait Islands, and New Guinea. Common names include: silk handkerchief tree, cascading bean, and native handkerchief tree.

Strophostyles helvola, commonly called amberique-bean, annual sand bean, or trailing fuzzybean is a species of flowering plant in the legume family. It is native to eastern Canada and the eastern United States.

Albinism is the congenital absence of melanin in an animal or plant resulting in white hair, feathers, scales and skin and reddish pink or blue eyes. Individuals with the condition are referred to as albinos.

Vigna luteola, commonly known as the hairy cowpea and the Nile bean, is a perennial vine found in many tropical areas.

Entada phaseoloides commonly named the box bean or St. Thomas’ bean, first described by Linnaeus, with its current name described by Merrill. E. phaseoloides is a liana in the pea family: called gugo, balugo, or tamayan in the Philippines and bàm bàm in Viet Nam. No subspecies are listed in the Catalogue of Life.

Mucuna gigantea, commonly known as burny bean, burney bean, velvet bean or sea bean is a species of liana from the legume family Fabaceae. Its natural range roughly follows the perimeter of the Indian Ocean and includes Africa, India, Malesia, New Guinea and northern Australia. Many parts of the plant - in particular the new growth, flowers and fruit - are covered in fine irritant hairs.

Mucuna urens is a species of large liana from the family Fabaceae. The plant is native to tropical Central and South America, and has been introduced into the Republic of the Congo. Common names include horse-eye bean and ox-eye bean.

















