R, or r, is the eighteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ar, plural ars, or in Ireland or. In some varieties of African-American Vernacular English, the name of the letter is pronounced as "arruh".
V, or v, is the twenty-second letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is vee, plural vees.
The Coptic script is the script used for writing the Coptic language, the latest stage of Egyptian. The repertoire of glyphs is based on the uncial Greek alphabet, augmented by letters borrowed from the Egyptian Demotic. It was the first alphabetic script used for the Egyptian language. There are several Coptic alphabets, as the script varies greatly among the various dialects and eras of the Coptic language.
Koppa or qoppa is a letter that was used in early forms of the Greek alphabet, derived from Phoenician qoph (𐤒). It was originally used to denote the sound, but dropped out of use as an alphabetic character and replaced by Kappa (Κ). It has remained in use as a numeral symbol (90) in the system of Greek numerals, although with a modified shape. Koppa is the source of Latin Q, as well as the Cyrillic numeral sign of the same name (Koppa).

Ezh, also called the "tailed z", is a letter, notable for its use in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) to represent the voiced postalveolar fricative consonant. For example, the pronunciation of "si" in vision and precision, or the ⟨s⟩ in treasure. See also the letter ⟨Ž⟩ as used in many Slavic languages, the Persian alphabet letter ⟨ژ⟩, the Cyrillic letter ⟨Ж⟩, and the Esperanto letter ⟨Ĵ⟩.

O is a letter of the Cyrillic script.
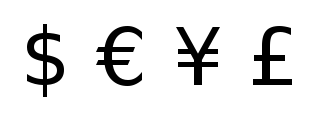
A currency symbol or currency sign is a graphic symbol used to denote a currency unit. Usually it is defined by a monetary authority, such as the national central bank for the currency concerned.

The r rotunda ⟨ ꝛ ⟩, "rounded r", is a historical calligraphic variant of the minuscule (lowercase) letter Latin r used in full script-like typefaces, especially blackletters.

Uk is a digraph of the early Cyrillic alphabet, although commonly considered and used as a single letter. It is an accent nasal vowel from the Slavonic language. To save space, it was often written as a vertical ligature (Ꙋ ꙋ), called "monograph Uk". In modern times, ⟨ѹ⟩ has been replaced by the simple ⟨у⟩.

Kra is a glyph formerly used to write the Kalaallisut language of Greenland and is now only found in Nunatsiavummiutut, a distinct Inuktitut dialect. It is visually similar to a Latin small capital letter K, a Greek letter Kappa: κ, or a Cyrillic small letter Ka: к.

Ou is a ligature of the Greek letters ο and υ which was frequently used in Byzantine manuscripts. This omicron-upsilon ligature is still seen today on icon artwork in Greek Orthodox churches, and sometimes in graffiti or other forms of informal or decorative writing.
Unicode has subscripted and superscripted versions of a number of characters including a full set of Arabic numerals. These characters allow any polynomial, chemical and certain other equations to be represented in plain text without using any form of markup like HTML or TeX.
L, or l, is the twelfth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is el, plural els.
Standard Sundanese script is a writing system which is used by the Sundanese people. It is built based on Old Sundanese script which was used by the ancient Sundanese from the 14th to the 18th centuries.

Monocular O is one of the rare glyph variants of Cyrillic letter O. This glyph variant was used in certain manuscripts in the root word ꙩко (eye), and also in some other functions, for example, in the word- and syllable-initial position. It is used in some late birchbark letters of the 14th and 15th centuries, where it is usually differentiated from a regular о, used after consonants, also by width, being a broad On (ѻ) with a dot inside.

Binocular O is one of the exotic glyph variants of Cyrillic letter O. This glyph variant can be found in certain manuscripts in the plural or dual forms of the root word eye, like Ꙫчи.

Double monocular O is one of the exotic glyph variants of the Cyrillic letter O. This glyph variant can be found in certain manuscripts in the plural or dual forms of the word eye, for example ꙭчи "[two] eyes". They were incorporated into Unicode as characters U+A66C and U+A66D in Unicode version 5.1 (2008).
Runic is a Unicode block containing runic characters. It was introduced in Unicode 3.0 (1999), with eight additional characters introduced in Unicode 7.0 (2014). The original encoding of runes in UCS was based on the recommendations of the "ISO Runes Project" submitted in 1997.

Crossed O is a letter of the Cyrillic script, similar to the Cyrillic letter O but with the addition of a cross.