
Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) is the 16-bit internal bus of IBM PC/AT and similar computers based on the Intel 80286 and its immediate successors during the 1980s. The bus was (largely) backward compatible with the 8-bit bus of the 8088-based IBM PC, including the IBM PC/XT as well as IBM PC compatibles.

A sound card is an internal expansion card that provides input and output of audio signals to and from a computer under the control of computer programs. The term sound card is also applied to external audio interfaces used for professional audio applications.

IBM 8514 is a graphics card manufactured by IBM and introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of personal computers in 1987. It supports a display resolution of 1024 × 768 pixels with 256 colors at 43.5 Hz (interlaced), or 640 × 480 at 60 Hz (non-interlaced). 8514 usually refers to the display controller hardware. However, IBM sold the companion CRT monitor which carries the same designation, 8514.

PC Card is a parallel peripheral interface for laptop computers and PDAs. The PCMCIA originally introduced the 16-bit ISA-based PCMCIA Card in 1990, but renamed it to PC Card in March 1995 to avoid confusion with the name of the organization. The CardBus PC Card was introduced as a 32-bit version of the original PC Card, based on the PCI specification. The card slots are backward compatible for the original 16-bit card, older slots are not forward compatible with newer cards.

In computing, an expansion card is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an electrical connector, or expansion slot on a computer's motherboard to add functionality to a computer system. Sometimes the design of the computer's case and motherboard involves placing most of these slots onto a separate, removable card. Typically such cards are referred to as a riser card in part because they project upward from the board and allow expansion cards to be placed above and parallel to the motherboard.

Micro Channel architecture, or the Micro Channel bus, is a proprietary 16- or 32-bit parallel computer bus publicly introduced by IBM in 1987 which was used on PS/2 and other computers until the mid-1990s. Its name is commonly abbreviated as "MCA", although not by IBM. In IBM products, it superseded the ISA bus and was itself subsequently superseded by the PCI bus architecture.

Sound Blaster is a family of sound cards and audio peripherals designed by Creative Technology/Creative Labs of Singapore. The first Sound Blaster card was introduced in 1989.
GeoPort is a serial data system used on some models of the Apple Macintosh that could be externally clocked to run at a 2 megabit per second data rate. GeoPort slightly modified the existing Mac serial port pins to allow the computer's internal DSP hardware or software to send data that, when passed to a digital-to-analog converter, emulated various devices such as modems and fax machines. GeoPort could be found on late-model 68K-based machines as well as many pre-USB Power Macintosh models and PiPPiN. Some later Macintosh models also included an internal GeoPort via an internal connector on the Communications Slot. Apple GeoPort technology is now obsolete, and modem support is typically offered through USB.

The Personal System/2 or PS/2 is IBM's second generation of personal computers. Released in 1987, it officially replaced the IBM PC, XT, AT, and PC Convertible in IBM's lineup. Many of the PS/2's innovations, such as the 16550 UART, 1440 KB 3.5-inch floppy disk format, 72-pin SIMMs, PS/2 port, and VGA video standard, went on to become standards in the broader PC market.
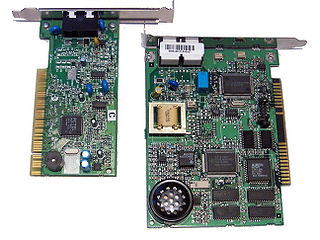
A software modem, commonly referred to as a softmodem, is a modem with minimal hardware that uses software running on the host computer, and the computer's resources, in place of the hardware in a conventional modem.

The game port is a device port that was found on IBM PC compatible and other computer systems throughout the 1980s and 1990s. It was the traditional connector for joystick input, and occasionally MIDI devices, until made obsolete by USB in the late 1990s.

IBM Aptiva is a line of personal computers that was produced by IBM. It was designed primarily for home use and offered a range of models with varying specifications and features. It was introduced in September 1994 as the replacement for the IBM PS/1.

The Gravis UltraSound or GUS is a sound card for the IBM PC compatible system platform, made by Canada-based Advanced Gravis Computer Technology Ltd. It was very popular in the demoscene during the 1990s.

The Sound Blaster 16 is a series of sound cards by Creative Technology, first released in June 1992 for PCs with an ISA or PCI slot. It was the successor to the Sound Blaster Pro series of sound cards and introduced CD-quality digital audio to the Sound Blaster line. For optional wavetable synthesis, the Sound Blaster 16 also added an expansion-header for add-on MIDI-daughterboards, called a Wave Blaster connector, and a game port for optional connection with external MIDI sound modules.
Sound Blaster Advanced Wave Effects 64 is an ISA sound card from Creative Technology. It is an add-on board for PCs. The card was launched in November 1996.

The PS/2 E or Energy is a member of the IBM Personal System/2 family of personal computers (PCs). It was the first Energy Star-compliant PC, consuming very little power relative to other contemporary PCs, and made extensive use of recycled materials in its enclosure.

IBM ThinkPad 760 was a notebook computer introduced in 1995 by the IBM corporation into the market as part of the ThinkPad 700-series. It was succeeded in 1998 by the ThinkPad 770 series.

The PS/1 is a brand for a line of personal computers that marked IBM's return to the home market in 1990, five years after the IBM PCjr. It was replaced by the IBM Aptiva in September 1994.

The IBM ThinkPad 600 series was a series of notebook computers introduced in 1998 by IBM as an lighter and slimmer alternative to the 770 series. Three models were produced, the 600, 600E, and 600X; the series was succeeded in 2000 by the ThinkPad T20 series.

The IBM ThinkPad T20 series was a series of notebook computers introduced in May 2000 by IBM as the successor of the 770 series and the first model of the T-series which exists today under Lenovo ownership. Four models were produced, the T20, T21, T22, and T23; the series was succeeded in May 2002 by the ThinkPad T30, but was produced until July 2003.



















