
The mouse-eared bats or myotises are a diverse and widespread genus (Myotis) of bats within the family Vespertilionidae. The noun "myotis" itself is a Neo-Latin construction, from the Greek "muós and "oûs", literally translating to "mouse-eared".

The black myotis is a vesper bat species from South and Central America.

The red myotis is a vesper bat species found in Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay.

The eastern long-fingered bat, or big-footed myotis is a species of vesper bat found in China, Japan, North Korea, South Korea, and Russia. Roosting in caves and rock crevices during the day, it forages at night for insects near rivers and streams.

The Far Eastern myotis or bombinus bat is a species of mouse-eared bat found in East Asia. It is widespread but uncommon across the Korean Peninsula, and spends the winter hibernating in caves.

The fringed long-footed myotis is a species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae. It is found in China, Taiwan and Hong Kong.

The pallid large-footed myotis or Philippine large-footed myotis is a species of vesper bat. It can be found in the following countries: Malaysia and Philippines. It is found in caves and arable land.
Schaub's myotis is a species of vesper bat. It is found in Armenia and Iran, and known from fossils from Hungary and Russia.

The cave myotis is a species of vesper bat (Vespertilionidae) in the genus Myotis.

Myotis vivesi, the fish-eating bat or fish-eating myotis, is a species of bat that lives around the Gulf of California, and feeds on fish and crustaceans. It is the largest species of the genus Myotis in the Americas, and has exceptionally large feet, which it uses in hunting. It was described in 1901 by Auguste Ménégaux. It was previously considered the only member of the Myotis subgenus Pizonyx, but Pizonyx is now considered to contain all American Myotis species, along with two Eurasian ones.

The long-legged myotis is a species of vesper bat that can be found in western Canada, Mexico, and the western United States.

The Yuma myotis is a species of vesper bat native to western North America.

Myotinae is a subfamily of vesper bats. It contains three genera: Eudiscopus, Myotis, and Submyotodon. Before the description of Submyotodon and analysis of its phylogenetics, as well as a phylogenetic analysis of Eudiscopus, the only member of Myotinae was Myotis.

The Petralona Cave a karst formation, is located at 300 m (984 ft) above sea-level on the western foot of Mount Katsika, about 1 km (0.62 mi) east of the village of Petralona, about 35 km (22 mi) south-east of Thessaloniki city on the Chalkidiki peninsula, Greece. The site came to public attention when in 1960 a fossilized archaic human skull was found. The cave had been discovered accidentally only a year earlier (1959) after erosion had left clefts in the rock. "Bejeweled" with impressive stalactite and stalagmite formations and holding an abundance of fossils, the cave soon attracted geologists and paleontologists. After decades of excavations the cave is open to the public and scientific work is documented and presented in an adjacent archaeological museum.

The Bocharic myotis or Bokhara whiskered bat is a species of mouse-eared bat in the family Vespertilionidae, described in 1950, and indigenous to Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan.

The Nepal myotis is a vesper bat of genus Myotis.

David's myotis is a species of microbat in the Vespertilionidae family native to China, Mongolia, Kazakhstan, and Russia. First identified in 1869 by Wilhelm Peters, it is similar in morphology to species like M. mystacinus, M. ikonnikovi, M. brandtii, and M. sibiricus. It was previously considered to be a subspecies of the whiskered bat.
Submyotodon is a genus of vespertilionid bats, published as a new taxon in 2003 to describe a Miocene fossil species. Extant species and subspecies previously included in Myotis were later transferred to this genus. Species in this genus are referred to as broad-muzzled bats or broad-muzzled myotises.
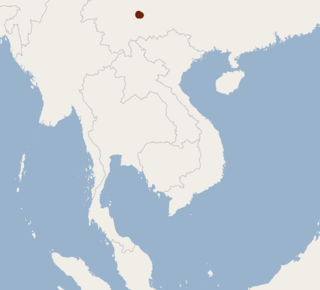
The chestnut myotis is a species of mouse-eared bat in the family Vespertilionidae. It is found in South Asia.

Myotis indochinensis, commonly known as the Indochinese mouse-eared bat, is a species of cave-dwelling bat in the family Vespertilionidae. It is found in Vietnam and China.

















