
The mouse-eared bats or myotises are a diverse and widespread genus (Myotis) of bats within the family Vespertilionidae. The noun "myotis" itself is a Neo-Latin construction, from the Greek "muós and "oûs", literally translating to "mouse-eared".

The silver-tipped myotis is a species of mouse-eared bat found in a range of lowland habitats in the Americas.

The velvety myotis, is a species of vesper bat from South America.

The little big-eared bat is a bat species in the order Chiroptera and family Phyllostomidae. It is from South and Central America particularly Colombia, Venezuela, Guyana, French Guiana, Brazil, Peru, Ecuador, Bolivia, Argentina, Paraguay, Suriname and Trinidad. Though its exact population is unknown, it is considered widespread and occurs in protected areas, although deforestation may be a minor threat, it is classified as Least Concern. It is found in multistratal evergreen forests and dry thorn forests and forages near streams and is found hollow trees, logs, caverns, or houses with groups up to twelve. The head and body length measures at 44 millimetres (1.7 in) for males and 45 millimetres (1.8 in) for females. Males usually weigh about 5 grams (0.18 oz) while females weigh 5.7 grams (0.20 oz).

The visored bat,, is a bat species from tropical South America. It is the only species in the genus Sphaeronycteris. Although visored bats have some unique characteristics, they are thought to be most closely related to little white-shouldered bats and wrinkle-faced bats.
Botta's serotine is a species of vesper bat, one of 25 in the genus Eptesicus. It is found in rocky areas and temperate desert.

The desert long-eared bat is a species of vesper bat found in North Africa and the Middle East.

The western small-footed bat, also known as the western small-footed myotis, is a species of vesper bat native to North America.
The inland forest bat is a vesper bat that occurs in central and arid regions in Australia. They were first described in 1987, published in a review of poorly surveyed microbat populations. A tiny flying mammal, it occupies small cavities in trees and buildings while roosting. The nocturnal activity is foraging for insects, typically moths.

Mehely's horseshoe bat is a species of insectivorous bat in the family Rhinolophidae found in Southern Europe and parts of the Middle East. It is distributed in a narrow band around the Mediterranean Sea from North-Western Africa across Portugal, Spain, the Balearics, southern France, Sardinia, Sicily and the Balkan Peninsula to Asia Minor.
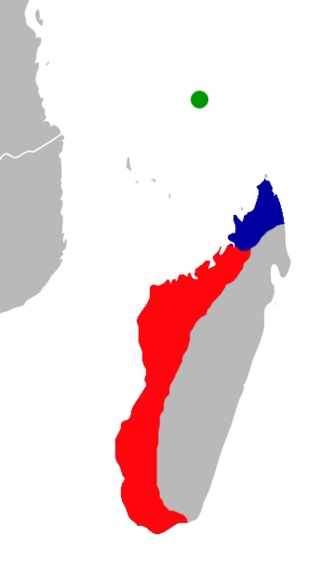
Grandidier's trident bat is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae endemic to Madagascar. It was formerly assigned to the genus Triaenops, but is now placed in the separate genus Paratriaenops.

The Hipposideridae are a family of bats commonly known as the Old World leaf-nosed bats. While it has often been seen as a subfamily, Hipposiderinae, of the family Rhinolophidae, it is now more generally classified as its own family. Nevertheless, it is most closely related to Rhinolophidae within the suborder Yinpterochiroptera.

Triaenops goodmani is an extinct bat from Madagascar in the genus Triaenops. It is known from three lower jaws collected in a cave at Anjohibe in 1996, and described as a new species in 2007. The material is at most 10,000 years old. A bat humerus from the same site could not be identified as either T. goodmani or the living T. menamena. T. goodmani is identifiable as a member of Triaenops or the related genus Paratriaenops by a number of features of the teeth, such as the single-cusped, canine-like fourth premolar and the presence of a gap between the entoconid and hypoconulid cusps on the first two molars. T. goodmani is larger than the living species of Triaenops and Paratriaenops on Madagascar, and on the first molar the protoconid cusp is only slightly higher than the hypoconid, not much higher as in the other species.
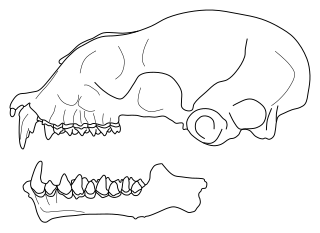
Triaenops menamena is a bat in the genus Triaenops found on Madagascar, mainly in the drier regions. It was known as Triaenops rufus until 2009, when it was discovered that that name had been incorrectly applied to the species. Triaenops rufus is a synonym of Triaenops persicus, a Middle Eastern species closely related to T. menamena— the Malagasy species had previously been placed as a subspecies of T. persicus by some authors. Triaenops menamena is mostly found in forests, but also occurs in other habitats. It often roosts in large colonies and eats insects such as butterflies and moths. Because of its wide range, common occurrence, and tolerance of habitat degradation, it is not considered to be threatened.

The Alcathoe bat is a European bat in the genus Myotis. Known only from Greece and Hungary when it was first described in 2001, its known distribution has since expanded as far as Portugal, England, Sweden, and Russia. It is similar to the whiskered bat and other species and is difficult to distinguish from them. However, its brown fur is distinctive and it is clearly different in characters of its karyotype and DNA sequences. It is most closely related to Myotis hyrcanicus from Iran, but otherwise has no close relatives.

Escalera's bat is a European bat in the genus Myotis, found in Spain, Portugal, and far southern France.
Chiroderma vizottoi is a species of frugivorous bat found in the northeast of Brazil.
The Anatolian serotine bat is a species of bat found in the Middle-East, Cyprus and Rhodes Island, Greece.

Gaisler's long-eared bat is a species of bat in the genus Plecotus. It is a medium-sized grayish-brown and found in Morocco, Algeria, Libya, and Tunisia.














