
Palmaria palmata, also called dulse, dillisk or dilsk, red dulse, sea lettuce flakes, or creathnach, is a red alga (Rhodophyta) previously referred to as Rhodymenia palmata. It grows on the northern coasts of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. It is a well-known snack food. In Iceland, where it is known as söl, it has been an important source of dietary fiber throughout the centuries.

Chordariaceae is a family of brown algae. Members of this family are may be filamentous, crustose with fused cells at the base, or they may be terete and differentiated into a central medulla and an outer photosynthetic cortex. They have a sporphytic thallus usually aggregated to form a pseudo-parenchyma.

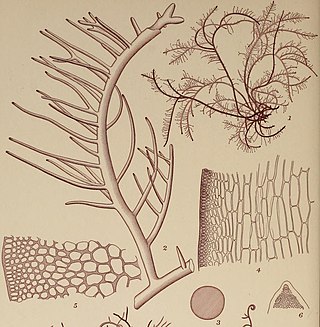
Atractophora hypnoides is a rare red alga (Rhodophyta) found in the British Isles, France and some Atlantic Islands and is the only species of the genus found in the British Isles. It is attached to the rock or other algae by a small basal disc and is much branched with downgrowing filaments which enclose the main branch or axis forming a cortex. Short filaments of limited growth radiate in whorls from the axis and frequently convert into hairs. The spreading filaments grow irregularly in a diffuse manner. Microscope examination is required for identification.

Polysiphonia is a genus of filamentous red algae with about 19 species on the coasts of the British Isles and about 200 species worldwide, including Crete in Greece, Antarctica and Greenland. Its members are known by a number of common names. It is in the order Ceramiales and family Rhodomelaceae.

Atractophora is a monotypic genus of red algae of the family Atractophoraceae. It only contains one known species Atractophora hypnoidesP.L.Crouan & H.M.Crouan, 1848.

Red algae, or Rhodophyta, are one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta comprises one of the largest phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 currently recognized species with taxonomic revisions ongoing. The majority of species (6,793) are found in the Florideophyceae (class), and mostly consist of multicellular, marine algae, including many notable seaweeds. Red algae are abundant in marine habitats but relatively rare in freshwaters. Approximately 5% of red algae species occur in freshwater environments, with greater concentrations found in warmer areas. Except for two coastal cave dwelling species in the asexual class Cyanidiophyceae, there are no terrestrial species, which may be due to an evolutionary bottleneck in which the last common ancestor lost about 25% of its core genes and much of its evolutionary plasticity.

Halymenia a genus of a macroscopic red algae that grows in oceans worldwide.
Bangia is an extant genus of division Rhodophyta that grows in marine or freshwater habitats. Bangia has small thalli with rapid growth and high reproductive output, and exhibits behavior characteristic of r-selected species. The plants are attached by down-growing rhizoids, usually in dense purple-black to rust-colored clumps. The chloroplasts of Bangia, like others in the division Rhodophyta, contain chlorophyll a and sometimes chlorophyll d, as well as accessory pigments such as phycobilin pigments and xanthophylls. Depending on the relative proportions of these pigments and the light conditions, the overall color of the plant can range from green to red to purple to grey; however, the red pigment, phycoerythrin, is usually dominant.

Galaxaura is a genus of thalloid red algae.
Hypnea is a genus of red algae, and a well known carrageenophyte.
Sirodotia Kylin (1912) is a genus of freshwater red alga which was described by Kylin in 1912, and placed in the Batrachospermaceae family.
Sirodotia huillensis Skuja is a freshwater red algal species belonging to the family Batrachospermaceae. This species mostly reported from high altitude forest streams.

Batrachospermaceae is a family of fresh water red algae (Rhodophyta). Genera within the Batrachospermaceae generally have a "Lemanea-type" life history with carpospores germinating to produce chantransia. Sporophyte phase with meiosis occurs in an apical cell to produce the gametophyte stage. Pit connections have two pit plug cap layers with the other layer enlarged. This family of freshwater red algae is uniaxial, meaning each filament with a single apical cell. The genera included within Batrachospermaceae are listed in the table below.
The Pterocladiophilaceae is a small family of red algae containing 2 genera of thallus parasitic algae.

Callithamnion is a genus of algae belonging to the family Callithamniaceae.

Liagoraceae is a family of red algae (Rhodophyta) in the order Nemaliales. The type genus is LiagoraJ.V.Lamouroux.

Thoreales is an order of red algae belonging to the class Florideophyceae. The order consists only one family, ThoreaceaeHassall, 1845. The family of Thoreaceae was circumscribed by Arthur Hill Hassall in A history of the British freshwater algae, including descriptions of the Desmideae and Diatomaceae in 1845.

Halymeniales is an order of red algae belonging to the class Florideophyceae and the subclass Rhodymeniophycidae.

Peyssonneliales is a monotypic order of red algae belonging to the class Florideophyceae and the subclass Rhodymeniophycidae. It contains only 1 known family, PeyssonneliaceaeDenizot, M., 1968.














