
Thermus is a genus of thermophilic bacteria. It is one of several bacteria belonging to the Deinococcota phylum. According to comparative analysis of 16S rRNA, this is one the most ancient group of bacteria Thermus species can be distinguished from other genera in the family Thermaceae as well as all other bacteria by the presence of eight conserved signature indels found in proteins such as adenylate kinase and replicative DNA helicase as well as 14 conserved signature proteins that are exclusively shared by members of this genus.

Pseudomonas putida is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped, saprophytic soil bacterium. It has a versatile metabolism and is amenable to genetic manipulation, making it a common organism used in research, bioremediation, and synthesis of chemicals and other compounds.

Tinea capitis is a cutaneous fungal infection (dermatophytosis) of the scalp. The disease is primarily caused by dermatophytes in the genera Trichophyton and Microsporum that invade the hair shaft. The clinical presentation is typically single or multiple patches of hair loss, sometimes with a 'black dot' pattern, that may be accompanied by inflammation, scaling, pustules, and itching. Uncommon in adults, tinea capitis is predominantly seen in pre-pubertal children, more often boys than girls.

Nitrosomonas is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria, belonging to the Betaproteobacteria. It is one of the five genera of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and, as an obligate chemolithoautotroph, uses ammonia as an energy source and carbon dioxide as a carbon source in the presence of oxygen. Nitrosomonas are important in the global biogeochemical nitrogen cycle, since they increase the bioavailability of nitrogen to plants and in the denitrification, which is important for the release of nitrous oxide, a powerful greenhouse gas. This microbe is photophobic, and usually generate a biofilm matrix, or form clumps with other microbes, to avoid light. Nitrosomonas can be divided into six lineages: the first one includes the species Nitrosomonas europea, Nitrosomonas eutropha, Nitrosomonas halophila, and Nitrosomonas mobilis. The second lineage presents the species Nitrosomonas communis, N. sp. I and N. sp. II. The third lineage includes only Nitrosomonas nitrosa. The fourth lineage includes the species Nitrosomonas ureae and Nitrosomonas oligotropha. The fifth and sixth lineages include the species Nitrosomonas marina, N. sp. III, Nitrosomonas estuarii, and Nitrosomonas cryotolerans.

Dermatophytosis, also known as tinea and ringworm, is a fungal infection of the skin, that may affect skin, hair, and nails. Typically it results in a red, itchy, scaly, circular rash. Hair loss may occur in the area affected. Symptoms begin four to fourteen days after exposure. The types of dermatophytosis are typically named for area of the body that they affect. Multiple areas can be affected at a given time.

Basidiobolus ranarum is a filamentous fungus with worldwide distribution. The fungus was first isolated by Eidam in 1886. It can saprophytically live in the intestines of mainly cold-blooded vertebrates and on decaying fruits and soil. The fungus prefers glucose as a carbon source and grows rapidly at room temperature. Basidiobolus ranarum is also known as a cause of subcutaneous zygomycosis, usually causing granulomatous infections on a host's limbs. Infections are generally geographically limited to tropical and subtropical regions such as East and West Africa. Subcutaneous zygomycosis caused by B. ranarum is a rare disease and predominantly affects children and males. Common subcutaneous zygomycosis shows characteristic features and is relatively easy to be diagnosed; while, certain rare cases might show non-specific clinical features that might pose a difficulty on its identification. Although disease caused by this fungus is known to resolve spontaneously on its own, there are a number of treatments available.

Diplocynodon is an extinct genus of alligatoroid crocodilian that lived during the Paleocene to Middle Miocene in Europe. Some species may have reached lengths of 3 metres (9.8 ft), while others probably did not exceed 1 metre (3.3 ft). They are almost exclusively found in freshwater environments. The various species are thought to have been opportunistic aquatic predators.
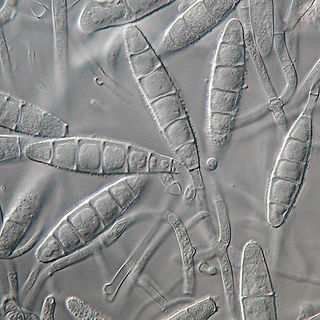
Microsporum gypseum is a soil-associated dermatophyte that occasionally is known to colonise and infect the upper dead layers of the skin of mammals. The name refers to an asexual "form-taxon" that has been associated with four related biological species of fungi: the pathogenic taxa Arthroderma incurvatum, A. gypsea, A. fulva and the non-pathogenic saprotroph A. corniculata. More recent studies have restricted M. gypseum to two teleomorphic species A. gypseum and A. incurvatum. The conidial states of A. fulva and A. corniculata have been assigned to M. fulvum and M. boullardii. Because the anamorphic states of these fungi are so similar, they can be identified reliably only by mating. Two mating strains have been discovered, "+" and "–". The classification of this species has been based on the characteristically rough-walled, blunt, club-shaped, multicelled macroconidia. Synonyms include Achorion gypseum, Microsporum flavescens, M. scorteum, and M. xanthodes. There has been past nomenclatural confusion in the usage of the generic names Microsporum and Microsporon.
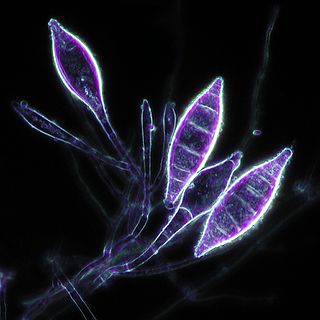
Microsporum canis is a pathogenic, asexual fungus in the phylum Ascomycota that infects the upper, dead layers of skin on domesticated cats, and occasionally dogs and humans. The species has a worldwide distribution.
Microsporum nanum is a pathogenic fungus in the family Arthrodermataceae. It is a type of dermatophyte that causes infection in dead keratinized tissues such as skin, hair, and nails. Microsporum nanum is found worldwide and is both zoophilic and geophilic. Animals such as pigs and sheep are the natural hosts for the fungus; however, infection of humans is also possible. Majority of the human cases reported are associated with pig farming. The fungus can invade the skin of the host; if it is scratched off by the infected animal, the fungus is still capable of reproducing in soil.
Nannizzia fulva is a species of fungus. It is a heterothallic species.
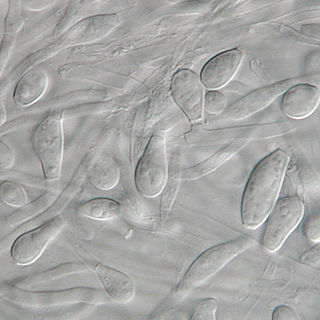
Chrysosporium keratinophilum is a mold that is closely related to the dermatophytic fungi and is mainly found in soil and the coats of wild animals to break down keratin. Chrysosporium keratinophilum is one of the more commonly occurring species of the genus Chrysosporium in nature. It is easily detected due to its characteristic "light-bulb" shape and flat base. Chrysosporium keratinophilum is most commonly found in keratin-rich, dead materials such as feathers, skin scales, hair, and hooves. Although not identified as pathogenic, it is a regular contaminant of cutaneous specimens which leads to the common misinterpretation that this fungus is pathogenic.
Micromonospora viridifaciens is an endophytic actinomycete.
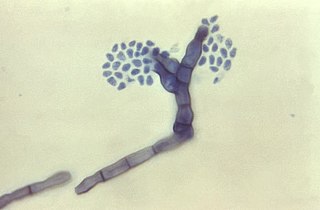
Fonsecaea compacta is a saprophytic fungal species found in the family Herpotrichiellaceae. It is a rare etiological agent of chromoblastomycosis, with low rates of correspondence observed from reports. The main active components of F. compacta are glycolipids, yet very little is known about its composition. F. compacta is widely regarded as a dysplastic variety of Fonsecaea pedrosoi, its morphological precursor. The genus Fonsecaea presently contains two species, F. pedrosoi and F. compacta. Over 100 strains of F. pedrosoi have been isolated but only two of F. compacta.
Paraburkholderia is a genus of Pseudomonadota that are gram negative, slightly curved rods that are motile by means of flagella. They have been reported to colonize endophytic tissues of hybrid spruce and lodgepole pine with a strong potential to perform biological nitrogen fixation and plant growth promotion. Unlike Burkholderia species, Paraburkholderia members are not commonly associated with human infection. Paraburkholderia members form a monophyletic clade within the Burkholderiaceae family, which is what prompted their distinction as a genus independent from Burkholderia species, in combination with the finding of robust conserved signature indels which are unique to Paraburkholderia species, and are lacking in members of the genus Burkholderia. These CSIs distinguish the genus from all other bacteria. Additionally, the CSIs that were found to be shared by Burkholderia species are absent in Paraburkholderia, providing evidence of separate lineages.

Trichophyton terrestre is a fungus of the genus Trichophyton.
Microsporum fulvum is a wildly-distributed dermatophyte species in the Fungi Kingdom. It is known to be a close relative to other dermatophytes such as Trichophyton andEpidermophyton. The fungus is common within soil environments and grows well on keratinized material, such as hair, nails and dead skin. It is recognized as an opportunistic fungal pathogen capable of causing cutaneous mycoses in humans and animals. Originally, the fungus was thought to be Microsporum gypseum until enhanced genetic examination separated the two as distinct species in 1963.

Nannizzia is a genus of fungus in the family Arthrodermataceae.
Scytalidium hyalinum is an ascomycete fungus currently in the genus Scytalidium. It causes dermatomycosis and systemic infections in humans and it is widespread throughout the world.













