
The Nautilida constitute a large and diverse order of generally coiled nautiloid cephalopods that began in the mid Paleozoic and continues to the present with a single family, the Nautilidae which includes two genera, Nautilus and Allonautilus, with six species. All told, between 22 and 34 families and 165 to 184 genera have been recognised, making this the largest order of the subclass Nautiloidea.

Nautiloids are a group of marine cephalopods (Mollusca) which originated in the Late Cambrian and are represented today by the living Nautilus and Allonautilus. Fossil nautiloids are diverse and speciose, with over 2,500 recorded species. They flourished during the early Paleozoic era, when they constituted the main predatory animals. Early in their evolution, nautiloids developed an extraordinary diversity of shell shapes, including coiled morphologies and giant straight-shelled forms (orthocones). Only a handful of rare coiled species, the nautiluses, survive to the present day.
The Rutocertina is one of only three suborders in Shimankiy's (1957) classification of the Nautilida, the other two being the Lirocerina and Nautilina. Genera in the Rutocerina are redistributed in the Rutoceratina, Tainoceratina, and Centroceratina. The Lirocerina is redefined as the Liroceratina, and Nautilina.remains as is. In general terms these are similar to the simpler classification proposed by Kümmel 1964, wherein the Nautilida is divided into five superfamilies, the Tainocerataceae, Trigonocerataceae, Clydonautilacea, Aipocerataceae, and Nautilaceae. Shimanskiy's classification involves 34 families, Kümmel's only twenty-seven.

Aturia is an extinct genus of Paleocene to Miocene nautilids within Aturiidae, a monotypic family, established by Campman in 1857 for Aturia Bronn, 1838, and is included in the superfamily Nautilaceae in Kümmel 1964.
Permoceras, the sole member of the family Permoceratidae, is a genus of coiled nautiloids with a smooth, compressed involute shell, whorls higher than wide, earlier whorls hidden from view. The venter is rounded as are the ventral and umbilical shoulders, the flanks flattened. The siphuncle is ventrally subcentral. The suture, which is most characteristic, has a deep, narrow pointed ventral lobe and large, asymmetrical pointed lobes on either side.

Hercoglossidae is a family of Nautilid in the superfamily Nautilaceae. It was established by Spath in 1927 for smooth, involute nautiloids characterized by a suture with differentiated elements, known from the Upper Jurassic to the Oligocene.
The Clydonautiloidea are a superfamily within the nautiloid order Nautilida characterized by smooth, generally globular, shells with nearly straight sutures, in early forms, but developing highly differentiated sutures in some later forms. Where known, the siphuncle tends to be central to subcentral.

The Trigonoceratoidea are a superfamily within the Nautilida that ranged from the Devonian to the Triassic, thought to have contained the source for the Nautilaceae in which Nautilus is found.

The Nautilaceae form one of five superfamilies that make up the Nautilida according to Bernard Kummel (1964), and the only one that survived past the Triassic. The Nautilaceae comprise six families: Nautilidae, Paracenoceratidae, Pseudonautilidae, Cymatoceratidae, Hercoglossidae, and Aturiidae. Shimanskiy (1957) separated the Paracenoceratidae and Pseudonautilidae from his near equivalent Nautilina and added them to the Lyroceratina, expanding the equivalent Clydonautilaceae and bringing it into the Jurassic. The Nautilaceae are represented by Nautilus and Allonautilus, genera included in the Nautilidae.
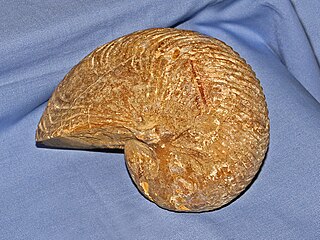
The Cymatoceratidae is a family of Mesozoic and early Cenozoic nautiloid cephalopods and the most abundant of this kind in the Cretaceous. They are characterized by ribbed, generally involute shells of varied form - coiled such that the outer whorl envelops the previous, as with Nautilus, and sutures that are variably sinuous.
Syringonautilidae is a family of Nautiloidea from the middle to late Triassic. Syringonautilidae comprise the last of the Trigonoceratoidea and are the source for the Nautilaceae which continued the Nautiloidea through the Mesozoic and into the Cenozoic right down to the recent. Syringonautilidae is a strictly Triassic family, derived early in the Triassic from the Grypoceratidae.

Grypoceratidae is the longest-lived family of the Trigonoceratoidea, or of the near equivalent Centroceratina; members of the Nautilida from the Upper Paleozoic and Triassic.
The Centroceratidae is the ancestral family of the Trigonoceratoidea and of the equivalent Centroceratina; extinct shelled cephalopods belonging to the order Nautilida
Liroceratidae is an extinct family of nautilids, shelled marine molluscs, belonging to the Clydonautiloidea, consisting of generally smooth, involute, nautiliconic forms with a small umbilicus. The whorl section is usually depressed and broadly rounded, the suture only slightly sinuous, and the siphuncle usually more or less central.
The Clydonautilidae are Middle and Upper Triassic nautiloid cephalopods, which are derivatives of the clydonautiloidean family Liroceratidae, that have generally smooth, involute, globular to compressed shells, characterized by a suture with prominent lobes and saddles. The family is known to contain five genera, These are:
Gonionautilidae is a family in the nautilid superfamily Clydonautiliaceae that contains only the genus Gonionautilus, known from the Upper Triassic (Norian) of Europe and North America.

Eutrephoceras is an extinct genus of nautilus from the Late Jurassic to the Miocene. They are characterized by a highly rounded involute shell with slightly sinuous suture patterns.
Grypoceras is a coiled nautiloid cephalopod from the Triassic of western North America, southern Asia, and Europe that belongs to the nautilid family Grypoceratidae. Named by Alpheus Hyatt in 1883, the shell of Grypoceras is essentially involute with a subtriangular cross section, widest across the umbilical shoulders, with flanks fairing toward a narrow flattened venter. Sutures on flanks are with smooth, deep lobes and with shallow ventral lobes.
Proclydonautilus is a genus of nautiloids belonging to the Clydonautilidae known from the Upper Triassic of North America, Europe, and India.
Styrionautilus is a genus of nautiloids and first of the Clydonautilidae with a range extending from the Middle Triassic, Anisian to the Upper Triassic, Norian. Its fossils have been found in North America (Nevada), Europe, and Timor.







