
Ammonoids are a group of extinct marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs, commonly referred to as ammonites, are more closely related to living coleoids than they are to shelled nautiloids such as the living Nautilus species. The earliest ammonites appeared during the Devonian, with the last species vanishing during or soon after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event.

Ammonitida is an order of ammonoid cephalopods that lived from the Jurassic through Paleocene time periods, commonly with intricate ammonitic sutures.

The Phylloceratina comprise a suborder of ammonoid cephalopods, belonging to the Ammonitida, whose range extends from the Lower Triassic to the Upper Cretaceous. Shells of the Phylloceratina are generally smooth with small to large umbilici and complex sutures with leaf-like phylloid saddle endings and lobes with thorn-like projections.

The Craniidae are a family of brachiopods, the only surviving members of the subphylum Craniiformea. They are the only members of the order Craniida, the monotypic suborder Craniidina, and the superfamily Cranioidea; consequently, the latter two taxa are at present redundant and rarely used.There are three living genera within Craniidae: Neoancistrocrania, Novocrania, and Valdiviathyris. As adults, craniids either live freely on the ocean floor or, more commonly, cement themselves onto a hard object with all or part of the ventral valve.

Lytoceratina is a suborder of Jurassic and Cretaceous ammonites that produced loosely coiled, evolute and gyroconic shells in which the sutural element are said to have complex moss-like endings.

Ammonitina comprises a diverse suborder of ammonite cephalopods that lived during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods of the Mesozoic Era. They are excellent index fossils, and it is often possible to link the rock layer in which they are found to specific geological time periods.

The Nautilaceae form one of five superfamilies that make up the Nautilida according to Bernard Kummel (1964), and the only one that survived past the Triassic. The Nautilaceae comprise six families: Nautilidae, Paracenoceratidae, Pseudonautilidae, Cymatoceratidae, Hercoglossidae, and Aturiidae. Shimanskiy (1957) separated the Paracenoceratidae and Pseudonautilidae from his near equivalent Nautilina and added them to the Lyroceratina, expanding the equivalent Clydonautilaceae and bringing it into the Jurassic. The Nautilaceae are represented by Nautilus and Allonautilus, genera included in the Nautilidae.
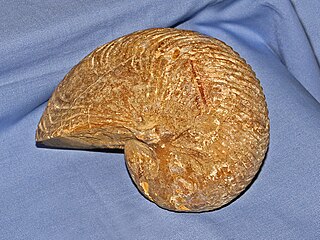
The Cymatoceratidae is a family of Mesozoic and early Cenozoic nautiloid cephalopods and the most abundant of this kind in the Cretaceous. They are characterized by ribbed, generally involute shells of varied form - coiled such that the outer whorl envelops the previous, as with Nautilus, and sutures that are variably sinuous.

Phylloceratidae is the predominant family of the Phylloceratina with some 15 or more genera found in rocks ranging from the Lower Jurassic to the Upper Cretaceous. Members of the Phylloceratidae are characterized by smooth, involute shells with very thin walls. Many are covered with fine growth lines but are usually without ribbing. Sutures are complex with the major and minor branches of the saddles with phylloid or spatulate endings.

Perisphinctoidea, formerly Perisphinctaceae, is a superfamily of Middle Jurassic (Bajocian) to Lower Cretaceous (Barremian) ammonites, commonly with evolute shells with strong ribbing that typically divides about mid flank before crossing the venter.
Pseudonautilidae is a family of Jurassic and Lower Cretaceous nautilid cephalopods belonging to the same superfamily as modern Nautilus, Nautilaceae, but forming a different branch from the family Nautilidae. Pseudonautilids, together with other nautilids, were contemporary with the ammonoids, which comprise an entirely different set of shelled cephalopod stocks more closely related to octopus and squid.

Oppeliidae are compressed to oxyconic, sculptured Haploceratoidea, either unkeeled, unicarinate, bicarinate, or tricarinate; with sutures in great variety, but ribbing usually more or less falcoid or falcate. The Oppeliidae is the principal family of the Haploceratoidea, with the longest duration, extending from the Middle Jurassic (Bajocian) to the Upper Cretaceous (Cenomanian) Their derivation is from the Hildoceratoidea.

Placenticeratidae is an extinct family of mostly Late Cretaceous ammonites included in the superfamily Hoplitoidea, derived from the Engonoceratidae by an increase in suture complexity.
Bochianites is a straight shelled ammonite which lived from the Upper Jurassic, Tithonian, to the Lower Cretaceous, Hauterivian in what is now Europe, Greenland, Africa, North America and Asia. The shell is long, narrow, moderately expanding; smooth or with weak to strong oblique annular ribs. Sutural elements are short and boxy. The umbilical lobe, which lies between the lateral lobe and dorsal lobe, on either side, is about the same size as the lobule dividing the first lateral saddle.

Eutrephoceras is an extinct genus of nautilus from the Late Jurassic to the Miocene. They are characterized by a highly rounded involute shell with slightly sinuous suture patterns.

Lytoceratidae is a taxonomic family of ammonoid cephalopods belonging to the suborder Lytoceratina, characterized by very evolute shells that generally enlarge rapidly, having whorls in contact but mostly overlapping very sightly, or not at all.

Lytoceratinae is a subfamily of ammonoid cephalopods that make up part of the family Lytoceratidae.
Streblitinae is a subfamily of Upper Jurassic and Lower Cretaceous ammonites within the family Oppeliidae characterized by compressed, involute shells; typically oxycones with complex sutures. Includes Streblites, Pseudoppelia, and Substreblites. Derivation is from the Taramelliceratinae. May have given rise to the Aconiceratinade.

The Lhasa terrane is a terrane, or fragment of crustal material, sutured to the Eurasian Plate during the Cretaceous that forms present-day southern Tibet. It takes its name from the city of Lhasa in the Tibet Autonomous Region, China. The northern part may have originated in the East African Orogeny, while the southern part appears to have once been part of Australia. The two parts joined, were later attached to Asia, and then were impacted by the collision of the Indian Plate that formed the Himalayas.

The Roca Formation is a Cretaceous to Paleogene lithostratigraphic unit, located in the Neuquén Basin. It crops out in the Argentinian provinces of Río Negro, Neuquén, La Pampa, and Mendoza. Its deposition is diachronous, beginning during the Maastrichtian in the north of its distribution, and later moving to the south, where its strata reached the Late Danian. It lies transitionally above the Jagüel Formation, and the top of the formation is marked by a regional unconformity due to an Eocene and Oligocene orogenic pulse. These two units belong to the Malargüe Group. The marine sediments of the Jagüel and Roca Formations were deposited during a transgression from the Atlantic Ocean, beginning in the Maastrichtian and ending in the Danian.
















