
The black sea bass is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a sea bass from the subfamily Serraninae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the groupers and anthias. It is found in the western Atlantic Ocean, where it is an important species for commercial and recreational fisheries.

The cownose ray is a species of Batoidea found throughout a large part of the western Atlantic and Caribbean, from New England to southern Brazil. These rays also belong to the order Myliobatiformes, a group that is shared by bat rays, manta rays, and eagle rays.

Carcinus maenas is a common littoral crab. It is known by different names around the world. In the British Isles, it is generally referred to as the shore crab, or green shore crab. In North America and South Africa, it bears the name European green crab.

The Veneridae or venerids, common name: Venus clams, are a very large family of minute to large, saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs. Over 500 living species of venerid bivalves are known, most of which are edible, and many of which are exploited as food sources.

The apron ray is a small electric ray in the numbfish family, Narcinidae, known for being able to generate electric shocks for defense. It is one of two species in the genus Discopyge.

Kaloula rugifera, the Sichuan digging frog or Szechwan narrowmouth toad, is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae found in China.
Freshwater bivalves are molluscs of the order Bivalvia that inhabit freshwater ecosystems. They are one of the two main groups of freshwater molluscs, along with freshwater snails.

Lasaeidae is a family of very small saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs in the order Galeommatida. These bivalves are sometimes called "kelly clams", because one of the genera in this family is Kellia.
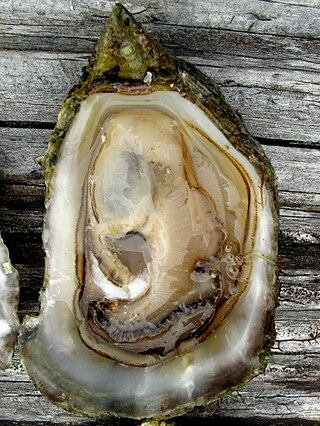
Ostrea conchaphila is a species of oyster, a marine bivalve mollusk which lives on the Pacific coast of Mexico south of Baja California. Until recently there was some confusion as to whether this more southern oyster species might in fact be the same species as Ostrea lurida, the well-known but more northerly "Olympia oyster", which it resembles in shell size and color. Because of this confusion, the name O. conchaphila was sometimes applied to various populations of what is now known to be O. lurida.

Ostrea lurida, common name the Olympia oyster, after Olympia, Washington in the Puget Sound area, is a species of small, edible oyster, a marine bivalve mollusk in the family Ostreidae. This species occurs on the northern Pacific coast of North America. Over the years the role of this edible species of oyster has been partly displaced by the cultivation of non-native edible oyster species.

Diademichthys lineatus, commonly known as the long-snout clingfish or urchin clingfish, is a species of marine fish in the family Gobiesocidae.

Neotrypaea californiensis, the Bay ghost shrimp, is a species of ghost shrimp that lives on the Pacific coast of North America. It is a pale animal which grows to a length of 11.5 cm (4.5 in). One claw is bigger than the other, especially in males, and the enlarged claw is thought to have a function in mating. N. californiensis is a deposit feeder that lives in extensive burrow systems, and is responsible for high rates of bioturbation. It adversely affects oyster farms, and its numbers are controlled in some places by the application of pesticides. It carries out an important role in the ecosystem, and is used by fishermen as bait.
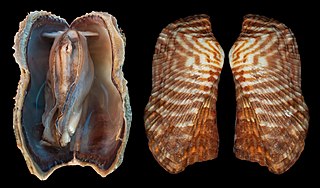
Arca zebra, or the turkey wing ark clam, is a bivalve mollusc in the family Arcidae, the ark clams.

Nodipecten nodosus, or the lion's paw scallop, is a species of bivalve mollusc in the family Pectinidae. It can be found along the Atlantic coast of North America, ranging from Cape Hatteras to the West Indies, including Brazil and Bermuda.

Dyspanopeus sayi is a species of mud crab that is native to the Atlantic coast of North America. It has also become established outside its native range, living in Swansea Docks since 1960, the Mediterranean Sea since the 1970s, the North Sea since 2007 and the Black Sea since 2010. It can reach a carapace width of 20 mm (0.8 in), and has black tips to its unequal claws. It feeds on bivalves and barnacles, and is in turn eaten by predators including the Atlantic blue crab, Callinectes sapidus. Eggs are produced from spring to autumn, the offspring reach sexual maturity the following summer, and individuals can live for up to two years. The closest relative of D. sayi is D. texanus, which lives in the Gulf of Mexico; the two species differ in subtle features of the genitalia and the last pair of walking legs.

The arrow goby is a species of goby native to marine and brackish waters of the Pacific coast of North America from British Columbia to Baja California. This species grows to a length of 6.4 centimetres (2.5 in) SL, though most do not exceed 4.2 centimetres (1.7 in) TL. This fish can also be found displayed in public aquaria. This species is the only known member of its genus.

The west coast seabream or west coast steenbras is a species of marine fish in the family Sparidae. It is found in very shallow water off the coasts of to Angola, Namibia and South Africa. The International Union for Conservation of Nature lists its conservation status as being "near threatened".
Upogebia pugettensis, also known as the blue mud shrimp, is a species of mud lobster from the West Coast of North America.

Orthione griffenis, or Griffen's isopod, is an isopod parasite present in the waters off East Asia and the West Coast of North America.

Pseudopythina is a genus of bivalves belonging to the family Lasaeidae.


















