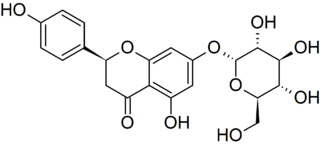Gin is a distilled alcoholic drink that derives its flavour from juniper berries and other botanical ingredients.

Kumquats, or cumquats in Australian English, are a group of small fruit-bearing trees in the flowering plant family Rutaceae. Their taxonomy is disputed. They were previously classified as forming the now-historical genus Fortunella or placed within Citrus, sensu lato. Different classifications have alternatively assigned them to anywhere from a single species, C. japonica, to numerous species representing each cultivar. Recent genomic analysis would define three pure species, Citrus hindsii, C. margarita and C. crassifolia, with C. x japonica being a hybrid of the last two.

Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone, sometimes abbreviated to neohesperidin DC or simply NHDC, is an artificial sweetener derived from citrus.

Earl Grey tea is a tea blend which has been flavoured with oil of bergamot. The rind's fragrant oil is added to black tea to give Earl Grey its unique taste. Traditionally, Earl Grey was made from black teas such as Chinese keemun, and therefore intended to be served without milk. Some blend the tea with lapsang souchong tea which lends a smoky character. Other varieties have been introduced as well, such as green or oolong.

Coriander, also known as cilantro, is an annual herb in the family Apiaceae. All parts of the plant are edible, but the fresh leaves and the dried seeds are the parts most traditionally used in cooking.

Polo is a brand of breath mint whose defining feature is the hole in the middle. The peppermint flavoured Polo was first manufactured in the United Kingdom in 1948, by employee John Bargewell at the Rowntree's Factory, York, and a range of flavours followed. The name may derive from "polar", referencing the cool, fresh taste of the mint. Polo mints are also sold in other countries such as India and Sri Lanka by Nestlé. Polo mints are usually sold in a 34g pack containing 23 individual mints.
Horilka is a Ukrainian alcoholic beverage.

Kofola is a carbonated soft drink produced by the eponymous Czech company, which is headquartered in Krnov, Czech Republic. It is the principal rival of Coca-Cola and Pepsi in the Czech Republic and Slovakia. The company is one of the leading soft drink producers and distributors in Central and Eastern Europe.

Citrus bergamia, the bergamot orange, is a fragrant citrus fruit the size of an orange, with a yellow or green color similar to a lime, depending on ripeness.

The mandarinquat, also misleadingly called orangequat, is any cross between a mandarin and a kumquat. Mandarinquats are members of the citrofortunella group.
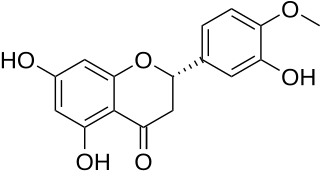
Hesperetin is the 4'-methoxy derivative of eriodictyol, a flavanone. Hesperetin's 7-O-glycoside, hesperidin, is a naturally occurring flavanon-glycoside, the main flavonoid in lemons and sweet oranges. Hesperetin are not found to a significant extent in Citrus spp.

Citrus glauca, commonly known as the desert lime, is a thorny shrub or small tree native to Queensland, New South Wales, and South Australia. The 1889 book The Useful Native Plants of Australia records common names native kumquat and desert lemon.
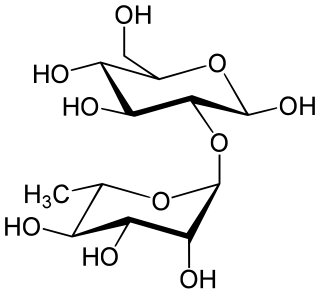
Neohesperidose is the disaccharide which is present in some flavonoids. It can be found in species of Typha.

Dihydrochalcone (DHC) is the organic compound with the formula C6H5C(O)(CH2)2C6H5. It is the reduced derivative of chalcone (C6H5C(O)(CH)2C6H5). It is white solid that is soluble in many organic solvents. Dihydrochalcone per se is often minor significance, but some derivatives occur in nature and have attracted attention as drugs.

Bergamot essential oil is a cold-pressed essential oil produced by cells inside the rind of a bergamot orange fruit. It is a common flavoring and top note in perfumes. The scent of bergamot essential oil is similar to a sweet light orange peel oil with a floral note.

Narirutin is a flavanone-7-O-glycoside, consisting of the flavanone naringenin bonded with the disaccharide rutinose.
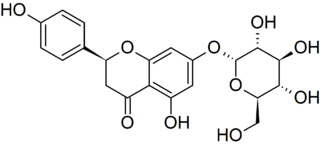
Prunin is a flavanone glycoside found in immature citrus fruits and in tomatoes. Its aglycone form is called naringenin.